paper - Pascal Michaillat
... development of New Keynesian models featuring matching frictions on the labor market has been a catalyst of this evolution.1 This paper proposes a model that goes one step further than existing New Keynesian models by bringing unemployment at the core of the analysis of optimal monetary policy, on p ...
... development of New Keynesian models featuring matching frictions on the labor market has been a catalyst of this evolution.1 This paper proposes a model that goes one step further than existing New Keynesian models by bringing unemployment at the core of the analysis of optimal monetary policy, on p ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES A JOBLESS RECOVERY
... inundated by liquidity, a fall in interest rates has no longer a stimulating effect on aggregate demand. The experience of Japan in the past two decades as well as the recent economic performance of the United States and other developed countries seems to suggest that zero nominal interest rates ar ...
... inundated by liquidity, a fall in interest rates has no longer a stimulating effect on aggregate demand. The experience of Japan in the past two decades as well as the recent economic performance of the United States and other developed countries seems to suggest that zero nominal interest rates ar ...
MARKING SCHEME
... The marking schemes which follow were those used by WJEC for the January 2009 examination in GCE ECONOMICS. They were finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that r ...
... The marking schemes which follow were those used by WJEC for the January 2009 examination in GCE ECONOMICS. They were finalised after detailed discussion at examiners' conferences by all the examiners involved in the assessment. The conferences were held shortly after the papers were taken so that r ...
Ready - Personal.psu.edu
... S2 f) (5 points) What would the BOJ have to do, in terms of the type and quantity of open market operations, to keep the price level at its original level, consistent with their price stability objective? Assume the money multiplier is equal to 1.00 in Japan. S2 g) (6 points) Explain how the AS - AD ...
... S2 f) (5 points) What would the BOJ have to do, in terms of the type and quantity of open market operations, to keep the price level at its original level, consistent with their price stability objective? Assume the money multiplier is equal to 1.00 in Japan. S2 g) (6 points) Explain how the AS - AD ...
5. F M F
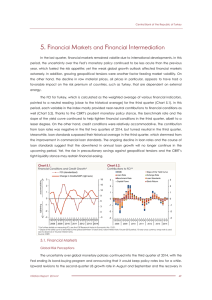
... The FCI for Turkey, which is calculated as the weighted average of various financial indicators, pointed to a neutral reading (close to the historical average) for the third quarter (Chart 5.1). In this period, each variable in the index mostly provided near-neutral contributions to financial condit ...
... The FCI for Turkey, which is calculated as the weighted average of various financial indicators, pointed to a neutral reading (close to the historical average) for the third quarter (Chart 5.1). In this period, each variable in the index mostly provided near-neutral contributions to financial condit ...
2. - IS MU
... It’s hard to tell how things would have been different had actual policies not been used. Most economists agree, though, that the U.S. economy has become much more stable since the late 1980s… CHAPTER 14 ...
... It’s hard to tell how things would have been different had actual policies not been used. Most economists agree, though, that the U.S. economy has become much more stable since the late 1980s… CHAPTER 14 ...
Chapter 7
... Is a 30 second ad during the Super Bowl really 85 times more expensive today ($4.25 million) compared to 1967 ...
... Is a 30 second ad during the Super Bowl really 85 times more expensive today ($4.25 million) compared to 1967 ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES PERCEPTIONS AND MISPERCEPTIONS OF FISCAL INFLATION
... increase demands on government expenditures in coming decades. It is widely perceived that fiscal policy is inflationary if and only if it leads the central bank to print new currency to monetize deficits. Monetization can be inflationary. But it is a misperception that this is the only channel for ...
... increase demands on government expenditures in coming decades. It is widely perceived that fiscal policy is inflationary if and only if it leads the central bank to print new currency to monetize deficits. Monetization can be inflationary. But it is a misperception that this is the only channel for ...
world trade - SICE (OAS)
... 2003 was developed in a difficult global economic environment. In this new context, different from what the country had experienced during most of the 1990's, trade policy took on an even more important role. Chile opted for an outward orientation as a key tool for achieving sustainable economic rec ...
... 2003 was developed in a difficult global economic environment. In this new context, different from what the country had experienced during most of the 1990's, trade policy took on an even more important role. Chile opted for an outward orientation as a key tool for achieving sustainable economic rec ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research
... Business cycles are a type of fluctuation found in the aggregate activity of nations that organize their work mainly in business enterprises: a cycle consists of expansions occurring at about the same time in many economic activities, followed by similarly general recessions, contractions, and reviv ...
... Business cycles are a type of fluctuation found in the aggregate activity of nations that organize their work mainly in business enterprises: a cycle consists of expansions occurring at about the same time in many economic activities, followed by similarly general recessions, contractions, and reviv ...
