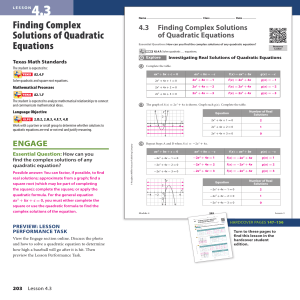
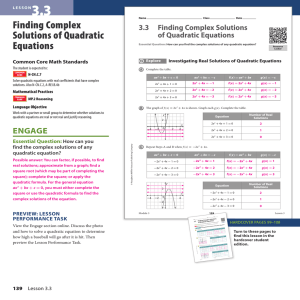
14.4 Solving Trigonometric Equations
... Matrix multiplication can be used to rotate a point (x, y) counter clockwise about the origin through an angle †. The coordinates of the resulting point (x§, y§) are determined by the following matrix equation: ...
... Matrix multiplication can be used to rotate a point (x, y) counter clockwise about the origin through an angle †. The coordinates of the resulting point (x§, y§) are determined by the following matrix equation: ...
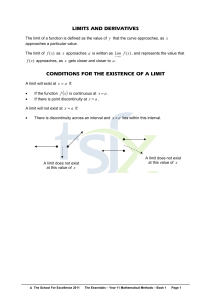
limits and derivatives conditions for the existence of a limit
... The gradient of a line is constant and does not change at different values of x . As the derivative represents the gradient to a curve, the derivative of a linear expressions will result in a constant (numeric) value. The gradient to a curve modelled by a non linear equation changes, and is dependen ...
... The gradient of a line is constant and does not change at different values of x . As the derivative represents the gradient to a curve, the derivative of a linear expressions will result in a constant (numeric) value. The gradient to a curve modelled by a non linear equation changes, and is dependen ...
Itô diffusion

In mathematics — specifically, in stochastic analysis — an Itô diffusion is a solution to a specific type of stochastic differential equation. That equation is similar to the Langevin equation used in physics to describe the Brownian motion of a particle subjected to a potential in a viscous fluid. Itô diffusions are named after the Japanese mathematician Kiyosi Itô.