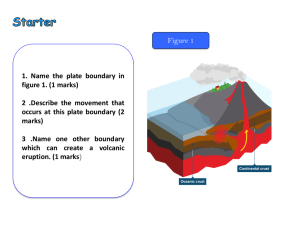
Volcanoes
... O They are formed from layers of lava and ash. O Composite Cones are also known as stratovolcanoes. ...
... O They are formed from layers of lava and ash. O Composite Cones are also known as stratovolcanoes. ...
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS: MENKE
... number for the average time between large eruptions. o Our ability to find all the past eruptions, date them, and most importantly measure their size is just too poor to spot cycles, How much warning do you think people will have before an eruption? o A week or two, if we’re lucky Can you talk about ...
... number for the average time between large eruptions. o Our ability to find all the past eruptions, date them, and most importantly measure their size is just too poor to spot cycles, How much warning do you think people will have before an eruption? o A week or two, if we’re lucky Can you talk about ...
Bill Menke answers questions about Mt Vesuvius
... number for the average time between large eruptions. o Our ability to find all the past eruptions, date them, and most importantly measure their size is just too poor to spot cycles, How much warning do you think people will have before an eruption? o A week or two, if we’re lucky Can you talk about ...
... number for the average time between large eruptions. o Our ability to find all the past eruptions, date them, and most importantly measure their size is just too poor to spot cycles, How much warning do you think people will have before an eruption? o A week or two, if we’re lucky Can you talk about ...
Volcano and extrusive igneous rock notes
... Some effects of volcanoes • Volcanic activity can lead to the creation of new land area • source of geothermal energy • concentration of economic minerals such as gold, silver, et cetera • might have played a role in providing the environment for development of life on Earth, perhaps along mid-ocean ...
... Some effects of volcanoes • Volcanic activity can lead to the creation of new land area • source of geothermal energy • concentration of economic minerals such as gold, silver, et cetera • might have played a role in providing the environment for development of life on Earth, perhaps along mid-ocean ...
volcano
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
... a magma chamber below the surface of the Earth. Volcanoes are generally found at different places on Earth. For example, in the oceans, Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volc ...
Types of Volcanoes Dangers from Composite Cones Pyroclastic
... When the pressure is released the gases escape. Common gases usually include water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur, nitrogen, and a little chlorine, hydrogen, and argon. Sulfur gases can be easily detected from their “rotten egg” odor. ...
... When the pressure is released the gases escape. Common gases usually include water vapor, carbon dioxide, sulfur, nitrogen, and a little chlorine, hydrogen, and argon. Sulfur gases can be easily detected from their “rotten egg” odor. ...
The Nature of Volcanoes and Types updated.notebook
... Dissolved Gases: Affect on Eruptions Dissolved gases are mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide. As magma moves toward the surface, pressure is greatly reduced in the magma. This reduction in pressure allows the gases to release suddenly. ...
... Dissolved Gases: Affect on Eruptions Dissolved gases are mostly water vapor and carbon dioxide. As magma moves toward the surface, pressure is greatly reduced in the magma. This reduction in pressure allows the gases to release suddenly. ...
composite volcanoes - Mesa Public Schools
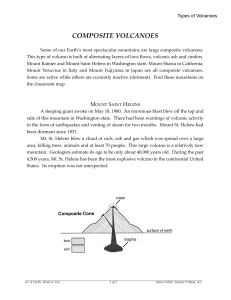
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
volcanoes-notes
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions Volcanic ash ...
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions Volcanic ash ...
Virtual Volcano
... Click “start eruption.” (Make sure your volume is ON but not too loud!) What kind of eruption have you created? _____________ Where are the lava tubes? __________________ Now click on “change settings” again. This time, make viscosity low and gas high. Click on “set conditions.” What kind of volcano ...
... Click “start eruption.” (Make sure your volume is ON but not too loud!) What kind of eruption have you created? _____________ Where are the lava tubes? __________________ Now click on “change settings” again. This time, make viscosity low and gas high. Click on “set conditions.” What kind of volcano ...
Preparing for Volcanoes
... hydrothermal systems. The gases are composed mainly of water vapour, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide. They are often acidic and can be harmful even at low concentrations. ...
... hydrothermal systems. The gases are composed mainly of water vapour, carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide. They are often acidic and can be harmful even at low concentrations. ...
