Volcanoes - The Open Mind Academy
... Volcanoes vary quite a bit in their structure - some are cracks in the earth's crust where lava erupts, and some are domes, shields, or mountain-like structures with a crater at the summit. Magma is molten rock within the Earth's crust. When magma erupts through the earth's surface it is called lava ...
... Volcanoes vary quite a bit in their structure - some are cracks in the earth's crust where lava erupts, and some are domes, shields, or mountain-like structures with a crater at the summit. Magma is molten rock within the Earth's crust. When magma erupts through the earth's surface it is called lava ...
Hotspots, Shield Volcanoes and Supervolcanoes
... The gases are the cause of the explosion that occurs once the eruption is underway - the magma pools below the surface under great pressure. When the steady build up of pressure finally forces a way through to the surface the effect is similar to removing the cork from champagne - the gases suddenl ...
... The gases are the cause of the explosion that occurs once the eruption is underway - the magma pools below the surface under great pressure. When the steady build up of pressure finally forces a way through to the surface the effect is similar to removing the cork from champagne - the gases suddenl ...
Volcanic activity
... Types of volcanoes Shield volcano Mountain w/ broad gently sloping sides that forms when basaltic rock is layered Cinder cone volcanoes Forms when material is ejected high in to the air and piles up around a vent Has steep sides More explosive Composite volcanoes Much larger than ci ...
... Types of volcanoes Shield volcano Mountain w/ broad gently sloping sides that forms when basaltic rock is layered Cinder cone volcanoes Forms when material is ejected high in to the air and piles up around a vent Has steep sides More explosive Composite volcanoes Much larger than ci ...
What is a volcano? - Mr. LaFranca`s Earth Science Class
... • Lava is magma that reaches the surface of the crust. Affects are very localized • Pyroclastic Ash is a mixture of tiny rocks and dust that form huge clouds. Affects are localized and regional. • Pyroclastic Ash can be very thick and block out sunlight destroying crops. • The ash can settle on loca ...
... • Lava is magma that reaches the surface of the crust. Affects are very localized • Pyroclastic Ash is a mixture of tiny rocks and dust that form huge clouds. Affects are localized and regional. • Pyroclastic Ash can be very thick and block out sunlight destroying crops. • The ash can settle on loca ...
Cause(s) - elearningadulted
... many cause-and-effect relationships. When the temperature rises deep under the Earth’s crust, it becomes hot enough to melt rock and turn it into magma. Sometimes this melted rock blasts through the Earth’s surface, which causes rock, ash, and deadly gases to fly into the air. The lava that flows ou ...
... many cause-and-effect relationships. When the temperature rises deep under the Earth’s crust, it becomes hot enough to melt rock and turn it into magma. Sometimes this melted rock blasts through the Earth’s surface, which causes rock, ash, and deadly gases to fly into the air. The lava that flows ou ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... Ash can reach the upper atmosphere and circle the Earth for years Larger pieces fall closer to the volcano Explosive eruption can blas millions of tons of lava and rock from a volcano In seconds an explosive eruption can demolish a mountainside ...
... Ash can reach the upper atmosphere and circle the Earth for years Larger pieces fall closer to the volcano Explosive eruption can blas millions of tons of lava and rock from a volcano In seconds an explosive eruption can demolish a mountainside ...
Volcanoes
... • Composite volcanoes – AKA stratovolcanoes – Moderately to steeply sloping – Constructed of alternating layers of pyroclastic debris and solidified lava flows – Composed primarily of intermediate composition volcanic rocks (i.e., andesite) – Most common type of volcano at convergent plate boundarie ...
... • Composite volcanoes – AKA stratovolcanoes – Moderately to steeply sloping – Constructed of alternating layers of pyroclastic debris and solidified lava flows – Composed primarily of intermediate composition volcanic rocks (i.e., andesite) – Most common type of volcano at convergent plate boundarie ...
VOLCANOES MR.OCHOA CHAPTER 6
... They are usually form from many layers of lava. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt. They result from quiet eruptions. The Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. It is a gently sloping mountain formed ...
... They are usually form from many layers of lava. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt. They result from quiet eruptions. The Hawaiian Islands are shield volcanoes. It is a gently sloping mountain formed ...
