Contents
... response to strong domestic inflation pressures. However, interest rates in many other countries were unusually low for several years. Large global imbalances have developed, with some countries including the United States, Australia and New Zealand experiencing large current account deficits partly ...
... response to strong domestic inflation pressures. However, interest rates in many other countries were unusually low for several years. Large global imbalances have developed, with some countries including the United States, Australia and New Zealand experiencing large current account deficits partly ...
Minutes of the Federal Open Market Committee June 23-24, 2009
... (SOMA) reported on recent developments in domestic and foreign financial markets. The Manager also reported on System open market operations in Treasury securities and in agency debt and agency mortgagebacked securities (MBS) during the period since the Committee’s April 28-29 meeting. By unanimous ...
... (SOMA) reported on recent developments in domestic and foreign financial markets. The Manager also reported on System open market operations in Treasury securities and in agency debt and agency mortgagebacked securities (MBS) during the period since the Committee’s April 28-29 meeting. By unanimous ...
Monetary Policy Statement December 2010 Contents
... The pace of economic growth appears to have moderated. Corporate investment intentions are now below average. Household spending also remains weak, with household credit still flat and housing market activity slowing further. House prices may decline a little further in the near term. This continued ...
... The pace of economic growth appears to have moderated. Corporate investment intentions are now below average. Household spending also remains weak, with household credit still flat and housing market activity slowing further. House prices may decline a little further in the near term. This continued ...
Exchange rate and monetary policy for Kazakhstan in light of
... Regardless what weights are put on such medium-term objectives as inflation and GDP growth, a separate question concerns what is the mechanism of transmission of monetary policy. Currently the NBK’s reference interest rate seems disconnected from the rest of the financial system, let alone the real ...
... Regardless what weights are put on such medium-term objectives as inflation and GDP growth, a separate question concerns what is the mechanism of transmission of monetary policy. Currently the NBK’s reference interest rate seems disconnected from the rest of the financial system, let alone the real ...
Chapter 15: Monetary Policy - the School of Economics and Finance
... The Fed does not set the federal funds rate, but its ability to increase or decrease bank reserves quickly through open market operations keeps the actual federal funds rate close to the Fed’s target rate. The orange line is the Fed’s target for the federal funds rate, and the jagged green line repr ...
... The Fed does not set the federal funds rate, but its ability to increase or decrease bank reserves quickly through open market operations keeps the actual federal funds rate close to the Fed’s target rate. The orange line is the Fed’s target for the federal funds rate, and the jagged green line repr ...
CHAPTER 12
... others, we know much more about the economy now, so this is unlikely. Automatic stabilizers also cushion the economy and help to prevent recessions from becoming depressions. 3. “If the U.S. government closed half its military bases, would there be a multiplier effect?” Talk the students through the ...
... others, we know much more about the economy now, so this is unlikely. Automatic stabilizers also cushion the economy and help to prevent recessions from becoming depressions. 3. “If the U.S. government closed half its military bases, would there be a multiplier effect?” Talk the students through the ...
Monetary Policy Statement September 2015
... During 2013 and 2014, high export commodity prices were a key driver of growth, along with increasing construction activity and rising net immigration. While export prices eased through the first three quarters of 2014, they remained very high by past standards. With inflationary pressures estimated ...
... During 2013 and 2014, high export commodity prices were a key driver of growth, along with increasing construction activity and rising net immigration. While export prices eased through the first three quarters of 2014, they remained very high by past standards. With inflationary pressures estimated ...
EC 102.07-08-09 Exercises for Chapter 33 SPRING 2006 1. Ceteris
... b. The Central Bank buys bonds in the open market. c. The price level falls. d. Net exports fall. ANSWER: b. The Central Bank buys bonds in the open market. ...
... b. The Central Bank buys bonds in the open market. c. The price level falls. d. Net exports fall. ANSWER: b. The Central Bank buys bonds in the open market. ...
Monetary Policy Statement June 2007 Contents
... risks, we consider a scenario where the economy is currently more stretched and world dairy prices prove to be higher for ...
... risks, we consider a scenario where the economy is currently more stretched and world dairy prices prove to be higher for ...
IMPACT OF INTEREST RATE AND INFLATION ON GDP IN
... Bruno and Easterly (1995) report the issue of inflation and growth and find no evidence of any consistent relationship between these variables up to a certain level of inflation. They evaluate that the growth falls during distinct high inflation crisis, above than 40 percent, and recovers after infl ...
