Flywheel - uidaho.edu
... Turn on the power strip. Verify that the DC bus has 450 volts on it. Verify that the flywheels is spinning at 1755 RPM with a strobe. Connect an oscilloscope to the sag bit line of the boards. Verify that the sag bit is in the low (0V) state. Initiate the 3 phase symmetrical fault on the ...
... Turn on the power strip. Verify that the DC bus has 450 volts on it. Verify that the flywheels is spinning at 1755 RPM with a strobe. Connect an oscilloscope to the sag bit line of the boards. Verify that the sag bit is in the low (0V) state. Initiate the 3 phase symmetrical fault on the ...
final presentation draft[12-6
... Turn on the power strip. Verify that the DC bus has 450 volts on it. Verify that the flywheels is spinning at 1755 RPM with a strobe. Connect an oscilloscope to the sag bit line of the boards. Verify that the sag bit is in the low (0V) state. Initiate the 3 phase symmetrical fault on the ...
... Turn on the power strip. Verify that the DC bus has 450 volts on it. Verify that the flywheels is spinning at 1755 RPM with a strobe. Connect an oscilloscope to the sag bit line of the boards. Verify that the sag bit is in the low (0V) state. Initiate the 3 phase symmetrical fault on the ...
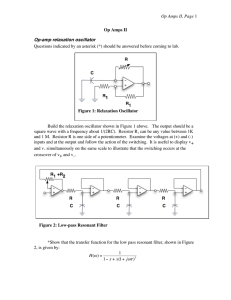
Op Amps II, Page
... die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. (You may need to decrease the input voltage considerably to avoid saturating the filter near resonance.) Check the high frequency roll off. It should be proportional to 1/ω3. Estimate the gain at re ...
... die exponentially. Find the resonant frequency by feeding in a sine signal from a function generator. (You may need to decrease the input voltage considerably to avoid saturating the filter near resonance.) Check the high frequency roll off. It should be proportional to 1/ω3. Estimate the gain at re ...
Exam 3 Practice
... Q4 A 3 phase, 50 Hz, 6 pole, Y-connected synchronous generator has a synchronous reactance of j1.0 ohms per phase. Assume the armature resistance (Ra) is zero. The field current is set to produce a terminal voltage of 480V (line–line) at full load. At full load the machine supplies 60 amps at 1.0 po ...
... Q4 A 3 phase, 50 Hz, 6 pole, Y-connected synchronous generator has a synchronous reactance of j1.0 ohms per phase. Assume the armature resistance (Ra) is zero. The field current is set to produce a terminal voltage of 480V (line–line) at full load. At full load the machine supplies 60 amps at 1.0 po ...
Resistance Review--Principles of Technology
... 16. the voltage drop across each device is the product of the lamp’s resistance and the current. ...
... 16. the voltage drop across each device is the product of the lamp’s resistance and the current. ...
A/D Converter and ECEbot Power
... For example, if a 5 k resistor has 5 V across it, the current through the resistor is given by Ohm's Law: I = V/R = 5/5k = 1 milliamp (mA). The power dissipated in the resistor is P = VI = 5 milliwatts (mW). The power is dissipated in the form of heat. Sometimes the conversion of electrical energy ...
... For example, if a 5 k resistor has 5 V across it, the current through the resistor is given by Ohm's Law: I = V/R = 5/5k = 1 milliamp (mA). The power dissipated in the resistor is P = VI = 5 milliwatts (mW). The power is dissipated in the form of heat. Sometimes the conversion of electrical energy ...
Highly efficient digitally-controlled AC-DC Converter
... 2. Key in required resistance value. 3. Press ENT key. Remember to increase or decrease the resistance in small steps to avoid voltage and current overshoot or undershoot. UNR refers to unregulated state and can be removed once Vin/Iin=R. Changing input AC voltage 1. Turn off the output of the AC so ...
... 2. Key in required resistance value. 3. Press ENT key. Remember to increase or decrease the resistance in small steps to avoid voltage and current overshoot or undershoot. UNR refers to unregulated state and can be removed once Vin/Iin=R. Changing input AC voltage 1. Turn off the output of the AC so ...
Electronic - Physics4IGCSE
... 7) The “reversed biased” diode is also placed in the circuit to act as a “_______” to prevent current flowing back into the transistor when the relay is switched _____ Words – base, buffer, on, increases, damaging, relay, off, larger, voltage, drop, NOT ...
... 7) The “reversed biased” diode is also placed in the circuit to act as a “_______” to prevent current flowing back into the transistor when the relay is switched _____ Words – base, buffer, on, increases, damaging, relay, off, larger, voltage, drop, NOT ...
