![Stops section 5.3 Dispersing and Reflecting Prisms [sections 5.5.1 and 5.5.2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008604038_1-7acbc4ef950c5d0dbe26513ab5ac922a-300x300.png)
Stops section 5.3 Dispersing and Reflecting Prisms [sections 5.5.1 and 5.5.2]
... 1. Determine the focal lengths of the two lenses, the object distance, and any other dimensions needed. 2. Predict the separation that the lenses must have to make the telescope. Predict the magnification of this telescope. 3. Describe what you see happening to the image as you increase the separati ...
... 1. Determine the focal lengths of the two lenses, the object distance, and any other dimensions needed. 2. Predict the separation that the lenses must have to make the telescope. Predict the magnification of this telescope. 3. Describe what you see happening to the image as you increase the separati ...
Snímka 1
... of M1 and M2 mirrors and helps to regain the collimation of the optics after recoating. The primary mirror is fixed radially by a 4 point preloaded spring pad system, which guarantees the permanent position of M1 during all telescope movements between zenith and horizon positions as well as at high ...
... of M1 and M2 mirrors and helps to regain the collimation of the optics after recoating. The primary mirror is fixed radially by a 4 point preloaded spring pad system, which guarantees the permanent position of M1 during all telescope movements between zenith and horizon positions as well as at high ...
HOW do astronomers work? How do they ana
... dome is opened as early in the evening as possible so that the inside temperature can become adjusted to that outside the dome. This is important- since both the tube and mirror are affected by changes in temperature. When ready to begin work, the astronomer rides the prime focus elevator to his obs ...
... dome is opened as early in the evening as possible so that the inside temperature can become adjusted to that outside the dome. This is important- since both the tube and mirror are affected by changes in temperature. When ready to begin work, the astronomer rides the prime focus elevator to his obs ...
Measuring the Solar Diameter with a Michelson Radio
... A work-around the diffraction limitation can be implemented when using two (or more) telescope apertures, where the distance B between the apertures is larger than each telescope diameter. The angular resolution limit of such an interferometer is then defined by λ/B, rather than λ/D. By using small- ...
... A work-around the diffraction limitation can be implemented when using two (or more) telescope apertures, where the distance B between the apertures is larger than each telescope diameter. The angular resolution limit of such an interferometer is then defined by λ/B, rather than λ/D. By using small- ...
Note: `n` - Centre for Astrophysics and Planetary Science
... 3. Mirrors are easier to support because they can be supported on the sides and the back; large lenses tend to sag because they can only be supported on the perimeter. Reflectors are also much more versatile than refractors because they can be used at several different foci. The world's largest opti ...
... 3. Mirrors are easier to support because they can be supported on the sides and the back; large lenses tend to sag because they can only be supported on the perimeter. Reflectors are also much more versatile than refractors because they can be used at several different foci. The world's largest opti ...
$doc.title
... • POS mode is used for astrometry by performing a positional measurement of multiple targets in the FGS1R aperture (the “pickle”). Because these targets can cover a large area across the pickle, it is ...
... • POS mode is used for astrometry by performing a positional measurement of multiple targets in the FGS1R aperture (the “pickle”). Because these targets can cover a large area across the pickle, it is ...
Telescopes
... Foci exist Telescope – Device used to detect light from a distance source o Optical telescope – Detects visible light only Reflecting telescope – Uses mirrors Refracting telescope – Uses lenses o Reflecting telescopes are much better than refracting telescopes Glass won’t sag under its own w ...
... Foci exist Telescope – Device used to detect light from a distance source o Optical telescope – Detects visible light only Reflecting telescope – Uses mirrors Refracting telescope – Uses lenses o Reflecting telescopes are much better than refracting telescopes Glass won’t sag under its own w ...
Telescopes
... Besides collecting light, telescopes also allow us to discern objects as single large object or several small individuals ______________________________ – The ability of a telescope or instrument to discern fine details. Larger diameter telescopes have greater resolving power than smaller ones. • Re ...
... Besides collecting light, telescopes also allow us to discern objects as single large object or several small individuals ______________________________ – The ability of a telescope or instrument to discern fine details. Larger diameter telescopes have greater resolving power than smaller ones. • Re ...
Binoculars and Telescopes - Shreveport
... of any amateur instrument. Another problem is that they do not gather much light. Most of them operate at around F 15 so that the image you see can be on the dim side. Therefore, they are not well suited for photography and for dim deep sky objects. However, for observation of bright objects such as ...