... Bruno and Easterly (1995) report the issue of inflation and growth and find no evidence of any consistent relationship between these variables up to a certain level of inflation. They evaluate that the growth falls during distinct high inflation crisis, above than 40 percent, and recovers after infl ...
the partisan model of macroeconomic cycles: more
... effects of associated policy changes on the macroeconomy likely existed (and so first year outcomes may to some degree reflect the policies of the previous administration). Cumulative inflation during each four year presidential term (measured here by changes in the GNP deflator) has typically been ...
... effects of associated policy changes on the macroeconomy likely existed (and so first year outcomes may to some degree reflect the policies of the previous administration). Cumulative inflation during each four year presidential term (measured here by changes in the GNP deflator) has typically been ...
Syllabus
... The GDP, being the value of goods and services produced in an economy during a given period of time is the measure of economic activities performed within the border of the country, such as Saudi Arabia. While GNP measures income accruing to national residents of the country whether it is generated ...
... The GDP, being the value of goods and services produced in an economy during a given period of time is the measure of economic activities performed within the border of the country, such as Saudi Arabia. While GNP measures income accruing to national residents of the country whether it is generated ...
Introduction to Economic Growth
... approximate percentage rate as economists currently define it. ...
... approximate percentage rate as economists currently define it. ...
Aggregate demand - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Aggregate supply is the quantity of goods and services that the economy produces. • The aggregate supply curve links the average price level of the economy with the quantity of goods and services produced. • The short-run aggregate supply curve is upwardsloping. • But, in the long term, aggregate ...
... • Aggregate supply is the quantity of goods and services that the economy produces. • The aggregate supply curve links the average price level of the economy with the quantity of goods and services produced. • The short-run aggregate supply curve is upwardsloping. • But, in the long term, aggregate ...
Syllabus and Semester Specific Guidelines
... The purpose of this Macroeconomics course is to give you, the student, a thorough understanding of the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. I believe in this course, because during this semester, you will develop an understanding of how economic forces influence the U ...
... The purpose of this Macroeconomics course is to give you, the student, a thorough understanding of the principles of economics that apply to an economic system as a whole. I believe in this course, because during this semester, you will develop an understanding of how economic forces influence the U ...
chapter 1 - MHHE.com
... 2. As the post-war period following World War II began, the CPI rose from 18.2 at the end of 1945 to 21.5 at the end of 1946. (Base year: Average 1982–1984 = 100) Estimate the inflation rate in 1946. a. 1.53% b. 15.3% c. 1.81% d. 18.1% 3. In the midst of the Great Depression, the CPI fell from 14.6 ...
... 2. As the post-war period following World War II began, the CPI rose from 18.2 at the end of 1945 to 21.5 at the end of 1946. (Base year: Average 1982–1984 = 100) Estimate the inflation rate in 1946. a. 1.53% b. 15.3% c. 1.81% d. 18.1% 3. In the midst of the Great Depression, the CPI fell from 14.6 ...
Lecture Notes on Macroeconomic Principles
... As noted above, Social Security benefits are indexed, that is, adjusted every year based on the percentage increase in the CPI. Union contracts often specify indexed wages that increase each year based on the inflation rate. Such a provision is often referred to as a cost‐of‐living allowance (COL ...
... As noted above, Social Security benefits are indexed, that is, adjusted every year based on the percentage increase in the CPI. Union contracts often specify indexed wages that increase each year based on the inflation rate. Such a provision is often referred to as a cost‐of‐living allowance (COL ...
Monetary Policy Functions and Transmission Mechanisms: An
... channels that follows here assumes that the central bank pursues an expansionary monetary policy by resetting its policy instrument, either increasing a monetary aggregate under its control or reducing its policy interest rate.3 The first transmission channel is the interest rate channel, the tradit ...
... channels that follows here assumes that the central bank pursues an expansionary monetary policy by resetting its policy instrument, either increasing a monetary aggregate under its control or reducing its policy interest rate.3 The first transmission channel is the interest rate channel, the tradit ...
short-run macroeconomic equilibrium
... Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium The economy is in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium when the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium is on the long-run aggregate supply curve. ...