Geology 101 Homework 4
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
... 4) Explain the three ways magma forms inside the Earth (p. 140). What is the relationship between plate tectonic setting and the way magma forms? (p. 156) Which magma formation process occurs most frequently inside the Earth? 5) What shapes do bodies of igneous rock form when they intrude the Earth? ...
Volcano - Muskegon Area ISD
... system in North America. It has been termed a "supervolcano" because the caldera was formed by exceptionally large explosive eruptions. • The amount of ash and gases released into the atmosphere probably caused significant impacts to world weather patterns and led to the extinction of many species, ...
... system in North America. It has been termed a "supervolcano" because the caldera was formed by exceptionally large explosive eruptions. • The amount of ash and gases released into the atmosphere probably caused significant impacts to world weather patterns and led to the extinction of many species, ...
Earth Science--Ch 9 Volcanoes Review Guide
... Name the 3 types of volcanoes. Compare & contrast the 3 types of volcanoes. (Think about what they look like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
... Name the 3 types of volcanoes. Compare & contrast the 3 types of volcanoes. (Think about what they look like/shape, how they erupt, what types of materials they are primarily made of, where they tend to form.) ...
Warm up question What hypothesis is Alfred Wegener known for
... volcanic vent. Become wider over time as materials fall back into the vent. Calderas – when a magma chamber is emptied the volcanic cone may collapse, forming a basin ...
... volcanic vent. Become wider over time as materials fall back into the vent. Calderas – when a magma chamber is emptied the volcanic cone may collapse, forming a basin ...
File
... 3. A composite volcano is formed when both lava and ash erupt from a vent. The materials pile up in alternate layers around the vent and form a cone-shaped mountain that comes to a point on top. (Examples: Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Vesuvius in Italy.) 4. Divide your class into three groups, and ass ...
... 3. A composite volcano is formed when both lava and ash erupt from a vent. The materials pile up in alternate layers around the vent and form a cone-shaped mountain that comes to a point on top. (Examples: Mount Fuji in Japan, Mount Vesuvius in Italy.) 4. Divide your class into three groups, and ass ...
Sample material for Geography Test I
... zone that marks the activity and determines both nature and intensity of volcanic eruptions. The plate boundaries are classified into three broad groups and volcanicity associates itself with all three. Most of the fissure ejections links itself with divergening or constructive plate margins. The su ...
... zone that marks the activity and determines both nature and intensity of volcanic eruptions. The plate boundaries are classified into three broad groups and volcanicity associates itself with all three. Most of the fissure ejections links itself with divergening or constructive plate margins. The su ...
Haystack Rock - City of Cannon Beach
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
... Height: 71.62 meters or 235 feet - comprised of about 1 million tons of rock Comprised of basalt, feldspar, silica, olivine and pyroxene “How did the Rock get here?” Around 15 million years ago molten lava flowed from the “Yellowstone Hotspot”. Of the 300 flows that happened, Haystack Rock arrived v ...
Earthquake, Volcano and Mountain Review Sheet
... i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform boundary) c. Focus: the point underground where the rocks first begin to move d. Epicenter: the point on earth’s surface directly above the focus e. Stress: pressing, pulling or pushing of one object ag ...
... i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform boundary) c. Focus: the point underground where the rocks first begin to move d. Epicenter: the point on earth’s surface directly above the focus e. Stress: pressing, pulling or pushing of one object ag ...
Volcanoes
... • Thick, sticky lava plugs vent like a cork and builds up pressure • Explodes and releases pyroclastic flow – Volcanic ash: fine, rock particles ...
... • Thick, sticky lava plugs vent like a cork and builds up pressure • Explodes and releases pyroclastic flow – Volcanic ash: fine, rock particles ...
10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions 10.1 The Nature of
... particles produced in volcanic eruptions. • The fragments ejected during eruptions range in size from very fine duct and volcanic ash (less than 2 millimeters) to pieces that weigh several ...
... particles produced in volcanic eruptions. • The fragments ejected during eruptions range in size from very fine duct and volcanic ash (less than 2 millimeters) to pieces that weigh several ...
GAPS Guidelines
... The explosion phenomena, aside from the audible report, is a strong airborne shock wave. The wave itself can carry several miles and, by virtue of the pressure, can be extremely damaging. The explosion surge may pick up and carry debris (projectiles). The Pyroclastic flow includes material ejected a ...
