AP ECON – Final Exam Review
... a. increase ; increase d. decrease ; decrease b. increase ; decrease e. increase ; no change c. decrease ; increase ____ 39. Suppose that you prefer reading a book you already own to watching TV and that you prefer watching TV to listening to music. If these are your only three choices, what is the ...
... a. increase ; increase d. decrease ; decrease b. increase ; decrease e. increase ; no change c. decrease ; increase ____ 39. Suppose that you prefer reading a book you already own to watching TV and that you prefer watching TV to listening to music. If these are your only three choices, what is the ...
Principles of Macroeconomics
... people’s health with vaccines and other life-saving tools and giving them the chance to lift themselves out of hunger and extreme poverty. In the United States, it seeks to significantly improve education so that all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential. Based in Seattle, ...
... people’s health with vaccines and other life-saving tools and giving them the chance to lift themselves out of hunger and extreme poverty. In the United States, it seeks to significantly improve education so that all young people have the opportunity to reach their full potential. Based in Seattle, ...
Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin)
... B) decreases as the price level increases because people demand fewer goods and services. C) might either increase or decrease as the price level increases, depending on whether aggregate demand increases or decreases. D) is independent of the price level. E) never changes. Answer: D Topic: Potentia ...
... B) decreases as the price level increases because people demand fewer goods and services. C) might either increase or decrease as the price level increases, depending on whether aggregate demand increases or decreases. D) is independent of the price level. E) never changes. Answer: D Topic: Potentia ...
Economics, by R. Glenn Hubbard and Anthony Patrick O'Brien
... © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 10 of 34 ...
... © 2007 Prentice Hall Business Publishing; Essentials of Economics, R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien 10 of 34 ...
Investing in Ontario`s Infrastructure for Economic Growth
... use of public utilities such as roads, railways, and human capital from a well-educated labour force. At the same time, there are several public sector infrastructure investments, such as highways and sewers, which could not have been profitably provided by the private sector. For these services it ...
... use of public utilities such as roads, railways, and human capital from a well-educated labour force. At the same time, there are several public sector infrastructure investments, such as highways and sewers, which could not have been profitably provided by the private sector. For these services it ...
Chapter 29
... A) increases as the price level increases because firms supply more goods and services. B) decreases as the price level increases because people demand fewer goods and services. C) might either increase or decrease as the price level increases, depending on whether aggregate demand increases or decr ...
... A) increases as the price level increases because firms supply more goods and services. B) decreases as the price level increases because people demand fewer goods and services. C) might either increase or decrease as the price level increases, depending on whether aggregate demand increases or decr ...
FREE Sample Here
... A) businesses, households, and consumers make decisions about how to spend their money. B) governments control their countries' economies by watching how much small businesses contribute to it. C) unemployment, interest rates, and inflation affect price levels. D) a country's economy is chosen and d ...
... A) businesses, households, and consumers make decisions about how to spend their money. B) governments control their countries' economies by watching how much small businesses contribute to it. C) unemployment, interest rates, and inflation affect price levels. D) a country's economy is chosen and d ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES WHY IS ECONOMIC POLICY
... Note further that the transition to democracy is often associated with large structural changes in the economy. This was particularly noticeable in the formerly socialist economies of Eastern Europe but also in Southern Europe and in some Latin American countries. The twin transitions may thus imply ...
... Note further that the transition to democracy is often associated with large structural changes in the economy. This was particularly noticeable in the formerly socialist economies of Eastern Europe but also in Southern Europe and in some Latin American countries. The twin transitions may thus imply ...
Preview Sample 2
... A) businesses, households, and consumers make decisions about how to spend their money. B) governments control their countries' economies by watching how much small businesses contribute to it. C) unemployment, interest rates, and inflation affect price levels. D) a country's economy is chosen and d ...
... A) businesses, households, and consumers make decisions about how to spend their money. B) governments control their countries' economies by watching how much small businesses contribute to it. C) unemployment, interest rates, and inflation affect price levels. D) a country's economy is chosen and d ...
Government Debt and Deficits
... the economy. While there are certainly many causes of the debt consequences that go beyond the scope of this review, these are two causes worthy of consideration in a moral context. 2. Biblical Principles Related to Debt One hermeneutic approach to use in discerning biblical principles related to go ...
... the economy. While there are certainly many causes of the debt consequences that go beyond the scope of this review, these are two causes worthy of consideration in a moral context. 2. Biblical Principles Related to Debt One hermeneutic approach to use in discerning biblical principles related to go ...
Mega Quiz File (ECO401) Shahzad Sadiq Attock VU Group
... a period during which aggregate output declines. a period of declining unemployment. a period of falling trade volumes. Involuntary unemployment means that people are not willing to work at the going wage rate. at the going wage rate, there are people who want to work but cannot find work. there are ...
... a period during which aggregate output declines. a period of declining unemployment. a period of falling trade volumes. Involuntary unemployment means that people are not willing to work at the going wage rate. at the going wage rate, there are people who want to work but cannot find work. there are ...
The Contributions of Milton Friedman to Economics
... from the prevailing intellectual mainstream. First, central banks are responsible for inflation and deflation. Second, markets work efficiently to allocate resources and to maintain macroeconomic equilibrium.2 Because of his success in advancing these ideas in a way that shaped the understanding of ...
... from the prevailing intellectual mainstream. First, central banks are responsible for inflation and deflation. Second, markets work efficiently to allocate resources and to maintain macroeconomic equilibrium.2 Because of his success in advancing these ideas in a way that shaped the understanding of ...
