Pacific waterleaf - University of Washington
... groundcover.8 Usually it reaches between one and two feet tall. It can be an aggressive grower, so it should be planted next to other similarly aggressive covers. Seeds should be collected in midsummer, usually late July and early August8 when the heads begin to yellow and the plants are declining.7 ...
... groundcover.8 Usually it reaches between one and two feet tall. It can be an aggressive grower, so it should be planted next to other similarly aggressive covers. Seeds should be collected in midsummer, usually late July and early August8 when the heads begin to yellow and the plants are declining.7 ...
Examining Sexual Reproduction of Flowering Plants - PHS
... The reproductive process begins with pollination. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Plants rely on wind and water to transfer the pollen. In addition, plants depend on animals to help with pollination. Birds, insects, bats ...
... The reproductive process begins with pollination. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Plants rely on wind and water to transfer the pollen. In addition, plants depend on animals to help with pollination. Birds, insects, bats ...
Pedicularis groenlandica - University of Washington
... ‐ Requires a host plant ‐ After 4 weeks, plant a host plant in container (5) ‐ may use carex nifricans (2) Moderate (4) Will start growth slow until roots penetrate host plant. (2) 16 weeks During this time, fertilize with liquid 20:20:20 NPK at 100 ppm once every month. (2) ...
... ‐ Requires a host plant ‐ After 4 weeks, plant a host plant in container (5) ‐ may use carex nifricans (2) Moderate (4) Will start growth slow until roots penetrate host plant. (2) 16 weeks During this time, fertilize with liquid 20:20:20 NPK at 100 ppm once every month. (2) ...
Research March 2017
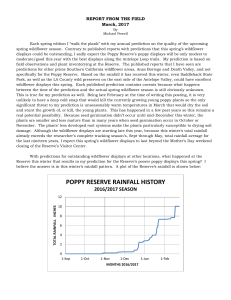
... very strong storms. Based on our years of field observations, the researchers have found very limited amount of poppy seed germination following rainstorms depositing less than at least 0.5-0.6 inches of rain. With more rainfall, increasing numbers of poppy seeds germinate until somewhere between on ...
... very strong storms. Based on our years of field observations, the researchers have found very limited amount of poppy seed germination following rainstorms depositing less than at least 0.5-0.6 inches of rain. With more rainfall, increasing numbers of poppy seeds germinate until somewhere between on ...
Class - Educast
... spermatozoids swim to it by chemotaxis. Although bryophytes are land plants, they are still dependent upon water for fertilization, as the sperm swim in a water film. The sporophyte is attached and dependent upon the gametophyte for nutrition i.e. is parasitic on the ...
... spermatozoids swim to it by chemotaxis. Although bryophytes are land plants, they are still dependent upon water for fertilization, as the sperm swim in a water film. The sporophyte is attached and dependent upon the gametophyte for nutrition i.e. is parasitic on the ...
PSec2REVIEW Flower Plant REVIEW.pps
... the female parts. Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it, down the style into the ovary. The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary becomes the fruit. The ovary first begins to grow into fruit, then the seeds develop. ...
... the female parts. Pollen grains land on the stigma and a tiny tube grows from it, down the style into the ovary. The fertilized ovule becomes the seed and the ovary becomes the fruit. The ovary first begins to grow into fruit, then the seeds develop. ...
Plant Propagation
... the soil where they will grow to a saleable size. • Germination flats are used if they are to be transplanted at a later time. • When reusing germination flats, be sure to sterilize the flats and soil. ...
... the soil where they will grow to a saleable size. • Germination flats are used if they are to be transplanted at a later time. • When reusing germination flats, be sure to sterilize the flats and soil. ...
4 plants come from
... seed certainly looks dead. It does not seem to move, to grow or do anything else. In fact, when tested for the processes we associate with life, the rate is so slow that it would be difficult to determine whether there was anything alive in the seed. But, inside every seed is a baby plant or embryo. ...
... seed certainly looks dead. It does not seem to move, to grow or do anything else. In fact, when tested for the processes we associate with life, the rate is so slow that it would be difficult to determine whether there was anything alive in the seed. But, inside every seed is a baby plant or embryo. ...
Flowering Plants: Reproduction
... • Seed dormancy increases the chances that germination will occur at a time and place most advantageous to the seedling • The breaking of seed dormancy often requires environmental cues, such as temperature or lighting changes ...
