Long-Term Analysis of a Budget Proposal by Chairman Ryan
... Federal payments for Medicaid under the proposal would be substantially smaller than currently projected amounts. States would have additional flexibility to design and manage their Medicaid programs, and they might achieve greater efficiencies in the delivery of care than under current law. Even wi ...
... Federal payments for Medicaid under the proposal would be substantially smaller than currently projected amounts. States would have additional flexibility to design and manage their Medicaid programs, and they might achieve greater efficiencies in the delivery of care than under current law. Even wi ...
Quarterly Report on the Euro Area Vol. 14, No. 1 (2015)
... transaction can be a real economy transaction, corresponding, for example, to an export/import of goods, which is recorded in the current account (CA). It can also be a purely financial transaction, like an interbank cross country loan, which is recorded in the financial account (FA). Whenever a tra ...
... transaction can be a real economy transaction, corresponding, for example, to an export/import of goods, which is recorded in the current account (CA). It can also be a purely financial transaction, like an interbank cross country loan, which is recorded in the financial account (FA). Whenever a tra ...
Chapter 26: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand
... decreases the real value of money and raises the interest rate. When the interest rate rises, people borrow and spend less, so the quantity of real GDP demanded decreases. Similarly, a fall in the price level increases the real value of money and lowers the interest rate. When the interest rate fall ...
... decreases the real value of money and raises the interest rate. When the interest rate rises, people borrow and spend less, so the quantity of real GDP demanded decreases. Similarly, a fall in the price level increases the real value of money and lowers the interest rate. When the interest rate fall ...
Chapter 11 All Markets Together. The AS-AD
... The process goes on until output has returned to its natural level. The process can be made faster by using either monetary policy (that is, by increasing the money stock, which leads to a larger decrease in the interest rate) or fiscal policy, which increases demand directly. At the core of the adju ...
... The process goes on until output has returned to its natural level. The process can be made faster by using either monetary policy (that is, by increasing the money stock, which leads to a larger decrease in the interest rate) or fiscal policy, which increases demand directly. At the core of the adju ...
aggregate supply (AS) curve
... If planned aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand exceed YF, however, there is an inflationary gap and the price level rises to P3. ...
... If planned aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand exceed YF, however, there is an inflationary gap and the price level rises to P3. ...
QUIZ 5: Macro – Fall 2014 Name: _ANSWERS____ Section
... All consumers are non-liquidity constrained, non-Ricardian PIH (as developed in class) Expected inflation has no effect on money demand; NX = 0 . All changes are permanent and unexpected unless told otherwise The economy is initially in long run equilibrium at Y* TFP, taxes, consumer confidence, val ...
... All consumers are non-liquidity constrained, non-Ricardian PIH (as developed in class) Expected inflation has no effect on money demand; NX = 0 . All changes are permanent and unexpected unless told otherwise The economy is initially in long run equilibrium at Y* TFP, taxes, consumer confidence, val ...
Fiscal Rules and Resource Funds in Nonrenewable Resource
... nonrenewable resources, governments have put in place fiscal rules or fiscal guidelines and/or nonrenewable resource funds (NRFs) in the expectation that these institutional mechanisms might help in the implementation of fiscal policy. This paper focuses on the experience of nonrenewable resource ex ...
... nonrenewable resources, governments have put in place fiscal rules or fiscal guidelines and/or nonrenewable resource funds (NRFs) in the expectation that these institutional mechanisms might help in the implementation of fiscal policy. This paper focuses on the experience of nonrenewable resource ex ...
18.3 aggregate demand
... When the price level rises, the real interest rate rises. An increase in the price level increases the amount of money that people want to hold—increases the demand for money. When the demand for money increases, the nominal interest rate rises. In the short run, the inflation rate doesn’t change, s ...
... When the price level rises, the real interest rate rises. An increase in the price level increases the amount of money that people want to hold—increases the demand for money. When the demand for money increases, the nominal interest rate rises. In the short run, the inflation rate doesn’t change, s ...
Household Debt and Business Cycles Worldwide January 2016
... Analysis of components of GDP reveal that increase in net exports, driven by decline in imports of consumption goods, helps cushion the blow to GDP, especially for more open economies ...
... Analysis of components of GDP reveal that increase in net exports, driven by decline in imports of consumption goods, helps cushion the blow to GDP, especially for more open economies ...
"Monetary Policy According to HANK"
... income effects on the consumption of rich households. Second, micro survey data on household portfolios show that a sizable fraction of households (between 1/4 and 1/3) hold close to zero liquid wealth and face high borrowing costs (Kaplan et al., 2014). Since these households are at a kink in thei ...
... income effects on the consumption of rich households. Second, micro survey data on household portfolios show that a sizable fraction of households (between 1/4 and 1/3) hold close to zero liquid wealth and face high borrowing costs (Kaplan et al., 2014). Since these households are at a kink in thei ...
Impact of Remittances on Growth
... Simulate aggregate supply? It is a long time solutions: Simulate aggregate demand? Yes and sooner better: But How? Economic theory suggests the use of following tools: a) decrease taxes, b) increase government spending, c) use both tools together. ...
... Simulate aggregate supply? It is a long time solutions: Simulate aggregate demand? Yes and sooner better: But How? Economic theory suggests the use of following tools: a) decrease taxes, b) increase government spending, c) use both tools together. ...
LERNER, Abba Ptachya (1903-1982) by Mathew Forstater* Working
... Landreth, 1996, p. 116). This accurately describes not only the book, but Lerner’s fifty years of economic scholarship, which covers both microeconomics and macroeconomics; neoclassical and Keynesian frameworks; theory and policy; and a faith in markets and a commitment to democratic socialism. Lern ...
