Validation of OMI L2 Sulfur Dioxide retrievals over volcanic
... above. We have assembled a list of eruptions detected by both OMI and AIRS in the same ATrain overpass for comparisons (Table 1), using a new technique described below. 2. Volcanic SO2 2.1 Volcanic clouds in the UTLS In addition to comparing the total SO2 loading in volcanic clouds measured by OMI a ...
... above. We have assembled a list of eruptions detected by both OMI and AIRS in the same ATrain overpass for comparisons (Table 1), using a new technique described below. 2. Volcanic SO2 2.1 Volcanic clouds in the UTLS In addition to comparing the total SO2 loading in volcanic clouds measured by OMI a ...
VIRTUAL FIELD TRIP
... Characteristics The explosiveness of a volcano eruption depends on how easy magma can flow and the amount of gas trapped in it. When a volcano erupts, the magma goes up to the earth’s surface. The magma that goes up to earth surface is called Lava. Magma is the molten rock within the earth’s crust. ...
... Characteristics The explosiveness of a volcano eruption depends on how easy magma can flow and the amount of gas trapped in it. When a volcano erupts, the magma goes up to the earth’s surface. The magma that goes up to earth surface is called Lava. Magma is the molten rock within the earth’s crust. ...
Petrogenesis and correlation of the mid
... caldera and was active from approximately 35 to 26 Ma (Lipman, 1982). Volcanism began with a period of intermediate composition eruptions which then changed to silicic ash flows from caldera centers at ~30 Ma, shortly after the eruption of the rhyolitic UBT. The Thirtynine Mile volcanic field lies t ...
... caldera and was active from approximately 35 to 26 Ma (Lipman, 1982). Volcanism began with a period of intermediate composition eruptions which then changed to silicic ash flows from caldera centers at ~30 Ma, shortly after the eruption of the rhyolitic UBT. The Thirtynine Mile volcanic field lies t ...
View paper
... character of high-temperature systems. These systems are generally situated in the core of central volcanoes within the fissure swarms of the volcanic zones. The main rock units are basaltic lava series intervened by hyaloclastite formations. At deeper levels, intrusive rocks (mostly dykes and sills ...
... character of high-temperature systems. These systems are generally situated in the core of central volcanoes within the fissure swarms of the volcanic zones. The main rock units are basaltic lava series intervened by hyaloclastite formations. At deeper levels, intrusive rocks (mostly dykes and sills ...
Geologic Map of the Frijoles Quadrangle, New Mexico
... the map area, these rocks consist of lahars, block and ash flows, dome collapse breccias, and other debris flows, with minor cinder cone and fluvial deposits (Goff et al., 1990). These deposits also include thin andesitic flows and andesitic to dacitic tuffs that are commonly too thin to be mapped i ...
... the map area, these rocks consist of lahars, block and ash flows, dome collapse breccias, and other debris flows, with minor cinder cone and fluvial deposits (Goff et al., 1990). These deposits also include thin andesitic flows and andesitic to dacitic tuffs that are commonly too thin to be mapped i ...
Lava is the molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption
... magma from a parental magma of calc-alkaline or alkaline composition.[8] Sulfur lava flows up to 250 metres (820 feet) long and 10 metres (33 feet) wide occur at Lastarria volcano, Chile. They were formed by the melting of sulfur deposits at temperatures as low as 113 °C (235 °F).[9] Olivine nepheli ...
... magma from a parental magma of calc-alkaline or alkaline composition.[8] Sulfur lava flows up to 250 metres (820 feet) long and 10 metres (33 feet) wide occur at Lastarria volcano, Chile. They were formed by the melting of sulfur deposits at temperatures as low as 113 °C (235 °F).[9] Olivine nepheli ...
Modelling satellite-derived magma discharge to explain
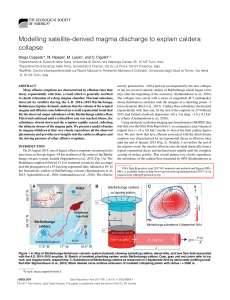
... may range between 101 and 104 Pa•s, which is typical for basalts. Given a dike length L equal to 45 km, the radius a of the flow channel, compatible with the calculated resistance of the flow, is constrained between 4 and 20 m (Equation 3). Therefore, the volume of the feeding flow channel is constr ...
... may range between 101 and 104 Pa•s, which is typical for basalts. Given a dike length L equal to 45 km, the radius a of the flow channel, compatible with the calculated resistance of the flow, is constrained between 4 and 20 m (Equation 3). Therefore, the volume of the feeding flow channel is constr ...
