Aggregate Demand
... In the long run, the quantity of real GDP supplied is potential GDP. As the price level rises and the money wage rate change by the same percentage, the quantity of real GDP supplied remains at potential GDP. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
... In the long run, the quantity of real GDP supplied is potential GDP. As the price level rises and the money wage rate change by the same percentage, the quantity of real GDP supplied remains at potential GDP. © 2012 Pearson Education ...
15.2 THE CPI AND OTHER PRICE LEVEL MEASURES The
... 15.2 THE CPI AND OTHER PRICE LEVEL MEASURES Suppose that the UAW and GM sign a 3 year wage deal: In the first year, the wage will be $30 an hour and will rise by the inflation rate in the next two years. If the inflation rate is 5 percent a year, the wage rises to $31.50 an hour in the second year ...
... 15.2 THE CPI AND OTHER PRICE LEVEL MEASURES Suppose that the UAW and GM sign a 3 year wage deal: In the first year, the wage will be $30 an hour and will rise by the inflation rate in the next two years. If the inflation rate is 5 percent a year, the wage rises to $31.50 an hour in the second year ...
The CPI and the Cost of Living C H A P T E R C H E C K L I S T
... 15.2 THE CPI AND OTHER PRICE LEVEL MEASURES Suppose that the UAW and GM sign a 3 year wage deal: In the first year, the wage will be $30 an hour and will rise by the inflation rate in the next two years. If the inflation rate is 5 percent a year, the wage rises to $31.50 an hour in the second year a ...
... 15.2 THE CPI AND OTHER PRICE LEVEL MEASURES Suppose that the UAW and GM sign a 3 year wage deal: In the first year, the wage will be $30 an hour and will rise by the inflation rate in the next two years. If the inflation rate is 5 percent a year, the wage rises to $31.50 an hour in the second year a ...
Advanced Macroeconomics - Juridica – Kolegji Evropian
... It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply what they have learned. Various industry-related examples such as exchange rate, inflation, domestic output and other data have been included to assist the understanding of macroeconomic issues. This book was writte ...
... It is hoped that this book’s contents will help students to think, analyze and apply what they have learned. Various industry-related examples such as exchange rate, inflation, domestic output and other data have been included to assist the understanding of macroeconomic issues. This book was writte ...
2011 International Symposium of the Banque de France
... Norman Sosnow Professor of Banking and Finance at LSE since 1985. Before then, he had worked at the Bank of England for seventeen years as a monetary adviser, becoming a Chief Adviser in 1980. In 1997 he was appointed one of the outside independent members of the Bank of England’s new Monetary Polic ...
... Norman Sosnow Professor of Banking and Finance at LSE since 1985. Before then, he had worked at the Bank of England for seventeen years as a monetary adviser, becoming a Chief Adviser in 1980. In 1997 he was appointed one of the outside independent members of the Bank of England’s new Monetary Polic ...
When is the Government Spending Multiplier Large? Northwestern University
... of their model to match the impulse response function of ten macro variables to a monetary shock, a neutral technology shock, and a capital-embodied technology shock. Our key findings based on the ACEL model can be summarized as follows. First, when the central bank follows a Taylor rule the value o ...
... of their model to match the impulse response function of ten macro variables to a monetary shock, a neutral technology shock, and a capital-embodied technology shock. Our key findings based on the ACEL model can be summarized as follows. First, when the central bank follows a Taylor rule the value o ...
Document
... includes only two assets: Money – liquid but pays no interest Bonds – pay interest but not as liquid A household’s “money demand” reflects its preference for liquidity. The variables that influence money demand: Y, r, and P. © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, sc ...
... includes only two assets: Money – liquid but pays no interest Bonds – pay interest but not as liquid A household’s “money demand” reflects its preference for liquidity. The variables that influence money demand: Y, r, and P. © 2012 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, sc ...
Price Level
... • In the long run, an economy’s production of goods and services depends on its supplies of labor, capital, and natural resources and on the available technology used to turn these factors of production into goods and services. • The price level does not affect these variables in the long run. • The ...
