Rethinking Reforms -How Latin America and the Caribbean Can
... However, such a policy mix will not by itself boost growth, nor could it be expected to do so. Rather, countries should consider further structural reform measures to enhance economic prospects, and to escape suppressed global growth. A review of the current status of reforms in the region in Chapte ...
... However, such a policy mix will not by itself boost growth, nor could it be expected to do so. Rather, countries should consider further structural reform measures to enhance economic prospects, and to escape suppressed global growth. A review of the current status of reforms in the region in Chapte ...
Term 2 Week 6 to 9 - Singapore A Level Notes
... Chinese yuan depreciated (mitigate the effect fall in X) while Brazil appreciated ...
... Chinese yuan depreciated (mitigate the effect fall in X) while Brazil appreciated ...
“Good Governance” in Monetary Policy and the Negative Real
... problems and challenges faced by these economies with respect to macroeconomic policies. Afterwards, the procyclical and asymmetrical nature of monetary policy will be analyzed, and the possible long-run effects on output and employment will be considered. Finally, a specification for testing whethe ...
... problems and challenges faced by these economies with respect to macroeconomic policies. Afterwards, the procyclical and asymmetrical nature of monetary policy will be analyzed, and the possible long-run effects on output and employment will be considered. Finally, a specification for testing whethe ...
Chapter 10: Classical Business Cycle Analysis: Market
... The theory predicts countercyclical movements of the price level, which seems to be inconsistent with the data. But Kydland and Prescott, when using some newer statistical techniques for calculating the trends in inflation and output, find evidence that the price level is countercyclical. Though the ...
... The theory predicts countercyclical movements of the price level, which seems to be inconsistent with the data. But Kydland and Prescott, when using some newer statistical techniques for calculating the trends in inflation and output, find evidence that the price level is countercyclical. Though the ...
The effect of the economic and financial crisis on government
... total revenue increased from 45.0 % of GDP in 1995 in the EU-27 to 45.7 % of GDP in 1996, then decreasing slightly to reach 45.4 % of GDP in 1998 only to reach its peak in the 1995-2010 period in 1999: then it stood at just under 45.8 % of GDP. Government revenue as a ratio of GDP then fell sharply ...
... total revenue increased from 45.0 % of GDP in 1995 in the EU-27 to 45.7 % of GDP in 1996, then decreasing slightly to reach 45.4 % of GDP in 1998 only to reach its peak in the 1995-2010 period in 1999: then it stood at just under 45.8 % of GDP. Government revenue as a ratio of GDP then fell sharply ...
CHAPTER 21: Open-Economy Macroeconomics: The Balance of
... An increase in U.S. imports increases other countries’ exports, which stimulates those countries’ economies and increases their imports, which increases U.S. exports, which stimulates the U.S. economy and increases its imports, and so on. This is the trade feedback effect. In other words, an increas ...
... An increase in U.S. imports increases other countries’ exports, which stimulates those countries’ economies and increases their imports, which increases U.S. exports, which stimulates the U.S. economy and increases its imports, and so on. This is the trade feedback effect. In other words, an increas ...
Secular stagnation, debt overhang and other rationales for sluggish
... market access and official rescue funds are insufficient to completely bridge the gap. Of course, the constraints that periphery countries faced were profoundly affected by northern Europe’s reluctance to allow restructuring of private debts, even in cases where sustainability was deeply in question ...
... market access and official rescue funds are insufficient to completely bridge the gap. Of course, the constraints that periphery countries faced were profoundly affected by northern Europe’s reluctance to allow restructuring of private debts, even in cases where sustainability was deeply in question ...
Riding the Roller Coaster: Fiscal Policies of Nonrenewable
... Has fiscal policy been expansionary in good times and contractionary in bad times? To what extent has fiscal policy helped to dampen business cycle fluctuations in NRECs? Our analysis starts by examining the evolution of one of the most widely used fiscal policy indicators, the primary balance-to-GD ...
... Has fiscal policy been expansionary in good times and contractionary in bad times? To what extent has fiscal policy helped to dampen business cycle fluctuations in NRECs? Our analysis starts by examining the evolution of one of the most widely used fiscal policy indicators, the primary balance-to-GD ...
Was the New Deal Contractionary?
... shocks that imply that a negative real interest rate is needed for the efficient equilbrium. In this case a central bank, having cut the interest rate to zero, cannot accommodate the shocks because that would require a negative nominal interest rate, and the nominal interest rate cannot be negative. T ...
... shocks that imply that a negative real interest rate is needed for the efficient equilbrium. In this case a central bank, having cut the interest rate to zero, cannot accommodate the shocks because that would require a negative nominal interest rate, and the nominal interest rate cannot be negative. T ...
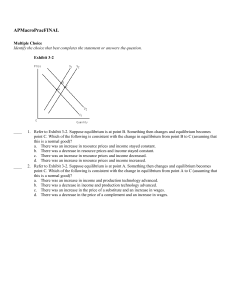
APMacroPracFIN
... b. is matched by an increase in private spending. c. results in an increase in aggregate supply. d. results in an increase in aggregate demand. ...