Economics R. Glenn Hubbard, Anthony Patrick O’Brien, 2e.
... Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue macroeconomic policy objectives. Fiscal policy Changes in federal taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives, such as high employment, price stability, and high rates of economic growth. ...
... Reserve takes to manage the money supply and interest rates to pursue macroeconomic policy objectives. Fiscal policy Changes in federal taxes and purchases that are intended to achieve macroeconomic policy objectives, such as high employment, price stability, and high rates of economic growth. ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES ON THE ORIGINS OF "A MONETARY HISTORY"
... a contraction. The contraction, which would also diffuse widely, then produced changes in relative prices, such as a fall in costs relative to final product prices, which produced expansion. Friedman and Schwartz agreed that adjustments in relative prices would reverse contractions, so that in the e ...
... a contraction. The contraction, which would also diffuse widely, then produced changes in relative prices, such as a fall in costs relative to final product prices, which produced expansion. Friedman and Schwartz agreed that adjustments in relative prices would reverse contractions, so that in the e ...
$doc.title
... Some scholars have already considered the effects on IMF lending as operating under the influence of a principal agent who controls the institution but has a different objective set than the o ...
... Some scholars have already considered the effects on IMF lending as operating under the influence of a principal agent who controls the institution but has a different objective set than the o ...
Prof. Eytan Sheshinski
... an investor-friendly environment in the economy. The last two objectives, related to public sector finance, are the reduction of borrowing requirements and the potential reallocation of expenditure towards social policy areas. Thus, privatization programs ought to be assessed by looking at the exten ...
... an investor-friendly environment in the economy. The last two objectives, related to public sector finance, are the reduction of borrowing requirements and the potential reallocation of expenditure towards social policy areas. Thus, privatization programs ought to be assessed by looking at the exten ...
Global Economic Prospects January 2015
... to rise slowly, supported by continued recovery in highincome countries, low oil prices, and receding domestic headwinds in developing economies. However, continued weak global trade growth and gradually tightening financial conditions will constrain the recovery. Risks to the outlook remain tilted ...
... to rise slowly, supported by continued recovery in highincome countries, low oil prices, and receding domestic headwinds in developing economies. However, continued weak global trade growth and gradually tightening financial conditions will constrain the recovery. Risks to the outlook remain tilted ...
Crisis and Consumption Smoothing
... a sharp correction in the exchange rate of a country. Currency crises are easier to measure and identify since data on exchange rates are widely available. Banking crises, on the other hand, require much more detailed data on bank runs, bank closures, and bailouts. Assembling data for a comprehensiv ...
... a sharp correction in the exchange rate of a country. Currency crises are easier to measure and identify since data on exchange rates are widely available. Banking crises, on the other hand, require much more detailed data on bank runs, bank closures, and bailouts. Assembling data for a comprehensiv ...
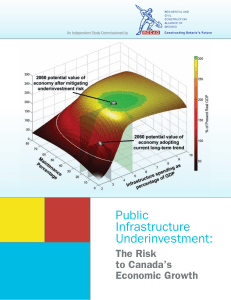
Public Infrastructure Underinvestment - ACEC
... the potential identified risk of underinvestment were to occur, it is estimated that employees would lose the opportunity of a 0.5 per cent per annum average increase of their real after-tax income over the next 50 years. In present value terms, this represents an average lost opportunity after tax ...
... the potential identified risk of underinvestment were to occur, it is estimated that employees would lose the opportunity of a 0.5 per cent per annum average increase of their real after-tax income over the next 50 years. In present value terms, this represents an average lost opportunity after tax ...
Download paper (PDF)
... government can fully commit to fiscal policy. In practice, a government chooses taxes, spending, and debt sequentially, taking into account its outstanding debt portfolio, as well as the behavior of future governments. Thus, a government can always pursue a fiscal policy which reduces (increases) th ...
... government can fully commit to fiscal policy. In practice, a government chooses taxes, spending, and debt sequentially, taking into account its outstanding debt portfolio, as well as the behavior of future governments. Thus, a government can always pursue a fiscal policy which reduces (increases) th ...
risk and business cycles
... first, monetary policy often is potent in the short run; second, monetary policy has unpredictable long-run effects; and third, monetary policy cannot improve economic welfare on average. Instead of producing an inflationary surprise, central banks sometimes increase monetary volatility. In this cas ...
... first, monetary policy often is potent in the short run; second, monetary policy has unpredictable long-run effects; and third, monetary policy cannot improve economic welfare on average. Instead of producing an inflationary surprise, central banks sometimes increase monetary volatility. In this cas ...
January 2015 - Public Documents Profile Viewer
... How does the recent decline in oil prices compare with previous episodes? 159 What are the causes of the sharp drop? 160 What are the macroeconomic and financial implications? 161 Global Growth 164 ...
... How does the recent decline in oil prices compare with previous episodes? 159 What are the causes of the sharp drop? 160 What are the macroeconomic and financial implications? 161 Global Growth 164 ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... of Economic Research Volume Title: Studies in the Economics of Aging
... 6. If the worry over low savings is that one’s child suffers for one’s current consumption, the concern can be alleviated individually. Any one person can save and pass income to his child directly, without the acquiescence of fellow citizens. Collective action is necessary only when one American ca ...
... 6. If the worry over low savings is that one’s child suffers for one’s current consumption, the concern can be alleviated individually. Any one person can save and pass income to his child directly, without the acquiescence of fellow citizens. Collective action is necessary only when one American ca ...