Active
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
... There are 33 active volcanoes in the US Most are at convergent plate boundaries in Alaska and N. California, Oregon, and Washington. These are all stratovolcanoes, which are the most dangerous in terms of explosive activity. Some are on or near hotspots: Hawaii’s volcanoes, and Yellowstone Some are ...
Volcanoes
... top of the buildings after the explosion • Considered to be one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world – 3,000,000 people live close to it ...
... top of the buildings after the explosion • Considered to be one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world – 3,000,000 people live close to it ...
- ILM.COM.PK
... • Magma compositions vary in SiO2 , iron, magnesium, and volatile gases • Mafic magma – low in SiO2 (45-50 %) but high in iron, and magnesium • Felsic magma – high in SiO2 (up to 75 %) but low in iron, and magnesium • Intermediate magma – intermediate range of SiO2 (50-65 %), iron, and magnesium • A ...
... • Magma compositions vary in SiO2 , iron, magnesium, and volatile gases • Mafic magma – low in SiO2 (45-50 %) but high in iron, and magnesium • Felsic magma – high in SiO2 (up to 75 %) but low in iron, and magnesium • Intermediate magma – intermediate range of SiO2 (50-65 %), iron, and magnesium • A ...
Shield Volcano
... • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate around the vent. (Describ ...
... • Cinder cones are the smallest volcanoes (< 500 ft), formed by explosive eruptions of explosive lava, and can form near other volcanoes (How does it form?) • Blown violently into the air, the erupting lava breaks apart into fragments called cinders that fall and accumulate around the vent. (Describ ...
HST_CRF_04_02_03.qxd
... 2. What is magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface called? lava magma ash rock 3. How are volcanoes created? by tectonic plates colliding by cracks in the Earth’s crust by collections of ash and rock by many eruptions of lava ...
... 2. What is magma that flows onto the Earth’s surface called? lava magma ash rock 3. How are volcanoes created? by tectonic plates colliding by cracks in the Earth’s crust by collections of ash and rock by many eruptions of lava ...
the free PDF resource
... Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fold mountains? A collision boundary. 4. Give two fe ...
... Magma is the name given to molten rock beneath the earth’s surface. It becomes lava once it erupts. 2. Which tectonic plate is also known as ‘the Ring of Fire’? The Pacific Plate. 3. Which type of plate boundary is responsible for the formation of fold mountains? A collision boundary. 4. Give two fe ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... High-silica lava exits from a vent. Due to its high viscosity (doesn’t flow very fast or far), it builds up into a dome. Effectively “plugs” the main vent. Can still emit ash, gases, and even lava. Example: Lava Dome in Mt St Helen’s crater. ...
... High-silica lava exits from a vent. Due to its high viscosity (doesn’t flow very fast or far), it builds up into a dome. Effectively “plugs” the main vent. Can still emit ash, gases, and even lava. Example: Lava Dome in Mt St Helen’s crater. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and lapili. • The most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity is water vapor. • A cinder cone is a type of volcano that is built almost entirely from ejected lava frag ...
... • The particles produced in volcanic eruptions are called pyroclastic material. • Pyroclastic materials include ash, cinders and lapili. • The most abundant gas associated with volcanic activity is water vapor. • A cinder cone is a type of volcano that is built almost entirely from ejected lava frag ...
Mount Pelée

Mount Pelée (/pəˈleɪ/; French: Montagne Pelée ""Bald Mountain"") is an active volcano at the northern end of Martinique, an island and French overseas department in the Lesser Antilles island arc of the Caribbean. Its volcanic cone is composed of layers of volcanic ash and hardened lava.The stratovolcano is famous for its eruption in 1902 and the destruction that resulted, dubbed the worst volcanic disaster of the 20th century. The eruption killed about 30,000 people. Most deaths were caused by pyroclastic flows and occurred in the city of Saint-Pierre, which was, at that time, the largest city on the island.Pyroclastic flows completely destroyed St. Pierre, a town of 30,000 people, within minutes of the eruption. The eruption left only two survivors in the direct path of the flows: Louis-Auguste Cyparis survived because he was in a poorly ventilated, dungeon-like jail cell; Léon Compère-Léandre, living on the edge of the city, escaped with severe burns. Havivra Da Ifrile, a young girl, reportedly escaped with injuries during the eruption by taking a small boat to a cave down shore, and was later found adrift two miles (3 km) from the island, unconscious. The event marked the only major volcanic disaster in the history of France and its overseas territories.