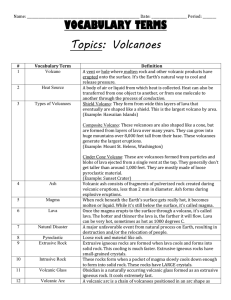
Volcanic Eruptions - During an eruption, molten rock, or magma, is
... - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano Vents – the cracks in the Earth’s crust through which volcanic material passe ...
... - Magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface is called lava Volcanoes – are areas of Earth’s surface through which magma and volcanic gases pass Magma chamber – is a body of molten rock deep underground that feeds a volcano Vents – the cracks in the Earth’s crust through which volcanic material passe ...
20150210090647
... Where are volcanoes located? • Volcanoes can be found: – Diverging Plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridge) – Converging plates with subduction zones • Oceanic plate vs. oceanic plate • Oceanic plate vs. continental plate ...
... Where are volcanoes located? • Volcanoes can be found: – Diverging Plate boundaries (mid-ocean ridge) – Converging plates with subduction zones • Oceanic plate vs. oceanic plate • Oceanic plate vs. continental plate ...
5volcano notes chapter
... Volcanos and plates Key point: most volcanoes form along diverging plate boundaries. I. Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of earth’s plates. Volcano –a weak spot in crust where magma comes to the surface. Ring of fire-major volcanic belt around rim of Pacific Ocean. (90% of volcanoes) Key poi ...
... Volcanos and plates Key point: most volcanoes form along diverging plate boundaries. I. Volcanic belts form along the boundaries of earth’s plates. Volcano –a weak spot in crust where magma comes to the surface. Ring of fire-major volcanic belt around rim of Pacific Ocean. (90% of volcanoes) Key poi ...
Volcano WebQuest Follow-Up
... cinders forming and falling straight back down • Found: typically found on sides of other volcanoes • Examples: Paricutin, Wizard Island ...
... cinders forming and falling straight back down • Found: typically found on sides of other volcanoes • Examples: Paricutin, Wizard Island ...
volcano
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
Types of Volcanoes
... cornfield and grew to be several hundred meters tall in just a few days. This volcano continued to erupt for 9 years and grew to be over 1,300 feet tall. ...
... cornfield and grew to be several hundred meters tall in just a few days. This volcano continued to erupt for 9 years and grew to be over 1,300 feet tall. ...
Section 13
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
... eruptions be more likely to increase the steepness of a volcanic cone? Explain your answer. Explosive eruption are more likely to increase volcano height, because the pyroclastic materials rise upward and fall close to the volcanic vent. ...
Section
... Unlike Kilauea, Mount St. Helens has a more silicic, viscous, stiff, gas-charged lava in which pressure can build up to cause an explosive eruption. Mount St. Helens is a volcano with predominantly andesitic magma as is characteristic of subductionzone volcanoes. 4. What are pyroclastics? Identify a ...
... Unlike Kilauea, Mount St. Helens has a more silicic, viscous, stiff, gas-charged lava in which pressure can build up to cause an explosive eruption. Mount St. Helens is a volcano with predominantly andesitic magma as is characteristic of subductionzone volcanoes. 4. What are pyroclastics? Identify a ...
Chapter 13 Section 2 Review Page 330
... Explain how the composition of magma affects the force of volcanic eruptions. More viscous magma traps gases more easily than less viscous magma, which may lead to more explosive eruptions. ...
... Explain how the composition of magma affects the force of volcanic eruptions. More viscous magma traps gases more easily than less viscous magma, which may lead to more explosive eruptions. ...
Section 13
... Explain how the composition of magma affects the force of volcanic eruptions. More viscous magma traps gases more easily than less viscous magma, which may lead to more explosive eruptions. ...
... Explain how the composition of magma affects the force of volcanic eruptions. More viscous magma traps gases more easily than less viscous magma, which may lead to more explosive eruptions. ...
_____ 1. What happens to the atmosphere after large
... _____ 2. As volcanic ash and gases spread throughout the atmosphere they can a. block enough sunlight to cause global temperatures to drop. b. reflect enough sunlight to cause global temperatures to rise. c. cause a drop only in local temperatures. d. cause a rise only in local temperatures. 3. What ...
... _____ 2. As volcanic ash and gases spread throughout the atmosphere they can a. block enough sunlight to cause global temperatures to drop. b. reflect enough sunlight to cause global temperatures to rise. c. cause a drop only in local temperatures. d. cause a rise only in local temperatures. 3. What ...
pyroclastic material combustible material an ancient
... Great pressure in the asthenosphere keeps the rock there: ...
... Great pressure in the asthenosphere keeps the rock there: ...
plosky tolbachik volcano in kamchatka erupts after 40 years
... are awesome manifestations of heat flowing at hot spots (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) and in subduction zones (e.g., along almost the entire Pacific Rim). ...
... are awesome manifestations of heat flowing at hot spots (e.g., Hawaii and Iceland) and in subduction zones (e.g., along almost the entire Pacific Rim). ...
Chapter 9 Test Review Notes
... fragments. These fragments pile up in a cone shape around the vent. Cinder cones tend to form in groups or on the sides of larger volcanoes. Compared to cinder cones, shield volcanoes are very large. They form when basaltic lava erupts and flows long distances before hardening. Over time, layers of ...
... fragments. These fragments pile up in a cone shape around the vent. Cinder cones tend to form in groups or on the sides of larger volcanoes. Compared to cinder cones, shield volcanoes are very large. They form when basaltic lava erupts and flows long distances before hardening. Over time, layers of ...
Positive effects of volcanic activity
... The Hawaiian Islands are at the southeastern end of a chain of volcanoes that began to form more than 70 million years ago. The largest and most southeastern island of the chain, Hawaii, consists of five volcanoes. Kilauea, Mauna Loa, and Hualalai have erupted in the past 200 years. Lo`ihi, the you ...
... The Hawaiian Islands are at the southeastern end of a chain of volcanoes that began to form more than 70 million years ago. The largest and most southeastern island of the chain, Hawaii, consists of five volcanoes. Kilauea, Mauna Loa, and Hualalai have erupted in the past 200 years. Lo`ihi, the you ...
Volcanic and Plutonic
... Sill: A sheet of magma that cuts horizontally between other layers of rock. Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, trapped from above by harder more ...
... Sill: A sheet of magma that cuts horizontally between other layers of rock. Laccolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, exerting pressure upwards so as to cause a bulge. Lopolith: A magmatic body formed horizontally between layers of rock, trapped from above by harder more ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
... Lassen Volcanic National Park is home to smoking fumaroles, meadows freckled with wildflowers, clear mountain lakes, and numerous volcanoes. Jagged peaks tell the story of its eruptive past while hot water continues to mold the land. Lassen Volcanic offers opportunities to discover the wonder and my ...
What is Lava?
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions ...
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions ...
Mount Garibaldi

Mount Garibaldi is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Sea to Sky Country of British Columbia, 80 km (50 mi) north of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Located in the southernmost Coast Mountains, it is one of the most recognized peaks in the South Coast region, as well as British Columbia's best known volcano. It lies within the Garibaldi Ranges of the Pacific Ranges.This heavily eroded dome complex occupies the southwest corner of Garibaldi Provincial Park overlooking the town of Squamish. It is the only major Pleistocene age volcano in North America known to have formed upon a glacier. Although part of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt within the Cascade Volcanic Arc, it is not considered part of the Cascade Range.