The Critical Zone What is a caldera? The Valles Caldera
... area is prone to wildfire. Fire has been a common occurrence in forests of the Southwest for a long time, and at low intensity, it can be healthy for growth of the forest. However, recently the fires have intensified by burning hotter, and across more acreage. What might be causing this change? 7. V ...
... area is prone to wildfire. Fire has been a common occurrence in forests of the Southwest for a long time, and at low intensity, it can be healthy for growth of the forest. However, recently the fires have intensified by burning hotter, and across more acreage. What might be causing this change? 7. V ...
Prof. Manoochehr Shirzaei Physical
... Volcanic debris flow—wetted debris that moves downhill Occur where volcanoes are covered with ice and snow or drenched in abundant rain Volcanic debris flows move downslope like wet concrete. Lahar—water-rich debris flow of ash and blocks ...
... Volcanic debris flow—wetted debris that moves downhill Occur where volcanoes are covered with ice and snow or drenched in abundant rain Volcanic debris flows move downslope like wet concrete. Lahar—water-rich debris flow of ash and blocks ...
Igneous Rocks - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... The nature of magma • Consists of three components: – A liquid portion, called melt, that is composed of mobile ions – Solids, if any, are silicate minerals that have already crystallized from the melt – Volatiles, which are gases dissolved in the melt, including water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (C ...
... The nature of magma • Consists of three components: – A liquid portion, called melt, that is composed of mobile ions – Solids, if any, are silicate minerals that have already crystallized from the melt – Volatiles, which are gases dissolved in the melt, including water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (C ...
Quantification of Extraterrestrial Lava Flow Effusion Rates Through
... By correlating natural lava flow morphologies with laboratory flow types, and calibrating estimated '¥ values with those calculated from observing active lava flows on Earth, we can assign a range of '¥ values to a planetary lava flow . If the eruption temperature and viscosity of the flow are also ...
... By correlating natural lava flow morphologies with laboratory flow types, and calibrating estimated '¥ values with those calculated from observing active lava flows on Earth, we can assign a range of '¥ values to a planetary lava flow . If the eruption temperature and viscosity of the flow are also ...
calcalk13
... (South Pacific arcs), which fall in the cpx-out field with OIB and flood high magnesian lavas in a plot of Al versus Si. Although the occurrence of low-Al ankaramites is relatively rare in calcalkaline volcanic suites, they do have compositions that can coexist with the mantle, and some have suggest ...
... (South Pacific arcs), which fall in the cpx-out field with OIB and flood high magnesian lavas in a plot of Al versus Si. Although the occurrence of low-Al ankaramites is relatively rare in calcalkaline volcanic suites, they do have compositions that can coexist with the mantle, and some have suggest ...
EN CRACK`N OPEN GEODES
... geodes is amethyst. Amethyst is often present in volcanic rocks; accumulated in small pyramidal clusters. It is commonly used in jewelry for its brightness and characteristic purple color which comes from traces of iron. Legend has it, Amethyst was a beautiful nymph that the God Bacchus loved. Bacch ...
... geodes is amethyst. Amethyst is often present in volcanic rocks; accumulated in small pyramidal clusters. It is commonly used in jewelry for its brightness and characteristic purple color which comes from traces of iron. Legend has it, Amethyst was a beautiful nymph that the God Bacchus loved. Bacch ...
Earth: Portrait of a Planet 3rd edition
... Pyroclastic flows (or, nuée ardentes - French): 200oC - 450oC avalanches of hot ash that race downslope. Moving up to 300 kph, they incinerate all in their path. Immediately deadly; they kill everything quickly. Many famous examples: Vesuvius, Mt. Pelée, Augustine. ...
... Pyroclastic flows (or, nuée ardentes - French): 200oC - 450oC avalanches of hot ash that race downslope. Moving up to 300 kph, they incinerate all in their path. Immediately deadly; they kill everything quickly. Many famous examples: Vesuvius, Mt. Pelée, Augustine. ...
Ch3_Igneous
... – Most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are higher in silica and therefore more viscous than other magmas – Because of their viscosity, they lose their mobility before reaching the surface – Tend to produce large plutonic structures ...
... – Most likely form as the end product of crystallization of andesitic magma – Granitic magmas are higher in silica and therefore more viscous than other magmas – Because of their viscosity, they lose their mobility before reaching the surface – Tend to produce large plutonic structures ...
Igneous rocks
... – An increase in confining pressure causes an increase in a rock’s melting temperature or conversely, reducing the pressure lowers the melting temperature – When confining pressures drop, decompression melting occurs ...
