Volcanoes Part I: classification, deposits, and their distribution
... 2/3 of all volcanoes are along the Ring of Fire that surrounds the Pacific Ocean. ...
... 2/3 of all volcanoes are along the Ring of Fire that surrounds the Pacific Ocean. ...
VOLCANOETYPES
... Viscous lava traps the gases until large pressures build up & the system explodes Pyroclastic flow (ash, rock fragments) flow out of vent ...
... Viscous lava traps the gases until large pressures build up & the system explodes Pyroclastic flow (ash, rock fragments) flow out of vent ...
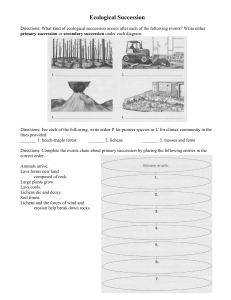
Ecological Succession
... C. Lichens grow on the rocks. D. The rocks melt back into lava. 7. All of the following are likely areas for secondary succession EXCEPT _____. A. flooded land B. volcanic island C. abandoned logging areas D. the land after a forest fire 8. Which plant characteristics are common to pioneer ...
... C. Lichens grow on the rocks. D. The rocks melt back into lava. 7. All of the following are likely areas for secondary succession EXCEPT _____. A. flooded land B. volcanic island C. abandoned logging areas D. the land after a forest fire 8. Which plant characteristics are common to pioneer ...
6.15 Eruptions and Volcano Types
... under the lithosphere. Where there are cracks, this pressure squeezes out magma. If the magma rises all the way to the surface, volcanic activity or volcanism results. But where are the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And ...
... under the lithosphere. Where there are cracks, this pressure squeezes out magma. If the magma rises all the way to the surface, volcanic activity or volcanism results. But where are the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And ...
and benefits - of volcanic eruptions
... was built by the steam explosions resulting from the incandescent torrent rushing into water, a crater being there formed, surrounded by a heap of black sand. This horse shoe heap was 75 feet high above sea level, and the front of it had broken down on the ocean side, revealing a section of bedded s ...
... was built by the steam explosions resulting from the incandescent torrent rushing into water, a crater being there formed, surrounded by a heap of black sand. This horse shoe heap was 75 feet high above sea level, and the front of it had broken down on the ocean side, revealing a section of bedded s ...
http://kids - wikifuller
... 33. Scroll Back up to the GAS AND VISCOSITY SETTINGS. Now, set the both levels of viscosity and gas to high. Be careful!! DO NOT click on “set conditions”. Look at the magma, is flowing faster or slower???? Does it have more or less gas bubbles???? 34. Scroll down to Eruption 2: Strato Cone Eruption ...
... 33. Scroll Back up to the GAS AND VISCOSITY SETTINGS. Now, set the both levels of viscosity and gas to high. Be careful!! DO NOT click on “set conditions”. Look at the magma, is flowing faster or slower???? Does it have more or less gas bubbles???? 34. Scroll down to Eruption 2: Strato Cone Eruption ...
PDF format
... 42. Some rocks contain fossils of species that only lived for a relatively short time in Earth history. These are called: A. index fossils B. fossil assemblages C. fossil successions D. trace fossils E. Vanilla Ice fossils 43. The time divisions in the Geologic Column that represent the longest len ...
... 42. Some rocks contain fossils of species that only lived for a relatively short time in Earth history. These are called: A. index fossils B. fossil assemblages C. fossil successions D. trace fossils E. Vanilla Ice fossils 43. The time divisions in the Geologic Column that represent the longest len ...
Word format
... an animal that only existed in the Cambrian and Ordovician Periods. Fossil B only existed in the Ordovician Period. Fossil C existed for a very long time on Earth- from the Cambrian to the Triassic Period. Based on this fossil assemblage, the age of the rock is: A. Cambrian B. Ordovician C. Silurian ...
... an animal that only existed in the Cambrian and Ordovician Periods. Fossil B only existed in the Ordovician Period. Fossil C existed for a very long time on Earth- from the Cambrian to the Triassic Period. Based on this fossil assemblage, the age of the rock is: A. Cambrian B. Ordovician C. Silurian ...
Igneous
... • Gently sloping flanks- between 2 and 10 degrees • Tend to be very large • Spatter Cone- minor feature ...
... • Gently sloping flanks- between 2 and 10 degrees • Tend to be very large • Spatter Cone- minor feature ...
Document
... Mountains can form when uplift forces hardened magma to bend rock upward, and is then exposed as the hardened magma wears away. After millions of years, what landform forms from hardened magma in the pipe of an extinct volcano? A landform that would form from hardened magma in the pipe of an extinct ...
