dl1.cuni.cz
... Fixed-but-adjustable exchange rates, Central role of the dollar, Government interventions used to peg the exchange rate (autonomous monetary policies), Limits on capital flows, Creation of IMF ...
... Fixed-but-adjustable exchange rates, Central role of the dollar, Government interventions used to peg the exchange rate (autonomous monetary policies), Limits on capital flows, Creation of IMF ...
Explaining rise of barter in Russia: Virtual Economy vs. Monetary Issues
... order for them to keep producing (and continue wasting), there must be a source in the system adding economic value; since otherwise it would run out of economic resources. Such economic values, Gaddy and Ickes argue, are transferred from value generating units through a complex network of transacti ...
... order for them to keep producing (and continue wasting), there must be a source in the system adding economic value; since otherwise it would run out of economic resources. Such economic values, Gaddy and Ickes argue, are transferred from value generating units through a complex network of transacti ...
PDF, 45 KB
... rise in real GDP of a good 2% would, on its own, lead to a reduction of the budget deficit of around 0.5 percentage points. However, it must be taken into account that major reform measures are meant to take effect in 2008, namely corporation tax reform and health care reform, whose actual design an ...
... rise in real GDP of a good 2% would, on its own, lead to a reduction of the budget deficit of around 0.5 percentage points. However, it must be taken into account that major reform measures are meant to take effect in 2008, namely corporation tax reform and health care reform, whose actual design an ...
Page 1 Econ 303: Intermediate Macroeconomics I Dr. Sauer
... C) increases GDP by $20,000. D) increases GDP by more than $20,000. 15. The panel of economists appointed by the Senate Finance Committee estimates that the CPI ______ inflation by approximately ______ percentage point(s) per year. A) overestimates; 1 B) overestimates; 10 C) underestimates; 1 D) und ...
... C) increases GDP by $20,000. D) increases GDP by more than $20,000. 15. The panel of economists appointed by the Senate Finance Committee estimates that the CPI ______ inflation by approximately ______ percentage point(s) per year. A) overestimates; 1 B) overestimates; 10 C) underestimates; 1 D) und ...
Fiscal Policy - SHS Debate team
... economy accordingly. The government’s main goals in doing so are to establish steady prices for goods and services, achieve high employment, and encourage economic growth. This is controlled by the central government , meaning Congress and the President. Ess ...
... economy accordingly. The government’s main goals in doing so are to establish steady prices for goods and services, achieve high employment, and encourage economic growth. This is controlled by the central government , meaning Congress and the President. Ess ...
Monetary policy
... transfers, and other items. It is also negative and has been growing more so. Are we borrowing too much from other countries? ...
... transfers, and other items. It is also negative and has been growing more so. Are we borrowing too much from other countries? ...
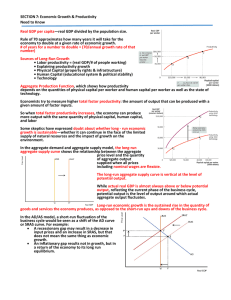
SECTION 7: Economic Growth & Productivity Need to Know —real GDP divided by the population size.
... depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
... depends on the quantities of physical capital per worker and human capital per worker as well as the state of technology. ...
International Political Economy
... A common distinction is made between 'goods' that are tangible property and services which are nonphysical Commodities may be used as a synonym for economic goods but often refer to marketable raw materials and primary products ...
... A common distinction is made between 'goods' that are tangible property and services which are nonphysical Commodities may be used as a synonym for economic goods but often refer to marketable raw materials and primary products ...
economic insight SOUTH EAST ASIA Quarterly briefing May 2012
... The oil price is the most important example of a realisation in global commodity markets: the rediscovery of scarcity. With hundreds of millions of Asian consumers starting to spend on consumer goods, transport and better food, prices for both mineral and agricultural commodities have risen sharply. ...
... The oil price is the most important example of a realisation in global commodity markets: the rediscovery of scarcity. With hundreds of millions of Asian consumers starting to spend on consumer goods, transport and better food, prices for both mineral and agricultural commodities have risen sharply. ...
Presentation to Community Leaders Salt Lake City, Utah
... year, prices rose much more quickly. We don’t have the June data for this measure yet, but the annualized price increase in the first half of this year looks to have been more like 3½ percent. This increase in inflation reflected sharp rises in many commodity prices, especially gasoline and other en ...
... year, prices rose much more quickly. We don’t have the June data for this measure yet, but the annualized price increase in the first half of this year looks to have been more like 3½ percent. This increase in inflation reflected sharp rises in many commodity prices, especially gasoline and other en ...
Speech by Finance MEC Mandla Nkomfe on the presentation of PERO
... The economic contribution of the agricultural sector has been declining both nationally and provincially. In the province, the subsector contributed 0.4% in 2011. Employment by the sub-sector has also been declining, ranging between 50,000 and 42,750 in 2002 and 2011 for the province. However, emplo ...