... • Seed dormancy increases the chances that germination will occur at a time and place most advantageous to the seedling • The breaking of seed dormancy often requires environmental cues, such as temperature or lighting changes ...
Erigenia bulbosa
... leaves must obtain enough food from photosynthesis before the leaves of other plant species have matured and have shaded out this plant. Basal Leaves: Its basal leaves are numerous Stem Leaves: Its 1-2 stem leaves are alternate, palmately compound, and are twice divided into 3 delicate, fern-like le ...
... leaves must obtain enough food from photosynthesis before the leaves of other plant species have matured and have shaded out this plant. Basal Leaves: Its basal leaves are numerous Stem Leaves: Its 1-2 stem leaves are alternate, palmately compound, and are twice divided into 3 delicate, fern-like le ...
Life Cycle of a Plant
... How a Seed Grows into a New Plant The life of a plant begins as a seed. Once a seed is watered and warmed, it germinates. The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the s ...
... How a Seed Grows into a New Plant The life of a plant begins as a seed. Once a seed is watered and warmed, it germinates. The root pushes through the seed coat. The roots of the seedling grow down into the soil and the leaves and stem push out of the ground. The stem and its leaves grow toward the s ...
Why should I care about native plants?
... An invasive plant is a species that has become a weed pest—one that grows aggressively, spreads, and displaces other plants. Although some native plants are aggressive on disturbed areas, most invasive plants are introduced from other regions, leaving behind the pests, diseases, predators, and other ...
... An invasive plant is a species that has become a weed pest—one that grows aggressively, spreads, and displaces other plants. Although some native plants are aggressive on disturbed areas, most invasive plants are introduced from other regions, leaving behind the pests, diseases, predators, and other ...
Introduction to Plants
... plants. They store sugars and starches to help plants over winter. • Sugar storage in roots also help to send up new shoots each spring, and to regenerate stems and leaves that were eaten or burned. • Radishes, carrots, turnips – store large amounts of food in the form of starch in their roots. We e ...
... plants. They store sugars and starches to help plants over winter. • Sugar storage in roots also help to send up new shoots each spring, and to regenerate stems and leaves that were eaten or burned. • Radishes, carrots, turnips – store large amounts of food in the form of starch in their roots. We e ...
Plant Ecology - Chapter 8
... weather, low pollen), low resource expenditures, greater likelihood of more reproduction next year ...
... weather, low pollen), low resource expenditures, greater likelihood of more reproduction next year ...
Chapter 32-Plant Reproduction
... • In order for fertilization to occur, a pollen tube must grow to an egg, and sperm must form. (pollen tubes take about a year to reach an egg in gymnosperms, a day or two for angiosperms) (1) Double-Fertilization (1st make the zygote, the 2nd makes the endosperm) • Following pollination, a pollen g ...
... • In order for fertilization to occur, a pollen tube must grow to an egg, and sperm must form. (pollen tubes take about a year to reach an egg in gymnosperms, a day or two for angiosperms) (1) Double-Fertilization (1st make the zygote, the 2nd makes the endosperm) • Following pollination, a pollen g ...
Examining Sexual Reproduction of Flowering Plants
... The reproductive process begins with pollination. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Plants rely on wind and water to transfer the pollen. In addition, plants depend on animals to help with pollination. Birds, insects, bats ...
... The reproductive process begins with pollination. Pollination is the transfer of the male sperm carried in the pollen to the female part of a flower, the stigma. Plants rely on wind and water to transfer the pollen. In addition, plants depend on animals to help with pollination. Birds, insects, bats ...
Linnaea borealis
... Seed Weight: 2 g/1,000 seeds Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 2008). Harvest Dates: August (Luna et al. 2008). Cleaning: Seeds are hand cleaned by rubbing capsules against screens (Luna et al. 2008). Storage Behaviour: Most likely orthodox; dry seed to low relative humidity and store cold but this is unpro ...
... Seed Weight: 2 g/1,000 seeds Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 2008). Harvest Dates: August (Luna et al. 2008). Cleaning: Seeds are hand cleaned by rubbing capsules against screens (Luna et al. 2008). Storage Behaviour: Most likely orthodox; dry seed to low relative humidity and store cold but this is unpro ...
Angiosperm Reproduction
... that for the most part is done by hand. The detasseling season lasts only about 20 days beginning in mid-July. Pioneer Hi-Bred International Inc., the world's largest seed company, employed about 35,000 detasselers in the U.S. last summer. ...
