Labour market adjustments during the Great Recession
... crisis on wages, unemployment and profits within different economies? In other words: who paid the price of the Great Recession? In order to provide an answer, we look at the development of the main components of GDP (compensation of employees and operating surplus). To address the impact of adjustm ...
... crisis on wages, unemployment and profits within different economies? In other words: who paid the price of the Great Recession? In order to provide an answer, we look at the development of the main components of GDP (compensation of employees and operating surplus). To address the impact of adjustm ...
ch21, lecture
... Automatic stabilizers are changes in taxes and government spending that occur automatically in response to changes in the level of real GDP. ...
... Automatic stabilizers are changes in taxes and government spending that occur automatically in response to changes in the level of real GDP. ...
cyclically adjusted budget balance
... • It takes into account the extra tax revenue the government would collect and the transfers it would save if a recessionary gap were eliminated—or the revenue the government would lose and the extra transfers it would make if an inflationary gap were eliminated. • If we adjust for the effects of th ...
... • It takes into account the extra tax revenue the government would collect and the transfers it would save if a recessionary gap were eliminated—or the revenue the government would lose and the extra transfers it would make if an inflationary gap were eliminated. • If we adjust for the effects of th ...
1 - Whitman People
... Fiscal policy directly causes an increase in aggregate demand by government purchase of goods or by people having more after tax income. Monetary policy works less directly as it takes people and firms longer to react to changes in interest rates. Difficulty: M ...
... Fiscal policy directly causes an increase in aggregate demand by government purchase of goods or by people having more after tax income. Monetary policy works less directly as it takes people and firms longer to react to changes in interest rates. Difficulty: M ...
GDP Power Point (Reg)
... “… does not allow for the health of our children, the quality of their education, or the joy of their play. It does not include the beauty of our poetry or the strength of our marriages, the intelligence of our public debate or the integrity of our public officials. It measures neither our courage, ...
... “… does not allow for the health of our children, the quality of their education, or the joy of their play. It does not include the beauty of our poetry or the strength of our marriages, the intelligence of our public debate or the integrity of our public officials. It measures neither our courage, ...
Document
... Automatic stabilizers are changes in taxes and government spending that occur automatically in response to changes in the level of real GDP. The business cycle therefore creates braking power: A budget surplus slows down an expanding economy. A budget deficit reverses a downturn in the economy. ...
... Automatic stabilizers are changes in taxes and government spending that occur automatically in response to changes in the level of real GDP. The business cycle therefore creates braking power: A budget surplus slows down an expanding economy. A budget deficit reverses a downturn in the economy. ...
Problems to Be Faced Measuring Real Income per Capita: The
... That procedure allows GDP figures to be as close as possible to the real physical growth of domestic production. In Figure 2 we see that the slope of GDP at constant prices—in deflated figures to the base year 2008—is much lower than the one of current prices and shows the real growth of our economy ...
... That procedure allows GDP figures to be as close as possible to the real physical growth of domestic production. In Figure 2 we see that the slope of GDP at constant prices—in deflated figures to the base year 2008—is much lower than the one of current prices and shows the real growth of our economy ...
Balancing the Three Approaches to Measuring Gross Domestic
... approaches. (For more information on data content, please see Skipper (2005), ‘Early estimates of GDP: information content and forecasting methods’.) The rate of change in output is, for this reason, used to set the rate of change of UK GDP. As more data from all three approaches become available, t ...
... approaches. (For more information on data content, please see Skipper (2005), ‘Early estimates of GDP: information content and forecasting methods’.) The rate of change in output is, for this reason, used to set the rate of change of UK GDP. As more data from all three approaches become available, t ...
What is macroeconomics?
... Difference between GDP deflator and CPI • Deflator based on all the goods and services produced in the economy so it includes government, investment and exports. • CPI is based on a fixed subset of consumption goods and services so it includes imports. • The set of goods and services on which the d ...
... Difference between GDP deflator and CPI • Deflator based on all the goods and services produced in the economy so it includes government, investment and exports. • CPI is based on a fixed subset of consumption goods and services so it includes imports. • The set of goods and services on which the d ...
Impact of Labour on Economic Growth in Bulgaria (1991
... was stronger relative to the preceding year, was compensated by the stimulating influence of the other factors and the rate of economic growth was slightly positive. This suggests that right after the last crisis, employment developments were a key factor suppressing growth. Such a conclusion can be ...
... was stronger relative to the preceding year, was compensated by the stimulating influence of the other factors and the rate of economic growth was slightly positive. This suggests that right after the last crisis, employment developments were a key factor suppressing growth. Such a conclusion can be ...
GDP
... Difference between GDP deflator and CPI • Deflator based on all the goods and services produced in the economy so it includes government, investment and exports. • CPI is based on a fixed subset of consumption goods and services so it includes imports. • The set of goods and services on which ...
... Difference between GDP deflator and CPI • Deflator based on all the goods and services produced in the economy so it includes government, investment and exports. • CPI is based on a fixed subset of consumption goods and services so it includes imports. • The set of goods and services on which ...
Chapter 11 Aggregate Demand and Supply
... A) may increase the level of equilibrium output as it raises the price level. B) may lower the price level and the level of equilibrium output. C) may reduce the equilibrium output as it raises the price level. D) is represented by shifting the aggregate supply curve downward. E) is represented by s ...
