WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment to the
... WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment defines the total scope of federal power as being that specifically granted by the Constitution of the United States and no more; and WHEREAS, the scope of power defined by the Tenth Amendment means that the federal government was created by the states specifically to be ...
... WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment defines the total scope of federal power as being that specifically granted by the Constitution of the United States and no more; and WHEREAS, the scope of power defined by the Tenth Amendment means that the federal government was created by the states specifically to be ...
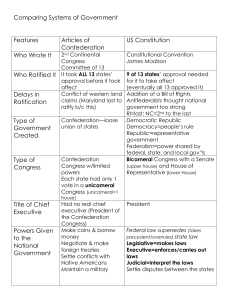
Comparing Systems of Government
... Enumerated powers=anything not specifically given to the national government belongs to the states Concurrent powers=powers shared by both national and state governments Could not regulate Do NOT have to worry about this trade between the box states *Government has been Difficulty enforcing function ...
... Enumerated powers=anything not specifically given to the national government belongs to the states Concurrent powers=powers shared by both national and state governments Could not regulate Do NOT have to worry about this trade between the box states *Government has been Difficulty enforcing function ...
Federalism
... States in the 10th Amendment. • Neither level can change the basic division of powers set in the Constitution without the cooperation of the other: Ex. both Congress and the States must take part in amending the Constitution. ...
... States in the 10th Amendment. • Neither level can change the basic division of powers set in the Constitution without the cooperation of the other: Ex. both Congress and the States must take part in amending the Constitution. ...
File
... “necessary and proper clause” also known as the “elastic clause” Implied powers: can take action not expressly authorized but that supports actions that are; examples? Article 1 Section 10: things the states can not do; why not? Article VI: Supremacy Clause; national law is supreme over state law ...
... “necessary and proper clause” also known as the “elastic clause” Implied powers: can take action not expressly authorized but that supports actions that are; examples? Article 1 Section 10: things the states can not do; why not? Article VI: Supremacy Clause; national law is supreme over state law ...
Police Powers The question that needs consideration is whether the
... omission of the Concurrent Legislative List. However, criminal law, evidence and criminal procedure have remained subjects that are within the legislative competence of both Parliament and the provincial legislatures with federal laws overriding any conflicting legislation by a province (Article 143 ...
... omission of the Concurrent Legislative List. However, criminal law, evidence and criminal procedure have remained subjects that are within the legislative competence of both Parliament and the provincial legislatures with federal laws overriding any conflicting legislation by a province (Article 143 ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... 3 lecture hours per week ...
... 3 lecture hours per week ...
Federalism - WordPress.com
... A confederation is similar to a federal system but gives less power to the central government. The loose alliances of countries or other political entities that make up a confederation seek to cooperate with one another while retaining ultimate control of their own internal policies. Unlike federal ...
... A confederation is similar to a federal system but gives less power to the central government. The loose alliances of countries or other political entities that make up a confederation seek to cooperate with one another while retaining ultimate control of their own internal policies. Unlike federal ...
85(R) HCR 26 - Introduced version
... directly in violation of the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution of ...
... directly in violation of the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution of ...
SENATE RESOLUTION - PA General Assembly
... protest "against the palpable and alarming infractions of the ...
... protest "against the palpable and alarming infractions of the ...
81R5789 MMS-F - Texas Legislature Online
... Constitution of the United States and no more; and WHEREAS, The scope of power defined by the Tenth Amendment means that the federal government was created by the states specifically to be an agent of the states; and WHEREAS, Today, in 2009, the states are demonstrably treated as agents of the feder ...
... Constitution of the United States and no more; and WHEREAS, The scope of power defined by the Tenth Amendment means that the federal government was created by the states specifically to be an agent of the states; and WHEREAS, Today, in 2009, the states are demonstrably treated as agents of the feder ...
The Virginia Resolutions (1798)
... into one sovereignty, the obvious tendency and inevitable consequence of which would be, to transform the present republican system of the United States, into an absolute, or at best a mixed monarchy. That the General Assembly doth particularly protest against the palpable and alarming infractions o ...
... into one sovereignty, the obvious tendency and inevitable consequence of which would be, to transform the present republican system of the United States, into an absolute, or at best a mixed monarchy. That the General Assembly doth particularly protest against the palpable and alarming infractions o ...
Model Tenth Amendment Resolution for State Legislatures
... WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States reads as follows: "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."; and WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment defines the to ...
... WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution of the United States reads as follows: "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people."; and WHEREAS, the Tenth Amendment defines the to ...
Chapter 3 – “Federalism” – Study Guide
... 7. How did the New Deal era bring an end to the era of dual federalism? What is the term for the new relationship between the national and state governments that began with the New Deal? 8. Historically, how have federal grants affected federal/state relations? What are categorical grants? 9. How di ...
... 7. How did the New Deal era bring an end to the era of dual federalism? What is the term for the new relationship between the national and state governments that began with the New Deal? 8. Historically, how have federal grants affected federal/state relations? What are categorical grants? 9. How di ...