... that for the most part is done by hand. The detasseling season lasts only about 20 days beginning in mid-July. Pioneer Hi-Bred International Inc., the world's largest seed company, employed about 35,000 detasselers in the U.S. last summer. ...
PLANT BREEDING SYSTEMS
... apetalous flowers that form directly into seed capsules. • Has evolved independently multiple times – throughout the angiosperms, including some basal lineages. ...
... apetalous flowers that form directly into seed capsules. • Has evolved independently multiple times – throughout the angiosperms, including some basal lineages. ...
Sycamore (PDF 1.08 MB)
... Sycamore trees are long-lived and are able to grow in a wide range of conditions. Each tree produces many seeds over it’s lifetime and these seeds are very efficiently wind dispersed. Seedlings are tolerant of shade and will produce dense stands, preventing native seedlings from establishing. Sycamo ...
... Sycamore trees are long-lived and are able to grow in a wide range of conditions. Each tree produces many seeds over it’s lifetime and these seeds are very efficiently wind dispersed. Seedlings are tolerant of shade and will produce dense stands, preventing native seedlings from establishing. Sycamo ...
PowerSeeds
... - It is important that the students be as accurate as possible when applying the covering. There is only half a centimeter to work with, so too much or too little could affect the results. - Timing is very important. It would be a good idea to try to plant everything on a Friday. This will allow a g ...
... - It is important that the students be as accurate as possible when applying the covering. There is only half a centimeter to work with, so too much or too little could affect the results. - Timing is very important. It would be a good idea to try to plant everything on a Friday. This will allow a g ...
seed plants
... Land plants evolved from aquatic species In water, gametes swim to reach each other Mosses and ferns retain their motile gametes As a result they have to live in moist areas Ferns developed a waterproof cuticle and vascular tissue to make them less dependent on water but they still need it for repro ...
... Land plants evolved from aquatic species In water, gametes swim to reach each other Mosses and ferns retain their motile gametes As a result they have to live in moist areas Ferns developed a waterproof cuticle and vascular tissue to make them less dependent on water but they still need it for repro ...
Evolution of the Flower
... embryo sac. After double fertilization takes place, development of the embryo and endosperm begins. The seed matures within the ripening fruit; the germination of the seed initiates another life cycle. Successful pollination in many angiosperms depends on the regular attraction of pollinators such a ...
... embryo sac. After double fertilization takes place, development of the embryo and endosperm begins. The seed matures within the ripening fruit; the germination of the seed initiates another life cycle. Successful pollination in many angiosperms depends on the regular attraction of pollinators such a ...
B-1-33 Sowing Seed Indoors.pmd
... be clean and have holes in the bottom to provide good drainage. There are many soilless type mixtures available for starting seeds. You can mix your own or purchase a prepackaged one that is “sterilized.” Most soilless mixes contain equal parts of peat moss and perlite and/or vermiculite. Be sure to ...
... be clean and have holes in the bottom to provide good drainage. There are many soilless type mixtures available for starting seeds. You can mix your own or purchase a prepackaged one that is “sterilized.” Most soilless mixes contain equal parts of peat moss and perlite and/or vermiculite. Be sure to ...
Reproduction of the Flowering Plant
... Describe 4 methods of artificial propagation in flowering plants. Carry out an investigation to show the effects of water, oxygen and temperature on Germination ...
... Describe 4 methods of artificial propagation in flowering plants. Carry out an investigation to show the effects of water, oxygen and temperature on Germination ...
Ecology of Banksia

The ecology of Banksia refers to all the relationships and interactions among the plant genus Banksia and its environment. Banksia has a number of adaptations that have so far enabled the genus to survive despite dry, nutrient-poor soil, low rates of seed set, high rates of seed predation and low rates of seedling survival. These adaptations include proteoid roots and lignotubers; specialised floral structures that attract nectariferous animals and ensure effective pollen transfer; and the release of seed in response to bushfire.The arrival of Europeans in Australia has brought new ecological challenges. European colonisation of Australia has directly affected Banksia through deforestation, exploitation of flowers and changes to the fire regime. In addition, the accidental introduction and spread of plant pathogens such as Phytophthora cinnamomi (dieback) pose a serious threat to the genus's habitat and biodiversity. Various conservation measures have been put in place to mitigate these threats, but a number of taxa remain endangered.