YCCC Jeopardy Vocabulary PowerPoint Presentation
... A collection of many billions of stars, gas and dust (including nebulae), all held together by the force of gravity. ...
... A collection of many billions of stars, gas and dust (including nebulae), all held together by the force of gravity. ...
Havana, 12 January, 2017 Dear Colleague This
... Researchers that need an invitation letter for the participation in the events are kindly asked to require it when filling the registration form which will be soon available to the participants. In view of our limited financial resources, we strongly recommend that participants request financial sup ...
... Researchers that need an invitation letter for the participation in the events are kindly asked to require it when filling the registration form which will be soon available to the participants. In view of our limited financial resources, we strongly recommend that participants request financial sup ...
Document
... Why is adaptive optics needed? Turbulence in earth’s atmosphere makes stars twinkle More importantly, turbulence spreads out light; makes it a blob rather than a point. This blob is a lot larger than the Point Spread Function (PSF) that would be limited by the size of the telescope only Even the la ...
... Why is adaptive optics needed? Turbulence in earth’s atmosphere makes stars twinkle More importantly, turbulence spreads out light; makes it a blob rather than a point. This blob is a lot larger than the Point Spread Function (PSF) that would be limited by the size of the telescope only Even the la ...
... A. A telescope in which the principal light-gathering component is a lens B. A slow, conical motion of the Earth's axis of rotation caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and Sun on the Earth's equatorial bulge. C. The distance between two successive peaks on a wave. D. The annual path of the ...
Telescopes, short
... Radio Telescopes Large metal dish acts as a mirror for radio waves. Radio receiver at prime focus. Surface accuracy not so important, so easy to make large one. ...
... Radio Telescopes Large metal dish acts as a mirror for radio waves. Radio receiver at prime focus. Surface accuracy not so important, so easy to make large one. ...
The Resolution Of A Telescope
... • Even the nearest stars are effectively point sources of light because they are so incredibly distant.( It may be considered a surprise that we can produce an image of them at all!) ...
... • Even the nearest stars are effectively point sources of light because they are so incredibly distant.( It may be considered a surprise that we can produce an image of them at all!) ...
The Milky Way
... The Hubble Space Telescope • Launched in 1990; maintained and upgraded by several space shuttle service missions throughout the 1990s and early 2000’s ...
... The Hubble Space Telescope • Launched in 1990; maintained and upgraded by several space shuttle service missions throughout the 1990s and early 2000’s ...
Various Types of Astronomy
... Limited to night viewing under clear skies, pollution free sky (light pollution as well as smoke, fog, clouds, etc) Observatories are placed in dry, high elevation places to minimize the pollution problem Hubble Space Telescope is in orbit around the Earth, above the pollution, and eliminating ...
... Limited to night viewing under clear skies, pollution free sky (light pollution as well as smoke, fog, clouds, etc) Observatories are placed in dry, high elevation places to minimize the pollution problem Hubble Space Telescope is in orbit around the Earth, above the pollution, and eliminating ...
Astronomy 212 EXAM 2 2011 October 26 Except for questions 38
... 32. Define resolution of a telescope. What determines the resolution of the telescopes we use in lab? 33. Why does a single-dish radio telescope produce images much more blurred than big single-mirror visible-light telescopes? How can we get detailed images using radio light? 34. Why are some telesc ...
... 32. Define resolution of a telescope. What determines the resolution of the telescopes we use in lab? 33. Why does a single-dish radio telescope produce images much more blurred than big single-mirror visible-light telescopes? How can we get detailed images using radio light? 34. Why are some telesc ...
Telescopes
... • Galileo (1609) is the first to use it for astronomy. • The objective lens gathers the light, and bends o refracts it to a focus near the back of the tube. The eyepiece lens brings the image to your eye, and magnifies the image. • Refractors have good resolution, high enough to see details in plane ...
... • Galileo (1609) is the first to use it for astronomy. • The objective lens gathers the light, and bends o refracts it to a focus near the back of the tube. The eyepiece lens brings the image to your eye, and magnifies the image. • Refractors have good resolution, high enough to see details in plane ...
Who Invented the Telescope?
... determined the distance of the Andromeda Nebula — far beyond the Milky Way. ...
... determined the distance of the Andromeda Nebula — far beyond the Milky Way. ...
Telescopes - ScienceRocks8
... Isaac Newton built the first in 1668 Uses a curved mirror to collect and focus light The larger the mirror, the more light that can be collected Largest optical telescopes today are reflecting ...
... Isaac Newton built the first in 1668 Uses a curved mirror to collect and focus light The larger the mirror, the more light that can be collected Largest optical telescopes today are reflecting ...
Ch.4 lecture
... because they are so readily absorbed by matter. Thus it is difficult to tell where they came from, and to reconstruct the image. ...
... because they are so readily absorbed by matter. Thus it is difficult to tell where they came from, and to reconstruct the image. ...
Introduction to the Solar System
... • The farther a planet is from the sun, the longer it takes to orbit. The time it takes to complete one trip around the sun is called a YEAR. • Earth’s year is about 365 days long. Mercury makes a complete orbit in just 88 days. Neptune takes about 165 Earth years to complete its orbit around the su ...