Chapter 3: Federalism
... themselves as Americans first and state citizens second (strong state loyalty) C. The Division of Power • 1. the writers of the Constitution carefully defined the powers of state and national governments • 2. the writers favored a stronger national government, but states were restrained as vital com ...
... themselves as Americans first and state citizens second (strong state loyalty) C. The Division of Power • 1. the writers of the Constitution carefully defined the powers of state and national governments • 2. the writers favored a stronger national government, but states were restrained as vital com ...
Chapter Study Outline
... decisions made by states. Likewise, when the federal government proves unable or unwilling to act, advocates and politicians try to achieve their goals in states and localities. In many cases, it is up to the courts to decide which level of government should have the final say. What are examples of ...
... decisions made by states. Likewise, when the federal government proves unable or unwilling to act, advocates and politicians try to achieve their goals in states and localities. In many cases, it is up to the courts to decide which level of government should have the final say. What are examples of ...
WE THE PEOPLE – LESSON ONE
... The power of state and local governments comes from the … How does the power of the central government compare to state and local governments? ...
... The power of state and local governments comes from the … How does the power of the central government compare to state and local governments? ...
Ex Post Facto Laws
... American federalism in stating that the powers not delegated to the national government are reserved to the states or the people ...
... American federalism in stating that the powers not delegated to the national government are reserved to the states or the people ...
What Are the Limits on the Implied Powers of Congress?
... put it, “the Government of the Union, though limited in its powers, is supreme within its sphere of action . . . and its laws, when made in pursuance of the Constitution, form the supreme law of the land . . . ” Marshall further argued that the nation’s political authority lies with the people of th ...
... put it, “the Government of the Union, though limited in its powers, is supreme within its sphere of action . . . and its laws, when made in pursuance of the Constitution, form the supreme law of the land . . . ” Marshall further argued that the nation’s political authority lies with the people of th ...
Strengthening the Federal Government through the Supreme Court
... river between New York and New Jersey. Gibbons had a license by the federal government to run steam ships between New York and New Jersey. Ogden sues Gibbons on the grounds that his monopoly was violated. New York decides in favor of Ogden. Gibbons appeals and case goes to Supreme Court. ...
... river between New York and New Jersey. Gibbons had a license by the federal government to run steam ships between New York and New Jersey. Ogden sues Gibbons on the grounds that his monopoly was violated. New York decides in favor of Ogden. Gibbons appeals and case goes to Supreme Court. ...
Document: Newlands Act - 1902
... Reclamation Act of 1902 Rep. Francis G. Newlands of Nevada was the prime moving force behind an effort to extend federal assistance to farmers and ranchers who worked the arid lands of the West. Under a measure passed in 1902, a self-perpetuating funding system was established: The federal governmen ...
... Reclamation Act of 1902 Rep. Francis G. Newlands of Nevada was the prime moving force behind an effort to extend federal assistance to farmers and ranchers who worked the arid lands of the West. Under a measure passed in 1902, a self-perpetuating funding system was established: The federal governmen ...
Federalism - Nueva history
... State Powers • “Privileges and Immunities” Clause: citizens of each state guaranteed the same rights as citizens of other states (Article 4) • Republican Form of Government (Article 4)- the power to create their own government • “Reserve”/ “Police” Powers: “powers not delegated to U.S., nor prohibi ...
... State Powers • “Privileges and Immunities” Clause: citizens of each state guaranteed the same rights as citizens of other states (Article 4) • Republican Form of Government (Article 4)- the power to create their own government • “Reserve”/ “Police” Powers: “powers not delegated to U.S., nor prohibi ...
The US is the oldest continuous democracy in the world. It was
... All representatives must reside in the state from which they are elected, although House members do not need to live in their congressional district. ...
... All representatives must reside in the state from which they are elected, although House members do not need to live in their congressional district. ...
Canadian federalism
.jpg?width=300)
Canadian federalism is concerned with the current nature and historical development of federal systems within Canada. Canada is a federation with 11 distinct jurisdictions of governmental authority: the country-wide federal Crown and the 10 provincial Crowns. (There are also three territorial governments in the far north that exercise delegated powers under the authority of the Parliament of Canada.) All are generally independent of one another in their respective areas of legislative authority and each derives its sovereignty and authority from the monolithic Canadian Crown; each jurisdiction includes the Queen-in-Parliament, the Queen-in-Council, and the Queen-on-the-Bench. Shared sectors include agriculture and immigration, but most are either entirely within federal jurisdiction, such as foreign affairs and telecommunications, or entirely within provincial jurisdiction, such as education and healthcare. The division of powers is outlined in the Constitution Act, 1867 (formerly the British North America Act 1867), a key document within the Constitution of Canada.The federal nature of the Canadian constitution was a response to the colonial-era diversity among the Maritimes and the Province of Canada, in particular the strong distinction between the French-speaking inhabitants of Lower Canada and the English-speaking inhabitants in Upper Canada and the Maritimes. John A. Macdonald, Canada's first prime minister, at first favoured a unitary system, but later, after witnessing the carnage of the American Civil War, supported the federal system; he sought to avoid violent conflicts by maintaining a fusion of powers rather than a separation of powers.