... Long-Run Macroeconomic Equilibrium The economy is in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium when the point of short-run macroeconomic equilibrium is on the long-run aggregate supply curve. ...
Article: Interest and inflation rates through the lens of the theory of
... is 1 percent and we need to add an amount of anticipated inflation that will result in a fed funds rate of 0.25 percent. The only way to get that is to add a negative number, in this case, −0.75 percent. To sum up, over the long run, a low fed funds rate must lead to consistent, but low, levels of d ...
... is 1 percent and we need to add an amount of anticipated inflation that will result in a fed funds rate of 0.25 percent. The only way to get that is to add a negative number, in this case, −0.75 percent. To sum up, over the long run, a low fed funds rate must lead to consistent, but low, levels of d ...
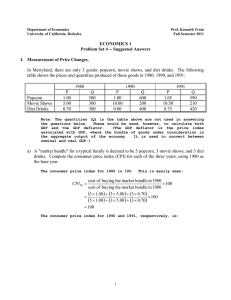
Answers. - University of California, Berkeley
... This differs from the inflation rate calculated in (b) because the “market bundle” is different. The rate of inflation is the percentage increase in the cost of buying a specific bundle of goods. Therefore it may be different for different bundles. Why might we want to change the bundle of goods use ...
... This differs from the inflation rate calculated in (b) because the “market bundle” is different. The rate of inflation is the percentage increase in the cost of buying a specific bundle of goods. Therefore it may be different for different bundles. Why might we want to change the bundle of goods use ...
Download (PDF)
... Households live for two periods and take prices as given. In the first period, they supply an exogenous amount of labor Nt which is measured in efficiency units, such that changes in labor supply reflect population growth, human capital formation, and labor-augmenting technical progress. Nominal wag ...
... Households live for two periods and take prices as given. In the first period, they supply an exogenous amount of labor Nt which is measured in efficiency units, such that changes in labor supply reflect population growth, human capital formation, and labor-augmenting technical progress. Nominal wag ...
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation reflects a reduction in the purchasing power per unit of money – a loss of real value in the medium of exchange and unit of account within the economy. A chief measure of price inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index (normally the consumer price index) over time. The opposite of inflation is deflation.Inflation affects an economy in various ways, both positive and negative. Negative effects of inflation include an increase in the opportunity cost of holding money, uncertainty over future inflation which may discourage investment and savings, and if inflation were rapid enough, shortages of goods as consumers begin hoarding out of concern that prices will increase in the future.Inflation also has positive effects: Fundamentally, inflation gives everyone an incentive to spend and invest, because if they don't, their money will be worth less in the future. This increase in spending and investment can benefit the economy. However it may also lead to sub-optimal use of resources. Inflation reduces the real burden of debt, both public and private. If you have a fixed-rate mortgage on your house, your salary is likely to increase over time due to wage inflation, but your mortgage payment will stay the same. Over time, your mortgage payment will become a smaller percentage of your earnings, which means that you will have more money to spend. Inflation keeps nominal interest rates above zero, so that central banks can reduce interest rates, when necessary, to stimulate the economy. Inflation reduces unemployment to the extent that unemployment is caused by nominal wage rigidity. When demand for labor falls but nominal wages do not, as typically occurs during a recession, the supply and demand for labor cannot reach equilibrium, and unemployment results. By reducing the real value of a given nominal wage, inflation increases the demand for labor, and therefore reduces unemployment.Economists generally believe that high rates of inflation and hyperinflation are caused by an excessive growth of the money supply. However, money supply growth does not necessarily cause inflation. Some economists maintain that under the conditions of a liquidity trap, large monetary injections are like ""pushing on a string"". Views on which factors determine low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attributed to fluctuations in real demand for goods and services, or changes in available supplies such as during scarcities. However, the consensus view is that a long sustained period of inflation is caused by money supply growing faster than the rate of economic growth.Today, most economists favor a low and steady rate of inflation. Low (as opposed to zero or negative) inflation reduces the severity of economic recessions by enabling the labor market to adjust more quickly in a downturn, and reduces the risk that a liquidity trap prevents monetary policy from stabilizing the economy. The task of keeping the rate of inflation low and stable is usually given to monetary authorities. Generally, these monetary authorities are the central banks that control monetary policy through the setting of interest rates, through open market operations, and through the setting of banking reserve requirements.