course description - Walker County Schools
... what, how, how much, and for whom to produce A. Identifying the positive and negative aspects of economic growth Example: opportunity cost B. Explaining how voluntary trade between nations illustrates the benefits of comparative advantage Example: geographic allocation of resources determining trade ...
... what, how, how much, and for whom to produce A. Identifying the positive and negative aspects of economic growth Example: opportunity cost B. Explaining how voluntary trade between nations illustrates the benefits of comparative advantage Example: geographic allocation of resources determining trade ...
New Structural Economics
... at Peking University. Several papers produced during that period are also included in this volume. I would like to take this opportunity to thank my former colleagues, Qiang Gong, Demin Huo, and Ho-Mou Wu, and former students, Binkai Chen, Shudong Hu, Feiyue Li, Yongjun Li, Zhiyun Li, Mingxing Liu, ...
... at Peking University. Several papers produced during that period are also included in this volume. I would like to take this opportunity to thank my former colleagues, Qiang Gong, Demin Huo, and Ho-Mou Wu, and former students, Binkai Chen, Shudong Hu, Feiyue Li, Yongjun Li, Zhiyun Li, Mingxing Liu, ...
NBER WORXING PAPER SERIES REAL RIGIDITIES AND NON-NEUTRALITY OF MONEY Laurence Ball
... and seminar participants at Harvard, Johns Hopkins, Michigan, Penn, Wisconsin, Yale and the NBER; and for financiel support from the NSF. The research reported here is part of the NBER's research program in Economic Fluctuations. Any opinions expressed are those of the authors and not those of the N ...
... and seminar participants at Harvard, Johns Hopkins, Michigan, Penn, Wisconsin, Yale and the NBER; and for financiel support from the NSF. The research reported here is part of the NBER's research program in Economic Fluctuations. Any opinions expressed are those of the authors and not those of the N ...
Size, Determinants, and Use in Macroeconomic Projections
... Multipliers are also important elements to take into consideration in policy advice and design.2 Underestimating multipliers may lead countries to set unachievable fiscal targets, and miscalculate the amount of adjustment necessary to curb their debt ratio (Eyraud and Weber, 2012, 2013). This could ...
... Multipliers are also important elements to take into consideration in policy advice and design.2 Underestimating multipliers may lead countries to set unachievable fiscal targets, and miscalculate the amount of adjustment necessary to curb their debt ratio (Eyraud and Weber, 2012, 2013). This could ...
The symmetry of demand and supply shocks in the
... They are caused by changes in technology, raw-materials price changes, mid- and long-term labour migration, or natural disasters. A detailed taxonomy of demand and supply shocks and sources of asymmetric shocks can be found in Borowski (2001, pp. 4−10). Within this framework, demand shocks have no l ...
... They are caused by changes in technology, raw-materials price changes, mid- and long-term labour migration, or natural disasters. A detailed taxonomy of demand and supply shocks and sources of asymmetric shocks can be found in Borowski (2001, pp. 4−10). Within this framework, demand shocks have no l ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from
... Market Economies 1. Introduction The performance of inflation-targeting regimes around the world has been positive. Average inflation in both emerging markets and developed economies is substantially lower after the adoption of the inflationtargeting regime than immediately before its adoption (Figu ...
... Market Economies 1. Introduction The performance of inflation-targeting regimes around the world has been positive. Average inflation in both emerging markets and developed economies is substantially lower after the adoption of the inflationtargeting regime than immediately before its adoption (Figu ...
The profit maximizing level of output is found by equating its
... Why calculations of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) count only final goods and services? ► Because it is difficult to measure the prices of intermediate goods produced. ► Because these are the only goods and services that are purchased in an economy. ► Because counting all goods and services would lead ...
... Why calculations of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) count only final goods and services? ► Because it is difficult to measure the prices of intermediate goods produced. ► Because these are the only goods and services that are purchased in an economy. ► Because counting all goods and services would lead ...
Chile`s new fiscal rule
... output. Although a variety of methods exist for calculating potential output and corresponding output gaps, all of them have major shortcomings (see e.g. Deutsche Bundesbank 1997). An additional caveat is that estimates of the structural balance are usually based on the assumption of constant revenu ...
... output. Although a variety of methods exist for calculating potential output and corresponding output gaps, all of them have major shortcomings (see e.g. Deutsche Bundesbank 1997). An additional caveat is that estimates of the structural balance are usually based on the assumption of constant revenu ...
analysing uk fiscal policy - UK Government Web Archive
... economic cycle. As the economy strengthens, incomes and expenditure tend to rise, resulting in higher tax receipts, while falling unemployment reduces social security spending. As the economy weakens, the opposite effect occurs. So government borrowing will be relatively low when the economy is oper ...
... economic cycle. As the economy strengthens, incomes and expenditure tend to rise, resulting in higher tax receipts, while falling unemployment reduces social security spending. As the economy weakens, the opposite effect occurs. So government borrowing will be relatively low when the economy is oper ...
