Chapter 33 Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
... Answer: To reduce inflation, the Federal funds rate should be raised. This would be accomplished typically through open-market operations (selling bonds), but could also be achieved with an increase in the reserve ratio or discount rate. The restrictive monetary policy would reduce the lending abili ...
... Answer: To reduce inflation, the Federal funds rate should be raised. This would be accomplished typically through open-market operations (selling bonds), but could also be achieved with an increase in the reserve ratio or discount rate. The restrictive monetary policy would reduce the lending abili ...
Principles of Economics
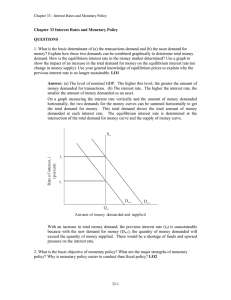
... The speculative demand for money (L2) is based on the desire to make wise decisions to invest in securities such as bonds. It mainly depends on the interest, so its function is: ...
... The speculative demand for money (L2) is based on the desire to make wise decisions to invest in securities such as bonds. It mainly depends on the interest, so its function is: ...
Understanding Money and Banking
... relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded 1. What happens to the quantity demanded of money when interest rates increase? Quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest earning assets instead 2. What happens to the quantity demanded whe ...
... relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded 1. What happens to the quantity demanded of money when interest rates increase? Quantity demanded falls because individuals would prefer to have interest earning assets instead 2. What happens to the quantity demanded whe ...
Week 20
... What is the nature of ‘the Keynes-Phillips orthodoxy’ and why was a collision inevitable? Keynes-Phillips say that if you grow money supply (MS), you won’t have inflation if, at the same time, you have unemployment. Steele’s approach tells us: The “inevitable collision” that Friedman-Phelps (expecta ...
... What is the nature of ‘the Keynes-Phillips orthodoxy’ and why was a collision inevitable? Keynes-Phillips say that if you grow money supply (MS), you won’t have inflation if, at the same time, you have unemployment. Steele’s approach tells us: The “inevitable collision” that Friedman-Phelps (expecta ...
Europe`s Stability and Growth Pact in the Context
... Two broad views of the current global economic slowdown • The result of weak aggregate demand that can be offset through appropriate adjustments to monetary policies • The results of a reduction in aggregate supply resulting from A downward revision in productivity growth in the OECD The colla ...
... Two broad views of the current global economic slowdown • The result of weak aggregate demand that can be offset through appropriate adjustments to monetary policies • The results of a reduction in aggregate supply resulting from A downward revision in productivity growth in the OECD The colla ...
Investments
... Current polls suggest the election outcome is highly uncertain – and so is the economic outlook The economy is a key focal point – in particular how to deal with the deficit. The major parties agree more needs to be done to reduce the deficit, but disagree on the method Public spending cuts can incr ...
... Current polls suggest the election outcome is highly uncertain – and so is the economic outlook The economy is a key focal point – in particular how to deal with the deficit. The major parties agree more needs to be done to reduce the deficit, but disagree on the method Public spending cuts can incr ...
UNDERSTANDING MONETARY POLICY SERIES NO 3 CENTRAL BANK OF NIGERIA
... aggregates and interest rates) monetary authorities should adopt. Generally, the choice between monetary aggregates and the interest rate depends on the policy objective of the monetary authorities, the structure of the economy and, to a lesser extent, the source of exogenous shocks to the economy. ...
... aggregates and interest rates) monetary authorities should adopt. Generally, the choice between monetary aggregates and the interest rate depends on the policy objective of the monetary authorities, the structure of the economy and, to a lesser extent, the source of exogenous shocks to the economy. ...
ECB response to the crisis
... Strengthen incentives that improve disciplining forces of competition Discourage “short-termism” and strengthen concept of liability and responsibility ...
... Strengthen incentives that improve disciplining forces of competition Discourage “short-termism” and strengthen concept of liability and responsibility ...
Study Questions concerning the Phillips Curve
... c. The misperception theory says that only unexpected inflation will lower unemployment because it fools businesses into thinking there’s an increase in demand for their product. ...
... c. The misperception theory says that only unexpected inflation will lower unemployment because it fools businesses into thinking there’s an increase in demand for their product. ...
2 more things about graphs
... What did Adidas do in 2005? What were the reasons for the deal? How did analysts see this? Why was it unlikely for Nike to take over Reebok? ...
... What did Adidas do in 2005? What were the reasons for the deal? How did analysts see this? Why was it unlikely for Nike to take over Reebok? ...
IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance (IOSR-JEF)
... investment and risk. The work of Lettau and Ludvigson (2002) focuses on investment decision and their relationship with the risk premium. They use Q theory and a consumption-wealth ratio as proxy for the future risk premium and then analyze the link between this proxy and future long-term investment ...
... investment and risk. The work of Lettau and Ludvigson (2002) focuses on investment decision and their relationship with the risk premium. They use Q theory and a consumption-wealth ratio as proxy for the future risk premium and then analyze the link between this proxy and future long-term investment ...
Answers to Second Midterm (version 2)
... briefly explain one reason for each type of unemployment. Frictional unemployment: unemployment caused by the time it takes workers to search for a job. (1 point) Reasons for frictional unemployment could be: different preferences and abilities of workers and jobs have different attributes, imperfec ...
