Chapter 4 Inflation and Deflation
... inflation, nor is there a common agrteement on what constitutes acceptable levels of inflation, bad inflation, or hyperinflation. Generally it can be said that inflation is a measure of a general increase of the price level in an economy, as represented typically by an inclusive price index, such as ...
... inflation, nor is there a common agrteement on what constitutes acceptable levels of inflation, bad inflation, or hyperinflation. Generally it can be said that inflation is a measure of a general increase of the price level in an economy, as represented typically by an inclusive price index, such as ...
Rudiger Dornbusch Working Paper No. i66
... ministers later, stability is a prospect far removed and the traditional conflicts about real wages; distribution, and inflation remain topical and are further complicated by an external debt crisis. In late 1983 production of manufactures and real GDP were still at ...
... ministers later, stability is a prospect far removed and the traditional conflicts about real wages; distribution, and inflation remain topical and are further complicated by an external debt crisis. In late 1983 production of manufactures and real GDP were still at ...
The Aggregate
... A. A ten-year-old investment tax credit expires. B. The U.S. exchange rate falls. C. A fall in prices increases the real value of ...
... A. A ten-year-old investment tax credit expires. B. The U.S. exchange rate falls. C. A fall in prices increases the real value of ...
Economics Explorer Series No. 3 - Inflation
... phenomenon of "too much money chasing after too few goods". This usually stems from persistent government budget deficits, which have to be continuously financed by printing money. In small, open economies like Singapore, demand pressures can also come from abroad. For example, when there is a large ...
... phenomenon of "too much money chasing after too few goods". This usually stems from persistent government budget deficits, which have to be continuously financed by printing money. In small, open economies like Singapore, demand pressures can also come from abroad. For example, when there is a large ...
Parkin-Bade Chapter 22
... A rise in the price level with no change in the money wage rate and other factor prices increases the quantity of real GDP supplied. The short-run aggregate supply curve (SAS) is upward ...
... A rise in the price level with no change in the money wage rate and other factor prices increases the quantity of real GDP supplied. The short-run aggregate supply curve (SAS) is upward ...
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... attempts to increase aggregate output result in an increase in both output and the price level. – When the demand for goods and services rises, firms increase their demand for inputs. • When all firms demand more inputs and the market supply of inputs is upward sloping, firms’ costs rise. • Firms re ...
... attempts to increase aggregate output result in an increase in both output and the price level. – When the demand for goods and services rises, firms increase their demand for inputs. • When all firms demand more inputs and the market supply of inputs is upward sloping, firms’ costs rise. • Firms re ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES PRODUCTION CHAINS David K. Levine Working Paper 16571
... Expected output is given by R(k )f (k ) . Notice that it is easy to construct models in which expected output is maximized as k → ∞ : if, for example, if f (k ) → ∞ much more quickly than R(k ) → 0 , or if R(k ) is bounded away from zero and f (k ) is not bounded away from infinity. However, such mo ...
... Expected output is given by R(k )f (k ) . Notice that it is easy to construct models in which expected output is maximized as k → ∞ : if, for example, if f (k ) → ∞ much more quickly than R(k ) → 0 , or if R(k ) is bounded away from zero and f (k ) is not bounded away from infinity. However, such mo ...
W Globalization and U.S. Inflation
... affect the demand for their products. In fact, there is abundant evidence that changes in exchange rates, and thus changes in the dollar costs faced by foreign producers, have only a modest effect on the dollar prices foreign producers charge in the United States. The debate over the degree of “pass ...
... affect the demand for their products. In fact, there is abundant evidence that changes in exchange rates, and thus changes in the dollar costs faced by foreign producers, have only a modest effect on the dollar prices foreign producers charge in the United States. The debate over the degree of “pass ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,9e
... Sustained Inflation as a Purely Monetary Phenomenon Virtually all economists agree that an increase in the price level can be caused by anything that causes the AD curve to shift to the right or the AS curve to shift to the left. It is also generally agreed that for a sustained inflation to occur, t ...
... Sustained Inflation as a Purely Monetary Phenomenon Virtually all economists agree that an increase in the price level can be caused by anything that causes the AD curve to shift to the right or the AS curve to shift to the left. It is also generally agreed that for a sustained inflation to occur, t ...