... • The farther a planet is from the sun, the longer it takes to orbit. The time it takes to complete one trip around the sun is called a YEAR. • Earth’s year is about 365 days long. Mercury makes a complete orbit in just 88 days. Neptune takes about 165 Earth years to complete its orbit around the su ...
Video. Hunting the Edge of Space. NOVA - d
... billion galaxies beyond our home, each made up of billion stars. Multiply those together and you have more stars than all the grains of sand on all the beaches and deserts of Earth. 12. Light is made up of and each color has its own ...
... billion galaxies beyond our home, each made up of billion stars. Multiply those together and you have more stars than all the grains of sand on all the beaches and deserts of Earth. 12. Light is made up of and each color has its own ...
Unit 5 Review Key - Grande Cache Community High School
... This is a rocket that is made of more than one section. The sections with initial fuel tanks and rocket engines drop off when used up. ...
... This is a rocket that is made of more than one section. The sections with initial fuel tanks and rocket engines drop off when used up. ...
Light and Telescopes - University of Redlands
... Resolution is inversely proportional to Telescope Diameter. = constant times 1/D Diffraction Limit If D increases then decreases by the same amount. ...
... Resolution is inversely proportional to Telescope Diameter. = constant times 1/D Diffraction Limit If D increases then decreases by the same amount. ...
Telescope set up
... B. With two people, attach telescope base to wedge on tripod with the three bolts, starting with top bolt that has a slip slot at top of wedge. C. Arrange tripod base so that top of fork (open end) is facing due North on horizon (directly below Polaris in tail of Little Dipper). D. Attach Power Supp ...
... B. With two people, attach telescope base to wedge on tripod with the three bolts, starting with top bolt that has a slip slot at top of wedge. C. Arrange tripod base so that top of fork (open end) is facing due North on horizon (directly below Polaris in tail of Little Dipper). D. Attach Power Supp ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... with two perfect surfaces; hard to support a large lens by edges; different colors are ...
... with two perfect surfaces; hard to support a large lens by edges; different colors are ...
UCSD engineers to guide Hubble Telescope to
... "It will be a very scary time for us," says William A. Baity, FOS science program manager. "We'll step up the voltage in 11 steps over 11 orbits, turning it on for two minutes, then off, and sending a bigger jolt each time. If we don't have a perfect vacuum, we'll see electrical noise bursts on ever ...
... "It will be a very scary time for us," says William A. Baity, FOS science program manager. "We'll step up the voltage in 11 steps over 11 orbits, turning it on for two minutes, then off, and sending a bigger jolt each time. If we don't have a perfect vacuum, we'll see electrical noise bursts on ever ...
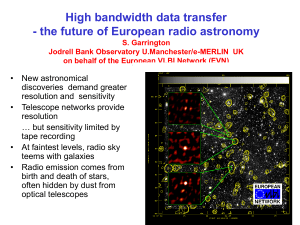
Radio Imaging
... Jodrell Bank Observatory U.Manchester/e-MERLIN UK on behalf of the European VLBI Network (EVN) ...
... Jodrell Bank Observatory U.Manchester/e-MERLIN UK on behalf of the European VLBI Network (EVN) ...
Radio Telescope Basics
... • What organization runs it? • What is the telescope’s diameter (in meters) • What wavelengths / frequencies does the telescope detect. • For what investigations is the telescope being used? • Name one fun fact about the telescope ...
... • What organization runs it? • What is the telescope’s diameter (in meters) • What wavelengths / frequencies does the telescope detect. • For what investigations is the telescope being used? • Name one fun fact about the telescope ...
Telescopes and Astronomical Observations
... What can we observe? Telescopes Optical, IR, Radio, High Energy ++ Limitations Angular resolution Spectroscopy Data Handling ...
... What can we observe? Telescopes Optical, IR, Radio, High Energy ++ Limitations Angular resolution Spectroscopy Data Handling ...
Lovell Telescope

The Lovell Telescope /ˈlʌvəl/ is a radio telescope at Jodrell Bank Observatory, near Goostrey, Cheshire in the north-west of England. When construction was finished in 1957, the telescope was the largest steerable dish radio telescope in the world at 76.2 m (250 ft) in diameter;it is now the third largest, after the Green Bank telescope in West Virginia, USA, and the Effelsberg telescope in Germany.It was originally known as the ""250 ft telescope"" or the Radio Telescope at Jodrell Bank, before becoming the Mark I telescope around 1961 when future telescopes (the Mark II, III, and IV) were being discussed. It was renamed to the Lovell Telescope in 1987 after Sir Bernard Lovell, and became a Grade I listed building in 1988. The telescope forms part of the MERLIN and European VLBI Network arrays of radio telescopes.Both Bernard Lovell and Charles Husband were knighted for their roles in creating the telescope. In September 2006, the telescope won the BBC's online competition to find the UK's greatest ""Unsung Landmark"". 2007 marked the 50th anniversary of the telescope.If the air is clear enough, the Mark I telescope can be seen from high-rise buildings in Manchester such as the Beetham Tower, and from as far away as the Pennines, Winter Hill in Lancashire, Snowdonia, Beeston Castle in Cheshire, and the Peak District. It can also be seen from the Terminal 1 restaurant area and departure lounges of Manchester Airport.