... b. is matched by an increase in private spending. c. results in an increase in aggregate supply. d. results in an increase in aggregate demand. ...
Fiscal policy challenges in oil-exporting countries - ECB
... inflationary pressure through monetary policy being constrained in view of the prevailing fixed exchange rate pegs or tightly managed floats, fiscal policy has been the main macroeconomic tool available to control inflation. At the same time, governments were facing various pressures to increase spe ...
... inflationary pressure through monetary policy being constrained in view of the prevailing fixed exchange rate pegs or tightly managed floats, fiscal policy has been the main macroeconomic tool available to control inflation. At the same time, governments were facing various pressures to increase spe ...
economic theory in transition
... of what happened to Keynesianism but can at most give thrusts to the right direction. Nonetheless, the paradigm shift from Keynesianism to neoclassical economic policy and the wide-spread popularity and discursive hegemony gained by the latter is so aggressive in the case of the United States that i ...
... of what happened to Keynesianism but can at most give thrusts to the right direction. Nonetheless, the paradigm shift from Keynesianism to neoclassical economic policy and the wide-spread popularity and discursive hegemony gained by the latter is so aggressive in the case of the United States that i ...
The Money Supply and the Federal Reserve System
... currently at Point A. A decrease in the interest rate to 5%, ceteris paribus, will likely A) decrease the quantity of money demanded from $200 million to $100 million. B) increase the quantity of money demanded from $100 million to $200 million. C) increase the quantity of money demanded from ...
... currently at Point A. A decrease in the interest rate to 5%, ceteris paribus, will likely A) decrease the quantity of money demanded from $200 million to $100 million. B) increase the quantity of money demanded from $100 million to $200 million. C) increase the quantity of money demanded from ...
CHAPTER 7 Measuring Domestic Output, National
... 46. The concept of net domestic investment refers to: A) the amount of machinery and equipment used up in producing the GDP in a specific year. B) the difference between the market value and book value of outstanding capital stock. C) gross domestic investment less net exports. D) total investment l ...
... 46. The concept of net domestic investment refers to: A) the amount of machinery and equipment used up in producing the GDP in a specific year. B) the difference between the market value and book value of outstanding capital stock. C) gross domestic investment less net exports. D) total investment l ...
3 estimation of the impact of single monetary policy on - Hal-SHS
... to expensive real adjustments given the impossibility of exchange rate adjustments. Indeed, the success in leading a single monetary policy depends not only on nominal convergence, which is considered successful globally, but also on the convergence of national economies sensitivity degrees to measu ...
... to expensive real adjustments given the impossibility of exchange rate adjustments. Indeed, the success in leading a single monetary policy depends not only on nominal convergence, which is considered successful globally, but also on the convergence of national economies sensitivity degrees to measu ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INFLATION: THEORY AND EVIDENCE Bennett 1. McCallum
... rates, which are likely to be unanticipated. While this distinction may be somewhat unclear in practice, it is an essential one in terms of theoretical analysis since the effects of anticipated and surprise inflation may be very ...
... rates, which are likely to be unanticipated. While this distinction may be somewhat unclear in practice, it is an essential one in terms of theoretical analysis since the effects of anticipated and surprise inflation may be very ...
Monetary Explanations of the Great Depression
... Empirical results from the more recent, sparser literature using dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) modeling also reveal no consensus that monetary policy caused the Great Depression.2 Each empirical literature requires sufficient structure of the economic model to isolate monetary policy ...
... Empirical results from the more recent, sparser literature using dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) modeling also reveal no consensus that monetary policy caused the Great Depression.2 Each empirical literature requires sufficient structure of the economic model to isolate monetary policy ...
Economics Mark Schemes for the Units January 2009
... socialist economies. The purpose is to increase the real income of consumers by keeping prices below what would otherwise be the market equilibrium. It is also a means of keeping supply at what might seem to be an artificially high level in order to guarantee supplies. Arguments against should focus ...
... socialist economies. The purpose is to increase the real income of consumers by keeping prices below what would otherwise be the market equilibrium. It is also a means of keeping supply at what might seem to be an artificially high level in order to guarantee supplies. Arguments against should focus ...
KOF - ETH Zürich
... • The downward slope of the aggregate demand curve shows that a fall in the price level raises the overall quantity of goods and services demanded. • Many other factors, however, affect the quantity of goods and services demanded at any given price level. • When one of these other factors changes, t ...
... • The downward slope of the aggregate demand curve shows that a fall in the price level raises the overall quantity of goods and services demanded. • Many other factors, however, affect the quantity of goods and services demanded at any given price level. • When one of these other factors changes, t ...
+ = GDP - Binus Repository
... indicator of living standards across countries? 4. GDP does not count services such as child care, food preparation, cleaning, and laundry within the household. Why not? Is GDP a sexist measure? Does it understate the productive contributions of women relative to men? Jump to first page ...
... indicator of living standards across countries? 4. GDP does not count services such as child care, food preparation, cleaning, and laundry within the household. Why not? Is GDP a sexist measure? Does it understate the productive contributions of women relative to men? Jump to first page ...