Transport Layer - Rose
... Internet transport protocol “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
... Internet transport protocol “best effort” service, UDP segments may be: lost delivered out of order to app connectionless: no handshaking between UDP sender, receiver each UDP segment handled independently of others ...
Router
... Well known ports indicate FTP, SMTP, HTTP, SIP, many others Dynamically negotiated ports indicate specific processes (for these and other protocols) ...
... Well known ports indicate FTP, SMTP, HTTP, SIP, many others Dynamically negotiated ports indicate specific processes (for these and other protocols) ...
Network - UniMAP Portal
... • Internet evolved from ARPANET – first operational packet network – applied to tactical radio & satellite nets also – had a need for interoperability – lead to standardized TCP/IP protocols ...
... • Internet evolved from ARPANET – first operational packet network – applied to tactical radio & satellite nets also – had a need for interoperability – lead to standardized TCP/IP protocols ...
CCNA2 3.0-09 Basic Router Troubleshooting
... • The more factors that make up a metric, the greater the flexibility to tailor network operations to meet specific needs. • By default, IGRP uses the static factors bandwidth and delay to calculate a metric value (so bandwidth and delay can actually be entered by the administrator). • IGRP may also ...
... • The more factors that make up a metric, the greater the flexibility to tailor network operations to meet specific needs. • By default, IGRP uses the static factors bandwidth and delay to calculate a metric value (so bandwidth and delay can actually be entered by the administrator). • IGRP may also ...
Discovery service
... Due to the unreliability of wireless networks these mechanisms are not efficient. Solutions: WAP and modified TCP. Modified TCP for wireless networks. Implement a TCP support component at the base station (gateway between wired and wireless networks). The support component snoops on TCP packets ...
... Due to the unreliability of wireless networks these mechanisms are not efficient. Solutions: WAP and modified TCP. Modified TCP for wireless networks. Implement a TCP support component at the base station (gateway between wired and wireless networks). The support component snoops on TCP packets ...
Application Layer Functionality and Protocols
... Identify the characteristics used to categorize connectors, describe some common uses for the same connectors, and identify the consequences for misapplying a connector in a given situation ...
... Identify the characteristics used to categorize connectors, describe some common uses for the same connectors, and identify the consequences for misapplying a connector in a given situation ...
ch01 - Montana State University
... Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that named in Section 117 of the United States Copyright Act without the express written consent of the copyright owner is unlawful. Requests for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Adopters of ...
... Reproduction or translation of this work beyond that named in Section 117 of the United States Copyright Act without the express written consent of the copyright owner is unlawful. Requests for further information should be addressed to the Permissions Department, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Adopters of ...
TCP/IP Discussion Related to Essay Question on Final
... Ethernet performs error correction (Stop-and-WaitARQ); Since there are no errors in transmission, R sends ACK for each packet it receives from A. After sending ACK, DL removes DLH and DLT; passes [IP|TCP|HTTP|User Data] to NL layer of R. ...
... Ethernet performs error correction (Stop-and-WaitARQ); Since there are no errors in transmission, R sends ACK for each packet it receives from A. After sending ACK, DL removes DLH and DLT; passes [IP|TCP|HTTP|User Data] to NL layer of R. ...
The Internet
... application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. The close relation with the IP means that the ...
... application program and passes it to the IP for transfer across the internet. The reverse operation is performed at the destination computer, i.e. the TCP reassembles the data (from individual packets) and forwards them to the user’s application program. The close relation with the IP means that the ...
Networks - Dr. Ramesh R. Manza
... Packaging of data into packets. Speed of transmission. Recreation of data to its original form. Eg: of network protocols: TCP/IP, AppleTalk , NetBEUI etc ...
... Packaging of data into packets. Speed of transmission. Recreation of data to its original form. Eg: of network protocols: TCP/IP, AppleTalk , NetBEUI etc ...
Networks - What are They
... In the sense that messages are not inherently acknowledged Connectionless protocol Alternative to TCP Designed for hosts who want to implement their own ...