... • In the long run, an economy’s production of goods and services depends on its supplies of labor, capital, and natural resources and on the available technology used to turn these factors of production into goods and services. • The price level does not affect these variables in the long run. • The ...
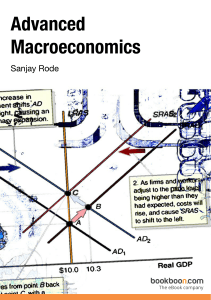
increase
... c. a decrease in savings by consumers 20. (58%) Which of the following would cause a rightward shift of the AS curve? a. an increase in interest rates b. a tax increase of 50 cents per gallon for gasoline c. an across-the-board reduction of wages in the manufacturing sector d. the passage of legisla ...
... c. a decrease in savings by consumers 20. (58%) Which of the following would cause a rightward shift of the AS curve? a. an increase in interest rates b. a tax increase of 50 cents per gallon for gasoline c. an across-the-board reduction of wages in the manufacturing sector d. the passage of legisla ...
PDF Download
... down in the real world. In fact, it can not be excluded that potential output had been overestimated in the boom-period before the financial crisis. An other important feature of the Secular Stagnation debate is the possibility of excess savings that would require real interest rates to be very low ...
... down in the real world. In fact, it can not be excluded that potential output had been overestimated in the boom-period before the financial crisis. An other important feature of the Secular Stagnation debate is the possibility of excess savings that would require real interest rates to be very low ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INFLATION AND LABOR—MARKET ADJUSTMENT Working Paper No. 1153
... y>O is given by Gray (1978), who shows that increased uncertainty about ...
... y>O is given by Gray (1978), who shows that increased uncertainty about ...
The globalisation of inflation - Bank for International Settlements
... services, is an important channel through which global economic slack influences domestic inflation. In particular, we document the extent to which the growth in GVCs explains the established empirical correlation between global economic slack and national inflation rates, both across countries and ...
... services, is an important channel through which global economic slack influences domestic inflation. In particular, we document the extent to which the growth in GVCs explains the established empirical correlation between global economic slack and national inflation rates, both across countries and ...
Full Paper - Centre for Macroeconomics
... area before 2007, suggests that fiscal rules will be rather different within a monetary union, or with fixed rather than floating exchange rates. The second reason why a fiscal equivalent of a Taylor rule may be elusive also reflects national differences, but in this case differences in political st ...
... area before 2007, suggests that fiscal rules will be rather different within a monetary union, or with fixed rather than floating exchange rates. The second reason why a fiscal equivalent of a Taylor rule may be elusive also reflects national differences, but in this case differences in political st ...
The Impact of Inflation - Rutgers New Jersey Agricultural Experiment
... Inflation risk is very common with cash equivalent assets such as savings accounts, money market funds, and certificates of deposit (CDs). The two enemies of anyone trying to accumulate money for future financial goals are inflation and taxes. With extremely low interest rates, the after-tax return ...
... Inflation risk is very common with cash equivalent assets such as savings accounts, money market funds, and certificates of deposit (CDs). The two enemies of anyone trying to accumulate money for future financial goals are inflation and taxes. With extremely low interest rates, the after-tax return ...
Lesson 4: The Impact of Inflation
... Inflation risk is very common with cash equivalent assets such as savings accounts, money market funds, and certificates of deposit (CDs). The two enemies of anyone trying to accumulate money for future financial goals are inflation and taxes. With extremely low interest rates, the after-tax return ...
... Inflation risk is very common with cash equivalent assets such as savings accounts, money market funds, and certificates of deposit (CDs). The two enemies of anyone trying to accumulate money for future financial goals are inflation and taxes. With extremely low interest rates, the after-tax return ...
Chapter 12: Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply model
... Monetary policy The actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates Fiscal policy Changes in federal taxes and purchases ...
... Monetary policy The actions the Federal Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates Fiscal policy Changes in federal taxes and purchases ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.