TZS - Skybergtech
... Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
... Nominal operating voltage Extent of operating currents Short-term overcurrent capacity: 50% In Protection class: IP00 Extent of operating temperature: 0°C + 40°C ...
9 – The Power MOSFET 3
... the power MOSFETs are maintained in either the on-state (conduction state) or the off-state (forward blocking) state. ...
... the power MOSFETs are maintained in either the on-state (conduction state) or the off-state (forward blocking) state. ...
Fundamentals of Linear Electronics Integrated & Discrete
... • Diodes can “pop”, often from too much surge current into the filter capacitor. ...
... • Diodes can “pop”, often from too much surge current into the filter capacitor. ...
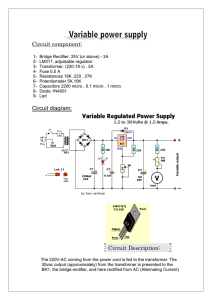
Circuit component
... pin and the 5K potentiometer P1. The large value of C1 makes for a good, low ripple output voltage. Why exactly 1.2V and not 0-volt? Very basic, the job of the regulator is two-fold; first, it compares the output voltage to an internal reference and controls the output voltage so that it remains con ...
... pin and the 5K potentiometer P1. The large value of C1 makes for a good, low ripple output voltage. Why exactly 1.2V and not 0-volt? Very basic, the job of the regulator is two-fold; first, it compares the output voltage to an internal reference and controls the output voltage so that it remains con ...
Circuit with partlist and explanation of how it works
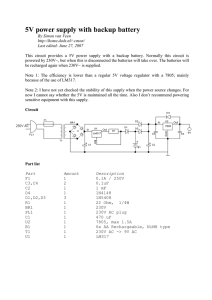
... plugged in at 230V, this means UC1 will be zero Volts, so the batteries will provide power. U2 then uses this power to regulate 5V between Gnd and Out. For information on this part of the circuit, read [2]. C2 is placed to smoothen out any voltage changes that may occur when the power source is chan ...
... plugged in at 230V, this means UC1 will be zero Volts, so the batteries will provide power. U2 then uses this power to regulate 5V between Gnd and Out. For information on this part of the circuit, read [2]. C2 is placed to smoothen out any voltage changes that may occur when the power source is chan ...
Bipolar transistors II, Page 1 Bipolar Transistors II
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
... Figure 4: Feedback Voltage Regulator. load conditions are variable. These can give output impedances less than an ohm and high stability against temperature variation. Figure 4 is a common example of a negative-feedback circuit. Transistor Q1 is normally conducting because of the bias current throug ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutr ...
... Static electricity is when (charges, circuits) accumulate on the (inside, surface) of an object which gains or loses (electrons, branches) which move more easily on a (conductor, insulator) than they do on a (conductor, insulator). A negatively charged object has (fewer, more) electrons than a neutr ...
EV3213DH-00A - Monolithic Power System
... 1.3MHz) of the MP3213 allows for smaller external components, producing a compact solution for a wide range of load currents. Two user-selectable frequency options offer flexibility for easy filtering and low noise. The PCB heatsink with the exposed pad improves thermal performance and efficiency at ...
... 1.3MHz) of the MP3213 allows for smaller external components, producing a compact solution for a wide range of load currents. Two user-selectable frequency options offer flexibility for easy filtering and low noise. The PCB heatsink with the exposed pad improves thermal performance and efficiency at ...
POWER QUALITY -- An Indian Perspective
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
... over-drawal : Maximize generation, and allow over-drawal, as long as grid can sustain it, and it is paid for. b) LOAD - SHEDDING to curtail over-loading or under-voltage : If too frequent, ask for system augmentation, additional capacitors. ...
A Novel Three-Phase Buck–Boost AC–DC
... variations of the converter proposed in and their output voltage is always higher than their input voltage because they are boost-type converters. This is a drawback if there is a need for a converter that needs to operate for a wide range of input ac voltages and/or produce a wide range of output d ...
... variations of the converter proposed in and their output voltage is always higher than their input voltage because they are boost-type converters. This is a drawback if there is a need for a converter that needs to operate for a wide range of input ac voltages and/or produce a wide range of output d ...
Rated at 6-kW output power, it is based on the new three
... on the recent AC-DC three-level ZVS converter topology and it is composed of a PFC stage combined with a buck converter into a single stage for a rated 6kW output power (PS120050 version, 120A@50V). The resonant nature of this power supply guarantees high efficiency, a crucial factor to take into ac ...
... on the recent AC-DC three-level ZVS converter topology and it is composed of a PFC stage combined with a buck converter into a single stage for a rated 6kW output power (PS120050 version, 120A@50V). The resonant nature of this power supply guarantees high efficiency, a crucial factor to take into ac ...
Buck converter
A buck converter is a voltage step down and current step up converter.The simplest way to reduce the voltage of a DC supply is to use a linear regulator (such as a 7805), but linear regulators waste energy as they operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Buck converters, on the other hand, can be remarkably efficient (95% or higher for integrated circuits), making them useful for tasks such as converting the main voltage in a computer (12V in a desktop, 12-24V in a laptop) down to the 0.8-1.8V needed by the processor.