... – An increase in confining pressure causes an increase in a rock’s melting temperature or conversely, reducing the pressure lowers the melting temperature – When confining pressures drop, decompression melting occurs ...
magma intrusion in `proto-caldera caldera` systems: example from
... of ~ 120 m. These faults have been traced also in the boreholes for geothennal energy on the caldera floor. Ill. The.!3 fault system trends at N400W or N320° and dips subvertically. It is a major fault system which has localized many of the main volcanic vents in the area (St. Seymour et al. 2006a) ...
... of ~ 120 m. These faults have been traced also in the boreholes for geothennal energy on the caldera floor. Ill. The.!3 fault system trends at N400W or N320° and dips subvertically. It is a major fault system which has localized many of the main volcanic vents in the area (St. Seymour et al. 2006a) ...
Silicic Magmatism and the Volcanic–Plutonic Connection
... an abundance of both liquid water and silicic igneous make them particularly resistant to erosion (FIG. 2). rocks at its surface. These seemingly unrelated features are linked by the phase equilibria that govern melting At the same time, silicic magmatism has the potential to end civilization (Self ...
... an abundance of both liquid water and silicic igneous make them particularly resistant to erosion (FIG. 2). rocks at its surface. These seemingly unrelated features are linked by the phase equilibria that govern melting At the same time, silicic magmatism has the potential to end civilization (Self ...
Ch05 Volcanism
... eruptions form shield volcanoes (Hawaii). Small pyroclastic eruptions form scoria cones. Alternating effusive and pyroclastic eruptions result in ...
... eruptions form shield volcanoes (Hawaii). Small pyroclastic eruptions form scoria cones. Alternating effusive and pyroclastic eruptions result in ...
Geology of Maui
... • The four islands of Maui, Molokai Mo Mauiloka‘i, Lana‘i, and Kaho‘olawe formed a single landmass in the past called Maui Nui (Greater Maui) formed of 6 or 7 shield volcanoes. It included Penguin Bank, now a submerged shelf between Molokai and Oahu. • Around 2 million years ago, volcanoes on all of ...
... • The four islands of Maui, Molokai Mo Mauiloka‘i, Lana‘i, and Kaho‘olawe formed a single landmass in the past called Maui Nui (Greater Maui) formed of 6 or 7 shield volcanoes. It included Penguin Bank, now a submerged shelf between Molokai and Oahu. • Around 2 million years ago, volcanoes on all of ...
Measuring Timescales of Magmatic Evolution
... Costa and Chakraborty 2004). The pattern that has emerged from these studies is that mixing between end-members that are compositionally similar (e.g. two mafic magmas) requires less time—only a few months—than the years to decades estimated for mixing between dacite and basaltic andesite. Compariso ...
... Costa and Chakraborty 2004). The pattern that has emerged from these studies is that mixing between end-members that are compositionally similar (e.g. two mafic magmas) requires less time—only a few months—than the years to decades estimated for mixing between dacite and basaltic andesite. Compariso ...
Igneous Rocks
... Assimilation and magmatic differentiation Why are the continents so silica rich? Weathering dissolves high-temp. minerals, but also: ...
... Assimilation and magmatic differentiation Why are the continents so silica rich? Weathering dissolves high-temp. minerals, but also: ...
Volcanic Tsunamis - Earth and Space Sciences
... because the summit of the volcano lies at a depth of approximately 150 m below sea level, where hydrostatic pressures inhibit the occurrence of large ...
... because the summit of the volcano lies at a depth of approximately 150 m below sea level, where hydrostatic pressures inhibit the occurrence of large ...
Licancabur

Licancabur is a highly symmetrical stratovolcano on the southernmost part of the border between Chile and Bolivia. It is located just southwest of Laguna Verde in Bolivia. The volcano dominates the landscape of the Salar de Atacama area. The lower two thirds of the northeastern slope of the volcano belong to Bolivia, 5,400 m (17,717 ft) from the foot at 4,360 m (14,304 ft), while the rest and biggest part, including the higher third of the northeastern slope, the crater and summit, belong to Chile.The summit and the crater are located entirely in Chile, slightly over 1 km (3,281 ft) to the southwest of the international borders. It is about 400 m (1,312 ft) wide and contains Licancabur Lake, a 70 m (230 ft) by 90 m (295 ft) crater lake which is ice-covered most of the year. This is one of the highest lakes in the world, and despite air temperatures which can drop to -30 °C, it harbors planktonic fauna.Licancabur's most recent volcanic activity produced extensive lava flows which extend 6 km down the northwest and southwest flanks, with older lava flows reaching 15 km (9 mi) and pyroclastic flow deposits as far as 12 km (7 mi) from the peak. Archaeological evidence at the summit provides proof of pre-Columbian ascents and suggests the importance of crater lakes in Inca culture. This also supports the absence of major eruptions over the past 500–1,000 years.