Different types of Money
... 1. Money is a medium of exchange with a uniform agreed-‐upon value. Money’s use speeds up transactions and increases the variety of possible transactions because nobody has to compute how many chickens a ...
... 1. Money is a medium of exchange with a uniform agreed-‐upon value. Money’s use speeds up transactions and increases the variety of possible transactions because nobody has to compute how many chickens a ...
Untitled
... in the real value of their holdings of fixed nominal value assets (thanks to a larger than average increase in their holdings of helicopter-dropped money or through deflation) or a fall in the real value of their fixed nominal value debt (through inflation) are just offset by a fall in spending by a ...
... in the real value of their holdings of fixed nominal value assets (thanks to a larger than average increase in their holdings of helicopter-dropped money or through deflation) or a fall in the real value of their fixed nominal value debt (through inflation) are just offset by a fall in spending by a ...
cyprus international university
... • Explain the slope of the supply and demand for loanable funds • Shift supply and demand curves in a model of the loanable funds market in response to a change in taxes on interest or investment • Shift supply and demand curves in a model of the loanable funds market in response to a change in the ...
... • Explain the slope of the supply and demand for loanable funds • Shift supply and demand curves in a model of the loanable funds market in response to a change in taxes on interest or investment • Shift supply and demand curves in a model of the loanable funds market in response to a change in the ...
Week 5 In Class CPI GDP
... ____ 30. Suppose that twenty-five years ago a country had nominal GDP of $1,000, a GDP deflator of 200, and a population of 100. Today it has nominal GDP of $3,000, a GDP deflator of 400, and population of 150. What happened to the real GDP per person? a. It more than doubled. b. It increased, but i ...
... ____ 30. Suppose that twenty-five years ago a country had nominal GDP of $1,000, a GDP deflator of 200, and a population of 100. Today it has nominal GDP of $3,000, a GDP deflator of 400, and population of 150. What happened to the real GDP per person? a. It more than doubled. b. It increased, but i ...
Exam Questions
... Which of the following is NOT one of the effects of inflation? a. Firms incur costs associated with changing their prices. b. It redistributes wealth in an arbitrary way between borrowers and lenders. c. It causes tax distortions with respect to interest income and capital gains. d. It systematicall ...
... Which of the following is NOT one of the effects of inflation? a. Firms incur costs associated with changing their prices. b. It redistributes wealth in an arbitrary way between borrowers and lenders. c. It causes tax distortions with respect to interest income and capital gains. d. It systematicall ...
money supply
... bank lent some of the reserves • It could do this, since the flow of money in and out of the bank is fairly predictable and only a fraction of reserves are needed to meet the need for outflows • If the bank needs to keep only 25% of the amount of its deposits on reserve to meet the demand for funds, ...
... bank lent some of the reserves • It could do this, since the flow of money in and out of the bank is fairly predictable and only a fraction of reserves are needed to meet the need for outflows • If the bank needs to keep only 25% of the amount of its deposits on reserve to meet the demand for funds, ...
Discussion by J. Imbs
... In both cases, difference in differences estimation: relative to a treatment (non growing) economy, are GDP differences related with volatility differences in a given sector? Also important to control for aggregate developments, e.g. institutions (finance?) liable to affect aggregates. Focus on inte ...
... In both cases, difference in differences estimation: relative to a treatment (non growing) economy, are GDP differences related with volatility differences in a given sector? Also important to control for aggregate developments, e.g. institutions (finance?) liable to affect aggregates. Focus on inte ...
The Free Enterprise System
... United States to all the other economic systems of the world. You already have a role in the global economy. Chapter 13 Our Economic System ...
... United States to all the other economic systems of the world. You already have a role in the global economy. Chapter 13 Our Economic System ...
Price and Inflation
... 3. GDP sums the dollar value of what has been produced in the economy over the year, not what was actually sold. For example, used car sales are not included. ...
... 3. GDP sums the dollar value of what has been produced in the economy over the year, not what was actually sold. For example, used car sales are not included. ...
... “While similar information imperfections may affect other financial markets, government interventionists contend that the macroeconomic implications of even temporary exchange-market failures are great enough to warrant corrective actions.” Bailey et al (2000) note that one of the ways to deal with ...
04/2012 Rohit Azad and Anupam Das Abstract
... rate of unemployment (NAIRU), entailing an absence of involuntary unemployment. In other words, it is not in the hands of the policy makers to target a particular unemployment rate. Second, even if the economy were stuck at a higher rate of unemployment in the short run, fiscal policy would be ineff ...
... rate of unemployment (NAIRU), entailing an absence of involuntary unemployment. In other words, it is not in the hands of the policy makers to target a particular unemployment rate. Second, even if the economy were stuck at a higher rate of unemployment in the short run, fiscal policy would be ineff ...
Sample Chapter: Chapter 1
... Mao Tse-tung’s ethics teacher in Beijing, held that “a country is an organic whole, just as the human body is an organic whole. It is not like a machine which can be taken apart and put together again” (quoted in Johnson [1983, p. 197]). The individual has significance only as part of the community, ...
... Mao Tse-tung’s ethics teacher in Beijing, held that “a country is an organic whole, just as the human body is an organic whole. It is not like a machine which can be taken apart and put together again” (quoted in Johnson [1983, p. 197]). The individual has significance only as part of the community, ...