... Mountains can form when uplift forces hardened magma to bend rock upward, and is then exposed as the hardened magma wears away. After millions of years, what landform forms from hardened magma in the pipe of an extinct volcano? A landform that would form from hardened magma in the pipe of an extinct ...
chapter 6 - Geophile.net
... 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount St. Helens, Washington, you will see thousands of trees lying on the ground, all parallel to one another. Explain how they got that way. * Th ...
... 10. What causes a big bulge to slowly grow on the flank of an active Cascades volcano? * It grows because rising magma is pushing it up 11. If you visit Mount St. Helens, Washington, you will see thousands of trees lying on the ground, all parallel to one another. Explain how they got that way. * Th ...
Lahar in a jar - PRA Classical Academy for Homeschoolers
... However, the chamber is not completely filled with fluid magma. It contains a partial melt, meaning that only a portion of the rock is molten (about 10 to 30%); the rest of the material is solid but, of course, remains hot. The method that scientists use to discern this information is similar to med ...
... However, the chamber is not completely filled with fluid magma. It contains a partial melt, meaning that only a portion of the rock is molten (about 10 to 30%); the rest of the material is solid but, of course, remains hot. The method that scientists use to discern this information is similar to med ...
Ch 6 power point
... Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km • Produce pyroclastic flows – Hot volcanic fragments (tephra) that, buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow very rapidly ...
... Strombolian and, as a result, can generate billowing clouds of ash up to 10 km • Produce pyroclastic flows – Hot volcanic fragments (tephra) that, buoyed by heat and volcanic gases, flow very rapidly ...
Forces in Earth
... and secondary waves and cause the most damage • Primary waves- travel about twice as fast as secondary waves • Secondary waves- travel faster than surface waves but slower than primary waves ...
... and secondary waves and cause the most damage • Primary waves- travel about twice as fast as secondary waves • Secondary waves- travel faster than surface waves but slower than primary waves ...
ttu_gs0001_000441.
... Chemically, rhyolite is high in silica and is the volcanic equivalent of granite. Among active volcanoes rhyolite is exceedingly rare. In the geologic past, ho-wever, rhyolitic eruptions were more common and among the most spectacular of natural phenomena. Over 600 cubic miles of rhyolite erupted fr ...
... Chemically, rhyolite is high in silica and is the volcanic equivalent of granite. Among active volcanoes rhyolite is exceedingly rare. In the geologic past, ho-wever, rhyolitic eruptions were more common and among the most spectacular of natural phenomena. Over 600 cubic miles of rhyolite erupted fr ...
10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions
... Other Volcanic Landforms Volcanic Neck • A volcanic neck is a cylindrical-shaped landform standing above the surface created by magma solidifying in the vent of a volcano. Erosion of the sides of the volcano exposes the neck. ...
... Other Volcanic Landforms Volcanic Neck • A volcanic neck is a cylindrical-shaped landform standing above the surface created by magma solidifying in the vent of a volcano. Erosion of the sides of the volcano exposes the neck. ...
Scientists are monitoring volcanic activity at Yellowstone and if it
... 640,000 years ago, covered all or parts of 19 western states, plus parts of Canada and Mexico, nearly all of the United States west of the Mississippi River. Keep in mind this is the breadbasket of America, an area that produces roughly half the world’s cereals. And ash is not like a big snowfall th ...
... 640,000 years ago, covered all or parts of 19 western states, plus parts of Canada and Mexico, nearly all of the United States west of the Mississippi River. Keep in mind this is the breadbasket of America, an area that produces roughly half the world’s cereals. And ash is not like a big snowfall th ...
Predict Eruptions by
... Viscous lava traps the gases until large pressures build up & the system explodes Pyroclastic flow (ash, rock fragments) flow out of vent ...
... Viscous lava traps the gases until large pressures build up & the system explodes Pyroclastic flow (ash, rock fragments) flow out of vent ...
Compared to the desolate surface of the Moon, Earth must
... If it has already been degassed— the magma left over after an eruption (at the bottom of a magma chamber), it may ooze out, but doesn’t get far Forms domes -- Mt. St. Helens ...
... If it has already been degassed— the magma left over after an eruption (at the bottom of a magma chamber), it may ooze out, but doesn’t get far Forms domes -- Mt. St. Helens ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Frequently occur in groups Associated with subduction zones ...
... Frequently occur in groups Associated with subduction zones ...
Volcanic Eruptions 2 - Earth Science > Home
... Scientists cannot always predict where or when a volcano will erupt. However, by studying volcanoes, scientists have been able to identify some clues about when an eruption may happen. One way scientists predict volcanic eruptions is by studying the earthquakes that happen near a volcano. Just befor ...
... Scientists cannot always predict where or when a volcano will erupt. However, by studying volcanoes, scientists have been able to identify some clues about when an eruption may happen. One way scientists predict volcanic eruptions is by studying the earthquakes that happen near a volcano. Just befor ...