... The economic contribution of the agricultural sector has been declining both nationally and provincially. In the province, the subsector contributed 0.4% in 2011. Employment by the sub-sector has also been declining, ranging between 50,000 and 42,750 in 2002 and 2011 for the province. However, emplo ...
Government sums up results for 2016 and determines yearly
... growth and macroeconomic balance, increase of the level and quality of life of the population. During the discussion of the issues, included into the agenda of the meeting of the Cabinet of Ministers, it was highlighted that the gross domestic product of the country increased by 7,8% in 2016. The v ...
... growth and macroeconomic balance, increase of the level and quality of life of the population. During the discussion of the issues, included into the agenda of the meeting of the Cabinet of Ministers, it was highlighted that the gross domestic product of the country increased by 7,8% in 2016. The v ...
Theories of U.S. Economic Policy Economic policy refers to the
... Maynard Keynes, a 20th century British economist. Keynes’ central belief was that, in order to keep people employed, governments need to run up deficits during economic downturns through increased spending and tax breaks. Conversely, during prosperous times, governments should cut spending and insti ...
... Maynard Keynes, a 20th century British economist. Keynes’ central belief was that, in order to keep people employed, governments need to run up deficits during economic downturns through increased spending and tax breaks. Conversely, during prosperous times, governments should cut spending and insti ...
lecture 01: introduction to economics
... benefit analysis. Rational choice is a general theory of human behavior that assumes individuals try to make the most efficient decisions possible in an environment of scarce resources. By "efficient" it is meant that humans are "utility maximizers" - for any given choice a person seeks the most ben ...
... benefit analysis. Rational choice is a general theory of human behavior that assumes individuals try to make the most efficient decisions possible in an environment of scarce resources. By "efficient" it is meant that humans are "utility maximizers" - for any given choice a person seeks the most ben ...
- Troy Media
... Business conditions are never the result of general changes permeating through the whole economy. The causality is the other way ‘round. Businessmen use information specific to both time and place to alter their goods and services on offer. Consumers do the same thing – surely you don’t care what t ...
... Business conditions are never the result of general changes permeating through the whole economy. The causality is the other way ‘round. Businessmen use information specific to both time and place to alter their goods and services on offer. Consumers do the same thing – surely you don’t care what t ...
Full Paper
... mechanism would name workers the “leading force” of the new society building process to make them enthusiastic about future changes and not demanding about the living standards. Or the nationalization can be realized through the “hard” form of the control when the large part of the population is con ...
... mechanism would name workers the “leading force” of the new society building process to make them enthusiastic about future changes and not demanding about the living standards. Or the nationalization can be realized through the “hard” form of the control when the large part of the population is con ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Recessions and Depressions While Americans experienced remarkable growth in their standards of living in the 20th century, this growth did not occur evenly throughout the century. Instead, Americans experienced periods of rapid growth in their standards of living followed by periods of decline --- a ...
... Recessions and Depressions While Americans experienced remarkable growth in their standards of living in the 20th century, this growth did not occur evenly throughout the century. Instead, Americans experienced periods of rapid growth in their standards of living followed by periods of decline --- a ...
Unit 4 Filled In
... the economy. A positive rate of inflation does not mean that every single price increases, nor that all prices increase by the same amount, nor that the price of some goods didn't fall. It represents an average price increase for the goods and services in the economy. ...
... the economy. A positive rate of inflation does not mean that every single price increases, nor that all prices increase by the same amount, nor that the price of some goods didn't fall. It represents an average price increase for the goods and services in the economy. ...
Basics of Economics
... • Resources: things used to provide what we need or want • Factors of Production: – Land resources: land, soil, plants, animals, water, oil, and metals. – Labor resources: the work people do with their hands and their minds (carpenters, singers, teachers, etc.) – Capital resources: the goods used to ...
... • Resources: things used to provide what we need or want • Factors of Production: – Land resources: land, soil, plants, animals, water, oil, and metals. – Labor resources: the work people do with their hands and their minds (carpenters, singers, teachers, etc.) – Capital resources: the goods used to ...
- Centrum Badawcze Transformacji, Integracji i
... from settled among economists, and the debate continues. I think an answer to the question of who is right: the “gradualists” or the “shock-therapists”, can only be given if we have the proper definition of the process we are discussing. My definition is that transition to the market system is a lon ...
... from settled among economists, and the debate continues. I think an answer to the question of who is right: the “gradualists” or the “shock-therapists”, can only be given if we have the proper definition of the process we are discussing. My definition is that transition to the market system is a lon ...
Additions to study guide on material since the second exam:
... b. In Keynesian terms, list and explain what may have caused this performance, other than fiscal or monetary policies. c. Explain the appropriate fiscal policy responses according to the Keynesians. d. Name and define the three tools of the Fed and explain how each will be used in response to output ...
... b. In Keynesian terms, list and explain what may have caused this performance, other than fiscal or monetary policies. c. Explain the appropriate fiscal policy responses according to the Keynesians. d. Name and define the three tools of the Fed and explain how each will be used in response to output ...