... of any amateur instrument. Another problem is that they do not gather much light. Most of them operate at around F 15 so that the image you see can be on the dim side. Therefore, they are not well suited for photography and for dim deep sky objects. However, for observation of bright objects such as ...
Design and Fabrication of an Optical System for a Balloon
... The mirror is machined on a Nanoform 600 DTM coupled with the FLORA II fast tool servo built at the PEC. The off-axis parabolic section is machined on axis by translating the shape to the center of rotation, tilting it and finding the best fit rotationally symmetric surface with a sag of 13 mm for t ...
... The mirror is machined on a Nanoform 600 DTM coupled with the FLORA II fast tool servo built at the PEC. The off-axis parabolic section is machined on axis by translating the shape to the center of rotation, tilting it and finding the best fit rotationally symmetric surface with a sag of 13 mm for t ...
Document
... New backends built with 8-bit inputs to allow digitisers to catch up. Advanced ATNF Correlators ...
... New backends built with 8-bit inputs to allow digitisers to catch up. Advanced ATNF Correlators ...
2.1. Telescopes
... sides and the back; large lenses tend to sag because they can only be supported on the perimeter. Reflectors are also much more versatile than refractors because they can be used at several different foci. The world's largest optical/infrared telescopes are the twin 10-meter Keck Telescopes operated ...
... sides and the back; large lenses tend to sag because they can only be supported on the perimeter. Reflectors are also much more versatile than refractors because they can be used at several different foci. The world's largest optical/infrared telescopes are the twin 10-meter Keck Telescopes operated ...
Microsoft Word
... [1] A. Penguin, “Prospectives for a Robotic Observatory on the Moon”, Journal of Science and Nature, vol. 15, no. 450, pp. 345-378, 2006. [2] E. Seal, A. Student, B. Postdoc, et al., Robotic Telescopes in the Solar System, John Wiley and Grandsons, Antartica, 2009. [3] A. Visionary, “A robotic teles ...
... [1] A. Penguin, “Prospectives for a Robotic Observatory on the Moon”, Journal of Science and Nature, vol. 15, no. 450, pp. 345-378, 2006. [2] E. Seal, A. Student, B. Postdoc, et al., Robotic Telescopes in the Solar System, John Wiley and Grandsons, Antartica, 2009. [3] A. Visionary, “A robotic teles ...
ISON network development in 2015
... • ISON network is splitting on 3 segments that may be independent in near future: - KIAM scientific international cooperation; - Roscomsos segment (ASPOS OKP); - industry organizations (JSC Vimpel & ASC) • New segment of ISON network for observations under commercial contracts is arranged as part of ...
... • ISON network is splitting on 3 segments that may be independent in near future: - KIAM scientific international cooperation; - Roscomsos segment (ASPOS OKP); - industry organizations (JSC Vimpel & ASC) • New segment of ISON network for observations under commercial contracts is arranged as part of ...
Telescopes
... • But planets DO twinkle when close to the horizon. • For a telescope larger than 20-30 cm, twinkling is the limiting factor for resolution (<1’’ resolution). • How do we get rid of the twinkling? ...
... • But planets DO twinkle when close to the horizon. • For a telescope larger than 20-30 cm, twinkling is the limiting factor for resolution (<1’’ resolution). • How do we get rid of the twinkling? ...
Writing Effective Telescope Proposals
... “turn-around time”, ON-OFF transition time for position switching, etc. • Specify experimental parameters to enable cross checking, i.e. total bandwidth, channel width, assumed Tsys or SEFD, 3- or 9level sampling, etc. • For OTF mapping, specify scanning pattern, telescope drive speed, sampling cons ...
... “turn-around time”, ON-OFF transition time for position switching, etc. • Specify experimental parameters to enable cross checking, i.e. total bandwidth, channel width, assumed Tsys or SEFD, 3- or 9level sampling, etc. • For OTF mapping, specify scanning pattern, telescope drive speed, sampling cons ...
Lecture
... Secondary Optics In reflecting telescopes: Secondary mirror, to redirect the light path towards the back or side of the incoming light path. ...
... Secondary Optics In reflecting telescopes: Secondary mirror, to redirect the light path towards the back or side of the incoming light path. ...
Are Earth-like exoplanets common?
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
... number of lensing events at any given time of some baseline magnitude. ...
Chapter 6 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How does your eye form
... –! It uses refraction to bend parallel light rays so that they form an image. –! The image is in focus if the focal plane is at the retina. •! How do we record images? –! Cameras focus light like your eye and record the image with a detector. –! The detectors (CCDs) in digital cameras are like those ...