Inflation: Its Causes and Cures Inflation • Introduction
... Figure 8-3 The Adjustment Path of Inflation and Real GDP to an Acceleration of Nominal GDP Growth from Zero to 6 Percent When Expectations Fails to Adjust ...
... Figure 8-3 The Adjustment Path of Inflation and Real GDP to an Acceleration of Nominal GDP Growth from Zero to 6 Percent When Expectations Fails to Adjust ...
Document
... ● What actually happened? ♦ Interest rates did fall, just as predicted. ♦ The U.S. economy expanded rapidly between 1992 and 1998. ■The monetary stimulus overwhelmed the fiscal contraction. ...
... ● What actually happened? ♦ Interest rates did fall, just as predicted. ♦ The U.S. economy expanded rapidly between 1992 and 1998. ■The monetary stimulus overwhelmed the fiscal contraction. ...
Course Name: AP Macroeconomics and the Free Enterprise System
... The free-response questions will be taken from older AP test samples or variations of those questions. The main themes of free-response questions will be: aggregate models, Keynesian versus Monetary policies, money markets, stability and the Phillips Curve, international trade of currencies, compara ...
... The free-response questions will be taken from older AP test samples or variations of those questions. The main themes of free-response questions will be: aggregate models, Keynesian versus Monetary policies, money markets, stability and the Phillips Curve, international trade of currencies, compara ...
Global Imbalances and the Key Currency Regime: The Case for a
... So long as countries preferred the benefits of fast growth and increasing competitiveness to the cost of part financing the United States’ deficit (or what comes to the same thing, preferred selling more goods even if they received nothing more than bits of paper in return), and so long as a reasona ...
... So long as countries preferred the benefits of fast growth and increasing competitiveness to the cost of part financing the United States’ deficit (or what comes to the same thing, preferred selling more goods even if they received nothing more than bits of paper in return), and so long as a reasona ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES HOUSING AND THE MONETARY TRANSMISSION MECHANISM
... reason: Developments in the housing market have a major effect on economic activity. For example, as single-family housing starts in the United States dropped from their peak of 1.84 million units in January 2006 to the current level of 1.15 million units, the accompanying contraction in residential ...
... reason: Developments in the housing market have a major effect on economic activity. For example, as single-family housing starts in the United States dropped from their peak of 1.84 million units in January 2006 to the current level of 1.15 million units, the accompanying contraction in residential ...
IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM)
... check on private expenditure which is dependent upon government demand for goods and services in order to curb inflation. Also, personal consumption expenditure should be cut by raising the rates of direct taxes, in order to reduce the disposable income, but it does not adversely affect savings, inv ...
... check on private expenditure which is dependent upon government demand for goods and services in order to curb inflation. Also, personal consumption expenditure should be cut by raising the rates of direct taxes, in order to reduce the disposable income, but it does not adversely affect savings, inv ...
FRBSF E L CONOMIC ETTER
... the 1991 recession, vacancy rates declined to extremely low levels by historical standards. While these markets have not moved in perfect unison over this period, it seems clear that they all have some exposure to common factors. ...
... the 1991 recession, vacancy rates declined to extremely low levels by historical standards. While these markets have not moved in perfect unison over this period, it seems clear that they all have some exposure to common factors. ...
Chapter 8 - BCCBUSINESSSTUDIES
... It encourages consumers to buy goods and services sooner rather than later It reduces the real cost of loan repayments (think nominal and real values) But high or rising inflation can be bad for an economy: x Inflation erodes the value or purchasing power of money. People, especially those on lo ...
... It encourages consumers to buy goods and services sooner rather than later It reduces the real cost of loan repayments (think nominal and real values) But high or rising inflation can be bad for an economy: x Inflation erodes the value or purchasing power of money. People, especially those on lo ...
Chapter 14
... i.e. the economy will eventually recover to its long run Solow growth rate Keynesian say that this process takes too long, resulting in various social problems Rather than wait for this process (3 years?), the government should actively manage the economy via policies that increase aggregate d ...
... i.e. the economy will eventually recover to its long run Solow growth rate Keynesian say that this process takes too long, resulting in various social problems Rather than wait for this process (3 years?), the government should actively manage the economy via policies that increase aggregate d ...
Shocks and Frictions in US Business Cycles: A Bayesian DSGE
... seven data series. For example, CEE (2005) show that once one allows for nominal wage rigidity, there is no need for additional price rigidity in order to capture the impulse responses following a monetary policy shock. The Bayesian estimation methodology provides a natural framework for testing whi ...
... seven data series. For example, CEE (2005) show that once one allows for nominal wage rigidity, there is no need for additional price rigidity in order to capture the impulse responses following a monetary policy shock. The Bayesian estimation methodology provides a natural framework for testing whi ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.