
The Influence of Gaseous Media on Biefeld-Brown Effect
... asymmetrical electrodes in oxygen and sulfur hexafluoride empirically prove the formula (1) as it pertains to the ion mobility coefficient of the medium, in which the capacitor is placed. The lower the ion mobility coefficient µ, the higher the force F generated at the same electrical current. Anoth ...
... asymmetrical electrodes in oxygen and sulfur hexafluoride empirically prove the formula (1) as it pertains to the ion mobility coefficient of the medium, in which the capacitor is placed. The lower the ion mobility coefficient µ, the higher the force F generated at the same electrical current. Anoth ...
Specification/Data Sheet
... The major source of error in a transformer is a primary impedance drop due to magnetizing current, which is kept to a minimum by excitation at a fraction of rated voltage. By employing a design that meets both of these conditions along with the use of a null balance system, the turns ratio of a tran ...
... The major source of error in a transformer is a primary impedance drop due to magnetizing current, which is kept to a minimum by excitation at a fraction of rated voltage. By employing a design that meets both of these conditions along with the use of a null balance system, the turns ratio of a tran ...
(BIL) ratings for medium-voltage controllers
... specifies the required dielectric-withstand voltage values for the controllers. For controllers rated over 3.6 kV up to 7.2 kV, UL 347 specifies that the lightning-impulse withstand voltage should be either 45 kV or 60 kV. For controllers rated 1,500 V to 3,600 V, UL 347 specifies values of 30 kV or ...
... specifies the required dielectric-withstand voltage values for the controllers. For controllers rated over 3.6 kV up to 7.2 kV, UL 347 specifies that the lightning-impulse withstand voltage should be either 45 kV or 60 kV. For controllers rated 1,500 V to 3,600 V, UL 347 specifies values of 30 kV or ...
Ch01 - lmn.pub.ro
... the algebraic sum of all voltages across branches of any given loop is equal to zero. In the sum a voltage in the direction of the loop is to be taken with a plus sign, while a voltage in the direction opposite to that of the loop is to be taken with a minus sign. 3. Let the usual formulation of a D ...
... the algebraic sum of all voltages across branches of any given loop is equal to zero. In the sum a voltage in the direction of the loop is to be taken with a plus sign, while a voltage in the direction opposite to that of the loop is to be taken with a minus sign. 3. Let the usual formulation of a D ...
Capacitor Circuits
... or in parallel. • Determine the charge and voltage across any chosen capacitor in a network when given capacitances and the externally applied potential difference. ...
... or in parallel. • Determine the charge and voltage across any chosen capacitor in a network when given capacitances and the externally applied potential difference. ...
Small signal amplifiers
... This will result in loss of gain This can be avoided by connecting a transformer at the output stage The primary winding will match the high Zo of the amplifier while the secondary will match the low impedance of the speaker The ...
... This will result in loss of gain This can be avoided by connecting a transformer at the output stage The primary winding will match the high Zo of the amplifier while the secondary will match the low impedance of the speaker The ...
THS1230 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... VREFB. The VREFT and VREFB voltages set the analog input span limits FS+ and FS–, respectively. Any voltages at AIN greater than REFT or less than REFB causes ADC over-range, which is signaled by OVR going high when the conversion result is output. ...
... VREFB. The VREFT and VREFB voltages set the analog input span limits FS+ and FS–, respectively. Any voltages at AIN greater than REFT or less than REFB causes ADC over-range, which is signaled by OVR going high when the conversion result is output. ...
ElectricEnergyModuleNotes - Western Michigan University
... This module contains copyrighted material from several sources as noted. 1. "How does this battery work? The Copper (Cu) atoms attract electrons more than do the Zinc (Zn) atoms. If you place a piece of copper and a piece of zinc in contact with each other, many electrons will pass from the zinc to ...
... This module contains copyrighted material from several sources as noted. 1. "How does this battery work? The Copper (Cu) atoms attract electrons more than do the Zinc (Zn) atoms. If you place a piece of copper and a piece of zinc in contact with each other, many electrons will pass from the zinc to ...
Dynamically Parameterized Architectures for Power Aware Video
... Normalized Core Critical Path Delay vs. Vdd ...
... Normalized Core Critical Path Delay vs. Vdd ...
LM134 LM234
... At slew rates above a threshold (see curve) the LM134, LM234, LM334 can have a non-linear current characteristic. The slew rate at which this takes place is directly proportional to Iset. At Iset = 10µA, dv/dt max. = 0.01V/µs ; at Iset = 1mA, dv/dt max. = 1V/µs. Slew rates of more than 1V/µs do not ...