Achieving full employment in the transition economies
... return to a command economy, economic recovery became bound up with making those institutional reforms which would encourage a market economy to function. In this process some countries have met fewer impediments, whether they be of longstanding or more recently virtually self imposed, than others. ...
... return to a command economy, economic recovery became bound up with making those institutional reforms which would encourage a market economy to function. In this process some countries have met fewer impediments, whether they be of longstanding or more recently virtually self imposed, than others. ...
short-run aggregate supply curve
... in the face of high unemployment and slow to rise even in the face of labor shortages. ...
... in the face of high unemployment and slow to rise even in the face of labor shortages. ...
DOES HIGH INFLATION AFFECT GROWTH IN THE LONG
... issue is the length of the sample period relative to the length of what might be considered the long run. In Brazil, severe inflationary conditions have necessitated frequent index rebasing and lead to the complications of periodic introductions of new currencies. Consequently, the extremely truncat ...
... issue is the length of the sample period relative to the length of what might be considered the long run. In Brazil, severe inflationary conditions have necessitated frequent index rebasing and lead to the complications of periodic introductions of new currencies. Consequently, the extremely truncat ...
Gross National Happiness as an Answer to the Easterlin Paradox?
... provided an array of evidence showing that well-being data are correlated with physical reactions that are associated with true happiness. These include Pavot (1991) and Eckman, Davidson and Friesen (1990) who find that individuals reporting to be very happy tend to smile more (i.e. the duration of ...
... provided an array of evidence showing that well-being data are correlated with physical reactions that are associated with true happiness. These include Pavot (1991) and Eckman, Davidson and Friesen (1990) who find that individuals reporting to be very happy tend to smile more (i.e. the duration of ...
13.1 aggregate supply
... very slowly to the recessionary gap and real GDP does not return to potential GDP until another increase in aggregate demand occurs. Fluctuations in investment are the main source of aggregate demand fluctuations. A recession can occur if aggregate supply decreases to bring stagflation. Also, a rece ...
... very slowly to the recessionary gap and real GDP does not return to potential GDP until another increase in aggregate demand occurs. Fluctuations in investment are the main source of aggregate demand fluctuations. A recession can occur if aggregate supply decreases to bring stagflation. Also, a rece ...
No:10 Research Department Working Paper
... In so far as the literature is concerned, world commodity and raw material price shocks were not regarded as the main factors driving Turkish inflation. Most literature would suggest their subsidiary and transitory role. Dibooglu and Kibritcioglu (2001) found an evidence to play down the role by sup ...
... In so far as the literature is concerned, world commodity and raw material price shocks were not regarded as the main factors driving Turkish inflation. Most literature would suggest their subsidiary and transitory role. Dibooglu and Kibritcioglu (2001) found an evidence to play down the role by sup ...
Waco Metro Area Economic Outlook for 2016
... The BLS household survey is used to measure the unemployment rate equal to the percentage of unemployed persons in the labor force that consists of area residents above age 16 who are either employed or actively seeking employment and are not serving in the military or otherwise institutionalized. T ...
... The BLS household survey is used to measure the unemployment rate equal to the percentage of unemployed persons in the labor force that consists of area residents above age 16 who are either employed or actively seeking employment and are not serving in the military or otherwise institutionalized. T ...
Document
... policy action is necessary to achieve price stability once the effects have worked their way through the economy. In discussing the effects of inflation, it is important to distinguish between unanticipated and anticipated inflation. If instructors wish to spend more time on money creation and monet ...
... policy action is necessary to achieve price stability once the effects have worked their way through the economy. In discussing the effects of inflation, it is important to distinguish between unanticipated and anticipated inflation. If instructors wish to spend more time on money creation and monet ...
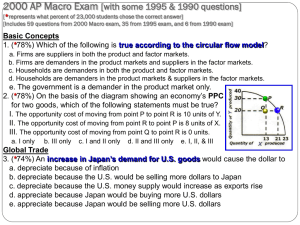
test #1 production possibilities / growth / circular flow
... e) an increase in inflationary expectations 16) which of the following would cause the unemployment rate to increase? I. a woman who quits her job to spend more time with his children II. a man who has not looked for a job in two years but is now looking III. a woman who quits her job and begins lo ...