... The explosion phenomena, aside from the audible report, is a strong airborne shock wave. The wave itself can carry several miles and, by virtue of the pressure, can be extremely damaging. The explosion surge may pick up and carry debris (projectiles). The Pyroclastic flow includes material ejected a ...
What are Volcanoes?
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
6.15 Eruptions and Volcano Types
... the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And there is where we find the main zones or section of volcanic activity. Magma is a liquid. When it reaches the earth’s surface, it may erupt In the form of solids, liquids, and gases. ...
... the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And there is where we find the main zones or section of volcanic activity. Magma is a liquid. When it reaches the earth’s surface, it may erupt In the form of solids, liquids, and gases. ...
Volcanoes by Marida Torosyan and Ani Tashyan
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
Volcanoes Answer Key
... • Did not take warnings seriously volcano was about to explode well • Politicans in Colombian Congress criticized the enough) scientists and civil defence authorities for scaremongering with hazard maps Could not say exactly when eruption would occur • Local officials failed to give warnings (as to ...
... • Did not take warnings seriously volcano was about to explode well • Politicans in Colombian Congress criticized the enough) scientists and civil defence authorities for scaremongering with hazard maps Could not say exactly when eruption would occur • Local officials failed to give warnings (as to ...
Tick, Tick, Boom Danger Zone
... When a volcano erupts it can do numerous amounts of things. Volcanoes can cause deaths, damage, and cause both local and global effects. Mt. Tambora’s explosion in 1815 caused both it created a 5-meter high tsunami, ash fall, disease, and global cooling, which resulted in 1816 “year without a summer ...
... When a volcano erupts it can do numerous amounts of things. Volcanoes can cause deaths, damage, and cause both local and global effects. Mt. Tambora’s explosion in 1815 caused both it created a 5-meter high tsunami, ash fall, disease, and global cooling, which resulted in 1816 “year without a summer ...
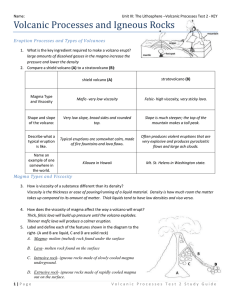
Volcanic Processes and Igneous Rocks
... Lava Tube – Underground pipe-like structures that carry lava far from vent. Stratovolcano Plume – Huge amounts of pressure cause the eruption to throw ash several miles into atmosphere Stratovolcano Pyroclastic Flow – A mass of very hot gas and rock that rush down the sides of a volcano ...
... Lava Tube – Underground pipe-like structures that carry lava far from vent. Stratovolcano Plume – Huge amounts of pressure cause the eruption to throw ash several miles into atmosphere Stratovolcano Pyroclastic Flow – A mass of very hot gas and rock that rush down the sides of a volcano ...
Nevado del Ruiz

The Nevado del Ruiz (Spanish pronunciation: [neβaðo ðel ˈrwis]), also known as La Mesa de Herveo (English: Mesa of Herveo (the nearby town)), or Kumanday in the language of the local pre-Columbian indigenous people, is a volcano located on the border of the departments of Caldas and Tolima in Colombia, about 129 kilometers (80 mi) west of the capital city Bogotá. It is a stratovolcano, composed of many layers of lava alternating with hardened volcanic ash and other pyroclastic rocks. Nevado del Ruiz has been active for about two million years, since the early Pleistocene or late Pliocene epoch, with three major eruptive periods. The current volcanic cone formed during the present eruptive period, which began 150 thousand years ago.The volcano usually generates Plinian eruptions, which produce swift-moving currents of hot gas and rock called pyroclastic flows. These eruptions often cause massive lahars (mud and debris flows), which pose a threat to human life and the environment. The impact of such an eruption is increased as the hot gas and lava melts the mountain's snowcap, adding large quantities of water to the flow. On November 13, 1985, a small eruption produced an enormous lahar that buried and destroyed the town of Armero in Tolima, causing an estimated 25,000 deaths. This event later became known as the Armero tragedy—the deadliest lahar in recorded history. Similar but less deadly incidents occurred in 1595 and 1845, consisting of a small explosive eruption followed by a large lahar.The volcano is part of Los Nevados National Natural Park, which also contains several other volcanoes. The summit of Nevado del Ruiz is covered by large glaciers, although these have retreated significantly since 1985 because of global warming. The volcano continues to pose a threat to the nearby towns and villages, and it is estimated that up to 500,000 people could be at risk from lahars from future eruptions.