... A) may increase the level of equilibrium output as it raises the price level. B) may lower the price level and the level of equilibrium output. C) may reduce the equilibrium output as it raises the price level. D) is represented by shifting the aggregate supply curve downward. E) is represented by s ...
thesis-presentation-v03
... • Slowing macroeconomic growth • Declining average economic growth rate each decade: ...
... • Slowing macroeconomic growth • Declining average economic growth rate each decade: ...
Macro 2.3- Inflation
... banks don’t lend and people don’t save. This decreases investment and GDP. ...
... banks don’t lend and people don’t save. This decreases investment and GDP. ...
The Effects of External Shocks on Business Cycles in Emerging Asia
... the industrialized countries, only had to pocket a short period of output loss. Some countries, like Indonesia, did not record any recession at all. Many observers have claimed that emerging Asia fully decoupled from the industrialized nations in the last decade, and there is some evidence to suppor ...
... the industrialized countries, only had to pocket a short period of output loss. Some countries, like Indonesia, did not record any recession at all. Many observers have claimed that emerging Asia fully decoupled from the industrialized nations in the last decade, and there is some evidence to suppor ...
SOLUTIONS TO MACRO END-OF-CHAPTER
... where in the world this income was generated. Thus to find GNP we add to GDP income that Canadians received from production activity outside their borders but subtract the income from Canadian production activity that was paid to investors who reside outside our borders. Since Canada is a net-debtor ...
... where in the world this income was generated. Thus to find GNP we add to GDP income that Canadians received from production activity outside their borders but subtract the income from Canadian production activity that was paid to investors who reside outside our borders. Since Canada is a net-debtor ...
The Keynesian Cross Model
... rates and investment exists because firms must either borrow or generate their own funds to invest. – As a result, firms are willing to invest in only those projects that pay a return in excess of the borrowing cost or rate of interest paid. • When rates are high, few projects are sufficiently profi ...
... rates and investment exists because firms must either borrow or generate their own funds to invest. – As a result, firms are willing to invest in only those projects that pay a return in excess of the borrowing cost or rate of interest paid. • When rates are high, few projects are sufficiently profi ...
1. Output gaps and productivity slowdown
... Note: Labor productivity gap implies a lose in GDP growth rates due to decreasing contribution of labor productivity. It is a difference between the actual GDP accumulated growth rates (contribution of employment and labor productivity) and simulated GDP accumulated growth rates. Simulation is based ...
... Note: Labor productivity gap implies a lose in GDP growth rates due to decreasing contribution of labor productivity. It is a difference between the actual GDP accumulated growth rates (contribution of employment and labor productivity) and simulated GDP accumulated growth rates. Simulation is based ...
monthly and quarterly gdp estimates for interwar britain
... Hayes and Turner used the Chow-Lin (1971) method to interpolate GDP estimates based on Quarterly Industrial Production as an indicator variable. They used a linear model rather than one specified in logarithms. Our methodology is an improvement on the Chow-Lin method and our use of a richer set of i ...
... Hayes and Turner used the Chow-Lin (1971) method to interpolate GDP estimates based on Quarterly Industrial Production as an indicator variable. They used a linear model rather than one specified in logarithms. Our methodology is an improvement on the Chow-Lin method and our use of a richer set of i ...
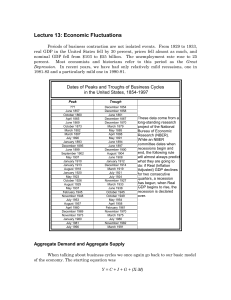
Lecture 13
... April 1958 February 1961 November 1970 March 1975 July 1980 November 1982 March 1991 ...
... April 1958 February 1961 November 1970 March 1975 July 1980 November 1982 March 1991 ...
Chapter 33 DEFICITS, MONETARY POLICY, AND GROWTH
... Deficits and Debt: Terminology and Facts ● Some Facts about the National Debt ♦ In absolute terms the debt is large, but as a proportion of GDP it is less than one half. ♦ Some, but not all, is backed by government assets. ♦ Before the 1980s, most of the debt was accumulated in times of war and rec ...
... Deficits and Debt: Terminology and Facts ● Some Facts about the National Debt ♦ In absolute terms the debt is large, but as a proportion of GDP it is less than one half. ♦ Some, but not all, is backed by government assets. ♦ Before the 1980s, most of the debt was accumulated in times of war and rec ...
Demand and Consumer Choice
... A Hypothetical Business Cycle • The phases of the business cycle are: ...
... A Hypothetical Business Cycle • The phases of the business cycle are: ...
2001 recession in market economies, healthy growth in
... a rather fragile state at the time of the terrorist attacks on 11 September. Short-term economic indicators released before the attacks were already pointing to a more protracted slowdown than had previously been expected by many forecasters. Against this background, the attacks were a profound psyc ...
... a rather fragile state at the time of the terrorist attacks on 11 September. Short-term economic indicators released before the attacks were already pointing to a more protracted slowdown than had previously been expected by many forecasters. Against this background, the attacks were a profound psyc ...
GDP
... that economists and policymakers use most often. Gross domestic product or GDP tells us the nation’s total income and the total expenditure on its output of goods and services. The consumer price index, CPI, measures the level of prices. The unemployment tells us the fraction of workers who are unem ...
... that economists and policymakers use most often. Gross domestic product or GDP tells us the nation’s total income and the total expenditure on its output of goods and services. The consumer price index, CPI, measures the level of prices. The unemployment tells us the fraction of workers who are unem ...