... Landreth, 1996, p. 116). This accurately describes not only the book, but Lerner’s fifty years of economic scholarship, which covers both microeconomics and macroeconomics; neoclassical and Keynesian frameworks; theory and policy; and a faith in markets and a commitment to democratic socialism. Lern ...
The IS-LM/AD-AS Model: A General Framework for Macroeconomic
... • An increase in the nominal money supply shifts both the LM and AD curves to the right. • The increase in the real money supply increases output but leaves the price level unchanged. ...
... • An increase in the nominal money supply shifts both the LM and AD curves to the right. • The increase in the real money supply increases output but leaves the price level unchanged. ...
Monetary Policy According to HANK ∗ Greg Kaplan Benjamin Moll
... income effects on the consumption of rich households. Second, micro survey data on household portfolios show that a sizable fraction of households (between 1/4 and 1/3) hold close to zero liquid wealth and face high borrowing costs (Kaplan et al., 2014). Since these households are at a kink in thei ...
... income effects on the consumption of rich households. Second, micro survey data on household portfolios show that a sizable fraction of households (between 1/4 and 1/3) hold close to zero liquid wealth and face high borrowing costs (Kaplan et al., 2014). Since these households are at a kink in thei ...
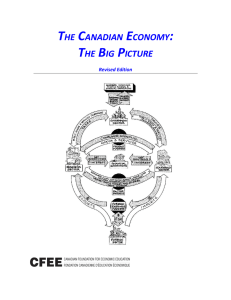
the canadian economy - Canadian Foundation for Economic
... and billions of exchanges, direct barter becomes very difficult. Some bartering still takes place, but, by and large, using money is easier. So economies use money as (1) a “unit of account” to establish prices, (2) a “medium of exchange” for transactions, and (3) a “store of value” to save for use ...
... and billions of exchanges, direct barter becomes very difficult. Some bartering still takes place, but, by and large, using money is easier. So economies use money as (1) a “unit of account” to establish prices, (2) a “medium of exchange” for transactions, and (3) a “store of value” to save for use ...
Modelling for monetary policy: the New Zealand experience
... Following the move to market-determined interest rates and the floating of the exchange rate in March 1985, the Reserve Bank gained greater control over monetary conditions. But the widespread economic and financial reforms also led to a period of considerable structural change and volatility in asset ...
... Following the move to market-determined interest rates and the floating of the exchange rate in March 1985, the Reserve Bank gained greater control over monetary conditions. But the widespread economic and financial reforms also led to a period of considerable structural change and volatility in asset ...
fgfdgfd
... Buiter, 1980) have provided empirical and theoretical evidences against the Ricardian equivalence, while empirical results of other studies (Evans, 1985, 1987b; Fackler and McMillin, 1989) have supported the proposition. Fiscal deficits can also have impact on other macroeconomic variables such as i ...
... Buiter, 1980) have provided empirical and theoretical evidences against the Ricardian equivalence, while empirical results of other studies (Evans, 1985, 1987b; Fackler and McMillin, 1989) have supported the proposition. Fiscal deficits can also have impact on other macroeconomic variables such as i ...
Impact Of Government Expenditure On Gross Domestic Product In
... Domestic Product is an essential topic of exploration (Stieglitz, 1989).The vision of ensuring sustainable development at a significant scale is enshrined in the government’s development strategy document of the country. The expenditure by governments has been observed to increase efficiency however ...
... Domestic Product is an essential topic of exploration (Stieglitz, 1989).The vision of ensuring sustainable development at a significant scale is enshrined in the government’s development strategy document of the country. The expenditure by governments has been observed to increase efficiency however ...
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
... Aggregate Demand • The aggregate demand curve slopes down because as the general price level rises, the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with the given stock of money and other financial assets declines. • In addition, the aggregate demand curve slopes down because as the price le ...
... Aggregate Demand • The aggregate demand curve slopes down because as the general price level rises, the amount of goods and services that can be purchased with the given stock of money and other financial assets declines. • In addition, the aggregate demand curve slopes down because as the price le ...
Public Sector Governance Course Schedule
... Transparency and Fiscal Discipline Fiscal discipline and fiscal sustainability represents major challenges for most especially decentralized countries. This session will examine legal frameworks for ensuring fiscal transparency, fiscal discipline and prudent fiscal management. The incentive compatib ...
... Transparency and Fiscal Discipline Fiscal discipline and fiscal sustainability represents major challenges for most especially decentralized countries. This session will examine legal frameworks for ensuring fiscal transparency, fiscal discipline and prudent fiscal management. The incentive compatib ...
China`s Growing Local Government Debt Levels
... public infrastructure improvements and other capital investments. Local indebtedness has increased dramatically since the global financial crisis of 2008, reaching 40 percent of GDP or RMB 24.0 trillion ($3.8 trillion) in 2014. With an economy growing at its slowest pace since the economic reforms o ...
... public infrastructure improvements and other capital investments. Local indebtedness has increased dramatically since the global financial crisis of 2008, reaching 40 percent of GDP or RMB 24.0 trillion ($3.8 trillion) in 2014. With an economy growing at its slowest pace since the economic reforms o ...
The Nordic model of economic development: shocks
... countries (with growth rates of slightly above 2%) perform neither better nor worse than the large majority of the other OECD economies. This puzzling empirical evidence for the Nordic countries as compared to the other OECD economies calls for a deeper analysis at the country-level (or by clusters ...
... countries (with growth rates of slightly above 2%) perform neither better nor worse than the large majority of the other OECD economies. This puzzling empirical evidence for the Nordic countries as compared to the other OECD economies calls for a deeper analysis at the country-level (or by clusters ...