... –! It uses refraction to bend parallel light rays so that they form an image. –! The image is in focus if the focal plane is at the retina. •! How do we record images? –! Cameras focus light like your eye and record the image with a detector. –! The detectors (CCDs) in digital cameras are like those ...
Astronomical e-Science in Edinburgh Introduction: astronomy and e-science Sky Survey Science Archives
... avalanche it is experiencing: the volume of astronomical data available online doubles every eighteen months or so, with the largest sky survey databases growing at several Terabytes per year. Conversely, astronomy data provide an ideal testbed for many e-science developments: in the words of Jim Gr ...
... avalanche it is experiencing: the volume of astronomical data available online doubles every eighteen months or so, with the largest sky survey databases growing at several Terabytes per year. Conversely, astronomy data provide an ideal testbed for many e-science developments: in the words of Jim Gr ...
Recent modification on Lindgren Feed
... • InP HEMTS - Indium-phosphide high-electron-mobility transistors have been implemented in almost all low-noise amplifiers in radio astronomy for the past 10 years with little change in performance. They are usually cooled to 15K to reduce the noise by an order of magnitude. The noise performance fr ...
... • InP HEMTS - Indium-phosphide high-electron-mobility transistors have been implemented in almost all low-noise amplifiers in radio astronomy for the past 10 years with little change in performance. They are usually cooled to 15K to reduce the noise by an order of magnitude. The noise performance fr ...
a new era in astronomical imaging and telescope control
... Planetary Imager/Autoguider): For all Meade telescopes equipped with Autostar II and #497 Autostar Computer Controllers**, complete with Autostar-PC interface cables – $149 Meade LPI imager mounted on LX200GPS telescope. ...
... Planetary Imager/Autoguider): For all Meade telescopes equipped with Autostar II and #497 Autostar Computer Controllers**, complete with Autostar-PC interface cables – $149 Meade LPI imager mounted on LX200GPS telescope. ...
chapter6Telescopes
... • Focusing of X-rays requires special mirrors • Mirrors are arranged to focus X-ray photons through grazing bounces off the surface ...
... • Focusing of X-rays requires special mirrors • Mirrors are arranged to focus X-ray photons through grazing bounces off the surface ...
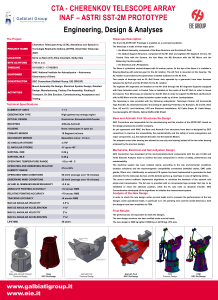
astri-design-poster_110x80
... Base and Azimuth Fork Structures Re-Design GEC Consortium was responsible for the manufacturing and the erection of the ASTRI SST, based on ...
... Base and Azimuth Fork Structures Re-Design GEC Consortium was responsible for the manufacturing and the erection of the ASTRI SST, based on ...
OLEARY_2004 - Armagh Observatory
... by rearranging the formula and using a time from my observations which was estimated to be in the middle of an eclipse. This value for n was then rounded to give the integer number of cycles that had occurred. From this, an accurate value for teclipse is found. Using the second formula, the times of ...
... by rearranging the formula and using a time from my observations which was estimated to be in the middle of an eclipse. This value for n was then rounded to give the integer number of cycles that had occurred. From this, an accurate value for teclipse is found. Using the second formula, the times of ...
Allen Telescope Array

The Allen Telescope Array (ATA), formerly known as the One Hectare Telescope (1hT) is a radio telescope array dedicated to astronomical observations and a simultaneous Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). The array is situated at the Hat Creek Radio Observatory, 290 miles (470 km) northeast of San Francisco, California.Originally developed as a joint effort between the SETI Institute and the Radio Astronomy Laboratory (RAL) at the University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkley) with funds obtained from an initial US$11.5 million donation by the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, the project completed the first phase of construction and become operational on 11 October 2007 with 42 antennas (ATA-42), after Paul Allen (co-founder of Microsoft) pledged an additional $13.5 million to support the construction of the first and second phases.Though overall Allen has contributed more than $30 million to the project, the project has not succeeded in building the 350 six metre (19.7 feet) dishes originally conceived, and suffered an operational hiatus due to funding shortfalls between April and August 2011. Subsequently, UC Berkeley exited the project, completing divestment in April 2012. The facility is now managed by SRI International (formerly Stanford Research Institute), an independent, nonprofit research institute.In August 2014 the installation was threatened by a forest fire in the area and was briefly forced to shut down, but ultimately emerged largely unscathed.