Chapter 7 Chile`s New Fiscal Rule
... output. Although a variety of methods exist for calculating potential output and corresponding output gaps, all of them have major shortcomings (see e.g. Deutsche Bundesbank 1997). An additional caveat is that estimates of the structural balance are usually based on the assumption of constant revenu ...
... output. Although a variety of methods exist for calculating potential output and corresponding output gaps, all of them have major shortcomings (see e.g. Deutsche Bundesbank 1997). An additional caveat is that estimates of the structural balance are usually based on the assumption of constant revenu ...
From Periphery to Core: Measuring Agglomeration Effects Using High-Speed Rail
... (Duranton and Turner, 2012), counterfactual least-cost networks (Faber, 2014) or straight-line connections among regional centers (Banerjee et al., 2012) have emerged as a standard approach to establishing a causal relationship. A complementary approach is to exploit the fact that the main purpose o ...
... (Duranton and Turner, 2012), counterfactual least-cost networks (Faber, 2014) or straight-line connections among regional centers (Banerjee et al., 2012) have emerged as a standard approach to establishing a causal relationship. A complementary approach is to exploit the fact that the main purpose o ...
Macroeconomics Principles
... project's attribution page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/attribution.html?utm_source=header). For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/). You can browse or download additional books there. ...
... project's attribution page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/attribution.html?utm_source=header). For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page (http://2012books.lardbucket.org/). You can browse or download additional books there. ...
Social construction of preferences: Advertising!
... consumers (“consumerism” together with ”preferences for status” and ”conspicuous consumption”) which is not “natural” as, e.g., it is not supported by psychological and anthropological data.2 As a consequence, the consumption and leisure choices of agents go against their more “fundamental” will (“s ...
... consumers (“consumerism” together with ”preferences for status” and ”conspicuous consumption”) which is not “natural” as, e.g., it is not supported by psychological and anthropological data.2 As a consequence, the consumption and leisure choices of agents go against their more “fundamental” will (“s ...
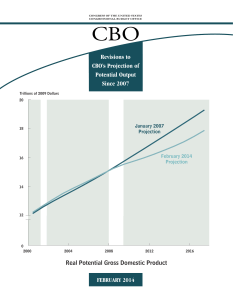
http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/attachments/45150-PotentialOutput.pdf
... National Bureau of Economic Research, which defines a recession as “a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales.” For more information, s ...
... National Bureau of Economic Research, which defines a recession as “a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales.” For more information, s ...
June 2014 | No. 90 A TAYLOR RULE FOR FISCAL POLICY IN A
... approach, the subsequent recession would have been much less severe, and, in particular, much more short-lived, as Denmark would have avoided a large loss of competitiveness. In addition, a tighter …scal policy before the crisis could have made room for additional …scal stimulus during the crisis, f ...
... approach, the subsequent recession would have been much less severe, and, in particular, much more short-lived, as Denmark would have avoided a large loss of competitiveness. In addition, a tighter …scal policy before the crisis could have made room for additional …scal stimulus during the crisis, f ...
Productivity Now
... The UK economy has been a star performer among advanced economies over the last few years. GDP growth has been impressive and the boom in jobs and new businesses has stood in sharp contrast to our neighbours across Europe. However, there is another important measure of economic success where the UK ...
... The UK economy has been a star performer among advanced economies over the last few years. GDP growth has been impressive and the boom in jobs and new businesses has stood in sharp contrast to our neighbours across Europe. However, there is another important measure of economic success where the UK ...
ABSTRACT Title of dissertation: ESSAYS ON FISCAL POLICY IN DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
... cost of the (current or future) tax burden needed to …nance these transfers, because it is borne by the entire polity. I take this logic a step further and study the cyclicality of policies arising from this political structure. In this model, a …scal agent with time-consistent preferences would con ...
... cost of the (current or future) tax burden needed to …nance these transfers, because it is borne by the entire polity. I take this logic a step further and study the cyclicality of policies arising from this political structure. In this model, a …scal agent with time-consistent preferences would con ...
The cyclicality of fiscal policy in South Asia
... in order to bring the economy out of recession. In other words, a counter cyclical fiscal policy occurs due to automatic stabilizers. For instance, government increases unemployment allowance and other welfare spending during an economic downturn and reduces the tax burden at the same time. Thus cou ...
... in order to bring the economy out of recession. In other words, a counter cyclical fiscal policy occurs due to automatic stabilizers. For instance, government increases unemployment allowance and other welfare spending during an economic downturn and reduces the tax burden at the same time. Thus cou ...
Document
... Japan's Recession and East Asia Japanese recession in 1990s reduced Japanese imports East Asian economies developed by promoting exports The decrease in exports to Japan decreased planned aggregate expenditures in these countries The decrease in planned spending caused the economies to cont ...
... Japan's Recession and East Asia Japanese recession in 1990s reduced Japanese imports East Asian economies developed by promoting exports The decrease in exports to Japan decreased planned aggregate expenditures in these countries The decrease in planned spending caused the economies to cont ...