... briefly explain one reason for each type of unemployment. Frictional unemployment: unemployment caused by the time it takes workers to search for a job. (1 point) Reasons for frictional unemployment could be: different preferences and abilities of workers and jobs have different attributes, imperfec ...
Ch.10- Aggregate Demand/Aggregate Supply
... Any non-price-level change that increases aggregate spending (on domestic goods) shifts AD to the right. A drop in the foreign exchange value of the dollar (weak dollar) Increased security about jobs and future income Improvements in economic conditions in other countries A reduction in real interes ...
... Any non-price-level change that increases aggregate spending (on domestic goods) shifts AD to the right. A drop in the foreign exchange value of the dollar (weak dollar) Increased security about jobs and future income Improvements in economic conditions in other countries A reduction in real interes ...
FRBSF E L
... In standard economic theory, the natural interest rate—that is, the short-term real interest rate at which the economy would stay at full employment—is related positively to the growth rate of potential output. Higher potential growth can affect the real interest rate via two key channels. First, it ...
... In standard economic theory, the natural interest rate—that is, the short-term real interest rate at which the economy would stay at full employment—is related positively to the growth rate of potential output. Higher potential growth can affect the real interest rate via two key channels. First, it ...
Inflation
... inflation and recessionary gap, noting that due instead to redistribution of income from firms to workers, it is the firms who will be laying workers off on account of higher real cost of production 2. Unanticipated Inflation in the Market for Financial Capital a. Redistribution of Income: When infl ...
... inflation and recessionary gap, noting that due instead to redistribution of income from firms to workers, it is the firms who will be laying workers off on account of higher real cost of production 2. Unanticipated Inflation in the Market for Financial Capital a. Redistribution of Income: When infl ...
1. Assume the following model of the economy, with the price level
... Central Bank of Alpha follows a policy of holding a constant money supply. The Central Bank of Beta follows a policy of holding a constant interest rate. Compare the impact of the tax cut on income and interest rates in the two countries. 6. Policymakers are contemplating undertaking either an incre ...
... Central Bank of Alpha follows a policy of holding a constant money supply. The Central Bank of Beta follows a policy of holding a constant interest rate. Compare the impact of the tax cut on income and interest rates in the two countries. 6. Policymakers are contemplating undertaking either an incre ...
Document
... At the beginning of the 21st century most economists (a) urged the Fed to focus on its goal of high employment. (b) urged central banks to focus their energy on low inflation. (c) believed the underlying inflation rate in the U.S. was higher than it had been in the late 1970s. (d) were critical of t ...
... At the beginning of the 21st century most economists (a) urged the Fed to focus on its goal of high employment. (b) urged central banks to focus their energy on low inflation. (c) believed the underlying inflation rate in the U.S. was higher than it had been in the late 1970s. (d) were critical of t ...
View - The IJBM
... The development of the capital market can be reflected on the stock market price fluctuations. Changes in stock prices are influenced by several factors, according to Samsul (2006) there are seven factors: (1) The gross domestic product; (2) inflation; (3) the unemployment rate; (4) the interest rat ...
... The development of the capital market can be reflected on the stock market price fluctuations. Changes in stock prices are influenced by several factors, according to Samsul (2006) there are seven factors: (1) The gross domestic product; (2) inflation; (3) the unemployment rate; (4) the interest rat ...
Two Days Left… SIGN UP FOR YOUR AP EXAM(S)!
... What makes money effective? 1. Generally Accepted - Buyers and sellers have confidence that it IS legal tender. 2. Scarce - Money must not be easily reproduced. 3. Portable and Dividable - Money must be easily transported and divided. The Purchasing Power of money is the amount of goods and services ...
... What makes money effective? 1. Generally Accepted - Buyers and sellers have confidence that it IS legal tender. 2. Scarce - Money must not be easily reproduced. 3. Portable and Dividable - Money must be easily transported and divided. The Purchasing Power of money is the amount of goods and services ...
14.02 Quiz 1 Solution
... it is clear from the graph of section 6. By considering the investment equation, and noting that the interest rate and GDP are the same in section 4 and 6, however the constant in the investment equation is lower in section 6, then it must be that the investment is section 6 is lower than in section ...
... it is clear from the graph of section 6. By considering the investment equation, and noting that the interest rate and GDP are the same in section 4 and 6, however the constant in the investment equation is lower in section 6, then it must be that the investment is section 6 is lower than in section ...
Monetary policy

Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.Further goals of a monetary policy are usually to contribute to economic growth and stability, to lower unemployment, and to maintain predictable exchange rates with other currencies.Monetary economics provides insight into how to craft optimal monetary policy.Monetary policy is referred to as either being expansionary or contractionary, where an expansionary policy increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual, and contractionary policy expands the money supply more slowly than usual or even shrinks it. Expansionary policy is traditionally used to try to combat unemployment in a recession by lowering interest rates in the hope that easy credit will entice businesses into expanding. Contractionary policy is intended to slow inflation in order to avoid the resulting distortions and deterioration of asset values.Monetary policy differs from fiscal policy, which refers to taxation, government spending, and associated borrowing.