... e) an increase in inflationary expectations 16) which of the following would cause the unemployment rate to increase? I. a woman who quits her job to spend more time with his children II. a man who has not looked for a job in two years but is now looking III. a woman who quits her job and begins lo ...
Enabling work
... that growth is returning to the UK’s economy.11 But historically, periods of economic growth have not had the same positive impact on disabled peoples’ employment rates as on non-disabled people. It is time to start looking at the structural inequalities that prevent many disabled people from being ...
... that growth is returning to the UK’s economy.11 But historically, periods of economic growth have not had the same positive impact on disabled peoples’ employment rates as on non-disabled people. It is time to start looking at the structural inequalities that prevent many disabled people from being ...
increase
... 7. (*79%) Which of the following would represent an addition to a nation’s GDP? a. Ms. Smith purchases a share of stock in an automobile company. b. A retailer increases her stock of imported shoes. c. The government increases its domestic purchases of food for use by the military. d. A corporation ...
... 7. (*79%) Which of the following would represent an addition to a nation’s GDP? a. Ms. Smith purchases a share of stock in an automobile company. b. A retailer increases her stock of imported shoes. c. The government increases its domestic purchases of food for use by the military. d. A corporation ...
Geographic concentration and territorial disparity in
... The drawback of this measure, however, is that it confuses inequality and concentration whereas these are two distinct concepts1. The locational Gini, therefore, is best suited as a measure of territorial disparity not geographic concentration. This point has been stressed by several authors (Arbia, ...
... The drawback of this measure, however, is that it confuses inequality and concentration whereas these are two distinct concepts1. The locational Gini, therefore, is best suited as a measure of territorial disparity not geographic concentration. This point has been stressed by several authors (Arbia, ...
Chapter 7: Putting All Markets Together: The AS
... on the interest rate disappear. The neutrality of money refers to the fact that an increase in the nominal money stock has no effect on output or the interest rate in the medium run. The increase in the nominal money stock is completely absorbed by an increase in the price level. ...
... on the interest rate disappear. The neutrality of money refers to the fact that an increase in the nominal money stock has no effect on output or the interest rate in the medium run. The increase in the nominal money stock is completely absorbed by an increase in the price level. ...
Full employment
Full employment, in macroeconomics, is the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. It is defined by the majority of mainstream economists as being an acceptable level of unemployment somewhere above 0%. The discrepancy from 0% arises due to non-cyclical types of unemployment, such as frictional unemployment (there will always be people who have quit or have lost a seasonal job and are in the process of getting a new job) and structural unemployment (mismatch between worker skills and job requirements). Unemployment above 0% is seen as necessary to control inflation in capitalist economies, to keep inflation from accelerating, i.e., from rising from year to year. This view is based on a theory centering on the concept of the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU); in the current era, the majority of mainstream economists mean NAIRU when speaking of ""full"" employment. The NAIRU has also been described by Milton Friedman, among others, as the ""natural"" rate of unemployment. Having many names, it has also been called the structural unemployment rate.The 20th century British economist William Beveridge stated that an unemployment rate of 3% was full employment. Other economists have provided estimates between 2% and 13%, depending on the country, time period, and their political biases. For the United States, economist William T. Dickens found that full-employment unemployment rate varied a lot over time but equaled about 5.5 percent of the civilian labor force during the 2000s. Recently, economists have emphasized the idea that full employment represents a ""range"" of possible unemployment rates. For example, in 1999, in the United States, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) gives an estimate of the ""full-employment unemployment rate"" of 4 to 6.4%. This is the estimated unemployment rate at full employment, plus & minus the standard error of the estimate.The concept of full employment of labor corresponds to the concept of potential output or potential real GDP and the long run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. In neoclassical macroeconomics, the highest sustainable level of aggregate real GDP or ""potential"" is seen as corresponding to a vertical LRAS curve: any increase in the demand for real GDP can only lead to rising prices in the long run, while any increase in output is temporary.