... At slew rates above a threshold (see curve) the LM134, LM234, LM334 can have a non-linear current characteristic. The slew rate at which this takes place is directly proportional to Iset. At Iset = 10µA, dv/dt max. = 0.01V/µs ; at Iset = 1mA, dv/dt max. = 1V/µs. Slew rates of more than 1V/µs do not ...
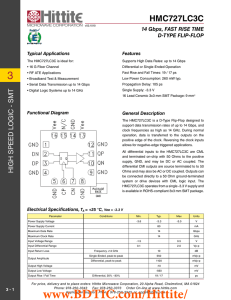
HMC727LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
... allows for negative-edge triggered applications. All differential inputs to the HMC727LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, GND, and may be DC or AC coupled. The differential CMl outputs are source terminated to to 50 Ohms and may also be AC or DC coupled. Outputs ...
... allows for negative-edge triggered applications. All differential inputs to the HMC727LC3C are CML and terminated on-chip with 50 Ohms to the positive supply, GND, and may be DC or AC coupled. The differential CMl outputs are source terminated to to 50 Ohms and may also be AC or DC coupled. Outputs ...
- Universal College of Engineering & Technology
... by dR. This can also be thought of as an extra dR added in series with R3. Now , we don’t know how much current flows through the branch when R3 is increased by dR , so to calculate the current flowing through the branch due to the effect of dR , as per Compensation theorem in fig: 2.c we add an ...
... by dR. This can also be thought of as an extra dR added in series with R3. Now , we don’t know how much current flows through the branch when R3 is increased by dR , so to calculate the current flowing through the branch due to the effect of dR , as per Compensation theorem in fig: 2.c we add an ...
BD9535MUV
... This is the power supply pin for IC internal circuits, except the FET driver. The maximum circuit current is 2.0mA. The input supply voltage range is 4.5V to 5.5V. It is recommended that a 0.1µF bypass capacitor be put in this pin. ・EN1/EN2 (4pin/20pin) When EN pin voltage is at least 2.3V, the stat ...
... This is the power supply pin for IC internal circuits, except the FET driver. The maximum circuit current is 2.0mA. The input supply voltage range is 4.5V to 5.5V. It is recommended that a 0.1µF bypass capacitor be put in this pin. ・EN1/EN2 (4pin/20pin) When EN pin voltage is at least 2.3V, the stat ...
TPS92691 Boost and Boost-to-Battery LED Driver Evaluation Board
... The TPS92691EVM-752 evaluation module (EVM) helps designers evaluate the operation and performance of the TPS92691-Q1 and TPS92691, a multi-topology controller designed for automotive lighting and general illumination applications. The TPS92691EVM-752 uses the TPS92691-Q1 (AEC Q100) IC; however, for ...
... The TPS92691EVM-752 evaluation module (EVM) helps designers evaluate the operation and performance of the TPS92691-Q1 and TPS92691, a multi-topology controller designed for automotive lighting and general illumination applications. The TPS92691EVM-752 uses the TPS92691-Q1 (AEC Q100) IC; however, for ...
Switched-mode power supply

A switched-mode power supply (switching-mode power supply, switch-mode power supply, SMPS, or switcher) is an electronic power supply that incorporates a switching regulator to convert electrical power efficiently. Like other power supplies, an SMPS transfers power from a source, like mains power, to a load, such as a personal computer, while converting voltage and current characteristics. Unlike a linear power supply, the pass transistor of a switching-mode supply continually switches between low-dissipation, full-on and full-off states, and spends very little time in the high dissipation transitions, which minimizes wasted energy. Ideally, a switched-mode power supply dissipates no power. Voltage regulation is achieved by varying the ratio of on-to-off time. In contrast, a linear power supply regulates the output voltage by continually dissipating power in the pass transistor. This higher power conversion efficiency is an important advantage of a switched-mode power supply. Switched-mode power supplies may also be substantially smaller and lighter than a linear supply due to the smaller transformer size and weight.Switching regulators are used as replacements for linear regulators when higher efficiency, smaller size or lighter weight are required. They are, however, more complicated; their switching currents can cause electrical noise problems if not carefully suppressed, and simple designs may have a poor power factor.














![[56] New“ Cm“ $351??? $11?` 32351351113252? 165E321](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016146596_1-acaf2de74ce00b9ff532c8943a5e3070-300x300.png)