... In the sense that messages are not inherently acknowledged Connectionless protocol Alternative to TCP Designed for hosts who want to implement their own ...
ppt
... breaking application message into smaller chunks Add transport-layer header to each chunk 4-PDU for TCP is called segment 4-PDU for UDP is called datagram ...
... breaking application message into smaller chunks Add transport-layer header to each chunk 4-PDU for TCP is called segment 4-PDU for UDP is called datagram ...
Slide 1
... that have a fast connection to the Internet via cable, satellite or DSL, the router can function as a hardware firewall. ...
... that have a fast connection to the Internet via cable, satellite or DSL, the router can function as a hardware firewall. ...
9-0 Internet Protocol Attacks and some Defenses
... • Responder’s state (IP addresses and ports of the connection) is stored in a cookie and sent to initiator • After initiator responds, cookie is regenerated and compared with the cookie returned by the initiator slide 15 ...
... • Responder’s state (IP addresses and ports of the connection) is stored in a cookie and sent to initiator • After initiator responds, cookie is regenerated and compared with the cookie returned by the initiator slide 15 ...
networking
... Connecting to a Network Hostname and IP Address assignment Configuration of hardware Default route (gateway) assignment Name Service Configuration ...
... Connecting to a Network Hostname and IP Address assignment Configuration of hardware Default route (gateway) assignment Name Service Configuration ...
Document
... of a protocol an agreed-upon series of rules and conventions Communication between machines is peer-to-peer process using protocols at any given layer Each layer adds information to the data – Headers are added to the data at layers 6, 5, 4, 3 and 2. Trailers are usually added at layer 2 Each laye ...
... of a protocol an agreed-upon series of rules and conventions Communication between machines is peer-to-peer process using protocols at any given layer Each layer adds information to the data – Headers are added to the data at layers 6, 5, 4, 3 and 2. Trailers are usually added at layer 2 Each laye ...
Document
... • The vast collection of computer networks which form and act as a single huge network for transport of data and messages across distances which can be anywhere from the same office to anywhere in the world. Written by William F. Slater, III ...
... • The vast collection of computer networks which form and act as a single huge network for transport of data and messages across distances which can be anywhere from the same office to anywhere in the world. Written by William F. Slater, III ...
Chapter 18 Internet Protocols
... • Assume that each network is connection oriented • ISs connect two or more networks —IS appear as ES to each network —Logical connection set up between ESs • Concatenation of logical connections across networks ...
... • Assume that each network is connection oriented • ISs connect two or more networks —IS appear as ES to each network —Logical connection set up between ESs • Concatenation of logical connections across networks ...
protocol review and monitoring committee
... Nurses Notes: (This area will not be transcribed in PRMC minutes, see below) ...
... Nurses Notes: (This area will not be transcribed in PRMC minutes, see below) ...
2.1 Chapter 2 Network Models
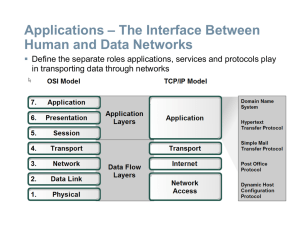
... 2-4 TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE The layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite do not exactly match those in the OSI model. The original TCP/IP protocol suite was defined as having four layers: host-tonetwork, internet, transport, and application. However, when TCP/IP is compared to OSI, we can say that the TCP ...
... 2-4 TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE The layers in the TCP/IP protocol suite do not exactly match those in the OSI model. The original TCP/IP protocol suite was defined as having four layers: host-tonetwork, internet, transport, and application. However, when TCP/IP is compared to OSI, we can say that the TCP ...
CS335 Sample Questions for Exam #2
... Answer: MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It is the maximum size for data link layer frames. When a datagram will not fit inside a single frame, it must be fragmented (divided into smaller packets). 5.) If a datagram is fragmented on the first hop on route to its destination, will the destinatio ...
... Answer: MTU is the Maximum Transmission Unit. It is the maximum size for data link layer frames. When a datagram will not fit inside a single frame, it must be fragmented (divided into smaller packets). 5.) If a datagram is fragmented on the first hop on route to its destination, will the destinatio ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).