FM SOLID STATE TRANSMITER PFS 30000/KS
... of individual modules. Standard or special remote control interface is also available. ° Power supply. A rugged, high-efficiency (> 93%) power supply support each PA module and can be on-air removed and replaced. Power supplies are protected from incoming AC line overvoltage, overcurrent, transient ...
... of individual modules. Standard or special remote control interface is also available. ° Power supply. A rugged, high-efficiency (> 93%) power supply support each PA module and can be on-air removed and replaced. Power supplies are protected from incoming AC line overvoltage, overcurrent, transient ...
lab2 - Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... 1: Theory The purpose of this experiment is to investigate several fundamental princip les in circuit theory. Thévenin's theorem tells us that for any linear network containing resistors, dependent and independent sources, there is an equivalent network, which is the series combination of an indepen ...
... 1: Theory The purpose of this experiment is to investigate several fundamental princip les in circuit theory. Thévenin's theorem tells us that for any linear network containing resistors, dependent and independent sources, there is an equivalent network, which is the series combination of an indepen ...
Operational Manual For A Voltage Stabilizing Ground Reference
... through the resistor in the series secondary circuit to lower the capacitive energy to non damaging level thus mitigating the arc flash potential. The series circuits in Phaseback have the same current through the entire circuit and circuits with equal ohms of impedance and equal current will mainta ...
... through the resistor in the series secondary circuit to lower the capacitive energy to non damaging level thus mitigating the arc flash potential. The series circuits in Phaseback have the same current through the entire circuit and circuits with equal ohms of impedance and equal current will mainta ...
Joe wants to heat his 12`X20` workshop with electric heat. He has
... Remember (from exercise S1E3: AC POWER) that AC power-line voltages and currents are specified as RMS values. So 120V AC heats a given resistance exactly as much as 120V DC would heat that same resistance. How much current is expected to be drawn from the power line by this heating system when all t ...
... Remember (from exercise S1E3: AC POWER) that AC power-line voltages and currents are specified as RMS values. So 120V AC heats a given resistance exactly as much as 120V DC would heat that same resistance. How much current is expected to be drawn from the power line by this heating system when all t ...
mmic amplifier biasing procedure
... for the drain-source and a negative supply for the gate-source. If there are multiple gate controls it is assumed for this procedure that they are connected together. Use knob style voltage power supplies – not key pad entry types. The supplies should be used in a floating manner with no connection ...
... for the drain-source and a negative supply for the gate-source. If there are multiple gate controls it is assumed for this procedure that they are connected together. Use knob style voltage power supplies – not key pad entry types. The supplies should be used in a floating manner with no connection ...
Interfacing with UltraVolt High Voltage Power Supplies Models A, AA
... Pin 4 – Enable/Disable: The enable function is the same for all models. A HIGH signal enables and a LOW signal disables the output. If pin 4 is left open, the power supply defaults to an enabled state. Pin 5 – Signal Ground Return: The signal ground should be used as the reference point for both th ...
... Pin 4 – Enable/Disable: The enable function is the same for all models. A HIGH signal enables and a LOW signal disables the output. If pin 4 is left open, the power supply defaults to an enabled state. Pin 5 – Signal Ground Return: The signal ground should be used as the reference point for both th ...
L550A_M5400EX (Page 1)
... Bank 5, High Current Outlets:____________________________60 db, 100 KHz – 2 MHz Common Mode (all banks)______________________________60 db, 100 KHz - 2 MHz DC Trigger Input Jacks:_______________________________________________3.5mm (1/8”) mini-plug Voltage and Polarity:______________________________ ...
... Bank 5, High Current Outlets:____________________________60 db, 100 KHz – 2 MHz Common Mode (all banks)______________________________60 db, 100 KHz - 2 MHz DC Trigger Input Jacks:_______________________________________________3.5mm (1/8”) mini-plug Voltage and Polarity:______________________________ ...
ENERGY ANALIZERS AND PROGRAMMABLE TRANSDUCERS P10
... apparent power and energy, power factors, frequency and active average power e.g. 15 min., harmonic distorsion coefficients for each phase and harmonic measurement from 1 to 25 th. Moreover, this P10 transducer shows the actual time and the time of extremal value occurrences. It has 4 relay outputs ...
... apparent power and energy, power factors, frequency and active average power e.g. 15 min., harmonic distorsion coefficients for each phase and harmonic measurement from 1 to 25 th. Moreover, this P10 transducer shows the actual time and the time of extremal value occurrences. It has 4 relay outputs ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.