Economic Development and Crisis Policy Responses in
... The main argument Krugman pointed out is that the rapid economic growth (measured by massive capital inflow) in developing countries in the 1990’s was not derived directly from the implementation of Washington Consensus (free market and sound money policies). Instead, there are three reasons why th ...
... The main argument Krugman pointed out is that the rapid economic growth (measured by massive capital inflow) in developing countries in the 1990’s was not derived directly from the implementation of Washington Consensus (free market and sound money policies). Instead, there are three reasons why th ...
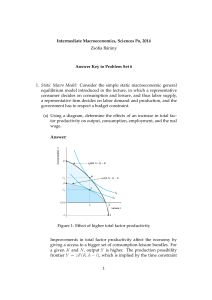
Intermediate Macroeconomics, Sciences Po, 2014 Zsófia Bárány
... to isolate this effect, we would move to a hypothetical point B on the figure below, where agents consume less of the consumption good and enjoy more leisure. To see this, recall that in the equilibrium the slope (in absolute value) of an indifference curve (M RS) must be equal to the wage rate. At ...
... to isolate this effect, we would move to a hypothetical point B on the figure below, where agents consume less of the consumption good and enjoy more leisure. To see this, recall that in the equilibrium the slope (in absolute value) of an indifference curve (M RS) must be equal to the wage rate. At ...
How Do We Measure the Economy`s Health?
... This investigation focuses on measuring the performance of the United States economy. It goes well beyond what students might learn from print or television media and tells much of the rest of the story. Students begin with the reading The Measurement of Economic Performance. This text summarizes th ...
... This investigation focuses on measuring the performance of the United States economy. It goes well beyond what students might learn from print or television media and tells much of the rest of the story. Students begin with the reading The Measurement of Economic Performance. This text summarizes th ...
Gross Domestic Product
... an economy, economists use a measurement of real GDP per capita. It is a measure of real GDP divided by the total population. Real GDP per capita is considered the best measure of a nation’s standard of living. GDP and Quality of Life Like measurements of GDP itself, the measurement of real GDP ...
... an economy, economists use a measurement of real GDP per capita. It is a measure of real GDP divided by the total population. Real GDP per capita is considered the best measure of a nation’s standard of living. GDP and Quality of Life Like measurements of GDP itself, the measurement of real GDP ...
Global-Local Relations, Economic Reformation and Instabilities in
... The studies about the so-called globalization started to be outstanding in the beginning of the nineties, with the overcoming of the Cold War and the proclaimed victory of the capitalistic Western or American democracy. Gradually, this term became to use in a more general way to explain a series of ...
... The studies about the so-called globalization started to be outstanding in the beginning of the nineties, with the overcoming of the Cold War and the proclaimed victory of the capitalistic Western or American democracy. Gradually, this term became to use in a more general way to explain a series of ...
G_______ S
... _________________________ is the total value of productive assets that provide a flow of revenue The decrease in value of capital assets are known as ____________________ Net investment is found by subtracting annual depreciation of an entire economy’s __________________________ from _______________ ...
... _________________________ is the total value of productive assets that provide a flow of revenue The decrease in value of capital assets are known as ____________________ Net investment is found by subtracting annual depreciation of an entire economy’s __________________________ from _______________ ...
IS –LM model
... • Initially, the economy is at point 1 at the intersection of AD1 and AS1, where the realized price level is at the expected price level P1 and aggregate output is at the natural rate level Yn. • Because point 1 is also on the long-run aggregate supply curve at Yn, there is no tendency for the aggre ...
... • Initially, the economy is at point 1 at the intersection of AD1 and AS1, where the realized price level is at the expected price level P1 and aggregate output is at the natural rate level Yn. • Because point 1 is also on the long-run aggregate supply curve at Yn, there is no tendency for the aggre ...
solution 2
... nature leaves the country in return for the money which is received e.g. accountants working in say Kenya on a project or foreigners spending their holidays in Rwanda; similarly the term invisible imports is applied to the purchase by Rwandan businesses of foreign services. It is extremely unlikely ...
... nature leaves the country in return for the money which is received e.g. accountants working in say Kenya on a project or foreigners spending their holidays in Rwanda; similarly the term invisible imports is applied to the purchase by Rwandan businesses of foreign services. It is extremely unlikely ...
Review of aggregate production function
... (2) ln(Yt) = ln(At )+ α ln(Kt) + (1 - α) ln(Lt ) Now take the time derivative. Note that ∂ln(x)/∂x=1/x and use chain rule: (3) ∂ln(Yt)/∂t= g[Yt] = g[At] )+ α g[Kt] + (1 - α) g[Lt ] In the C-D production function (see above), ) α is the competitive share of K sh(K); and (1 - α) the competitive share ...
... (2) ln(Yt) = ln(At )+ α ln(Kt) + (1 - α) ln(Lt ) Now take the time derivative. Note that ∂ln(x)/∂x=1/x and use chain rule: (3) ∂ln(Yt)/∂t= g[Yt] = g[At] )+ α g[Kt] + (1 - α) g[Lt ] In the C-D production function (see above), ) α is the competitive share of K sh(K); and (1 - α) the competitive share ...