IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSRJEEE)
... The three switching angles are depicted using αi1-αi3. Since the waveform has quarter wave and half wave symmetry, not even harmonics exist. Normalized with respect to dc voltage, the Fourier coefficient is magnitudes of the output voltage of the ith inverter unit is given by, ...
... The three switching angles are depicted using αi1-αi3. Since the waveform has quarter wave and half wave symmetry, not even harmonics exist. Normalized with respect to dc voltage, the Fourier coefficient is magnitudes of the output voltage of the ith inverter unit is given by, ...
6 - Binus Repository
... In the sinusoidal steady state, ac power is transferred from sources to various loads. To study the transfer process, we must calculate the power delivered in the sinusoidal steady state to any specified load. It turns out that there is an upper bound on the available load power; hence, we need to u ...
... In the sinusoidal steady state, ac power is transferred from sources to various loads. To study the transfer process, we must calculate the power delivered in the sinusoidal steady state to any specified load. It turns out that there is an upper bound on the available load power; hence, we need to u ...
Bip TR 160V, 0.7A VCE(sat); 0.5V max. PNP Single NMP
... rise to smoke or fire, or accidents that could cause damage to other property. When designing equipment, adopt safety measures so that these kinds of accidents or events cannot occur. Such measures include but are not limited to protective circuits and error prevention circuits for safe design, redu ...
... rise to smoke or fire, or accidents that could cause damage to other property. When designing equipment, adopt safety measures so that these kinds of accidents or events cannot occur. Such measures include but are not limited to protective circuits and error prevention circuits for safe design, redu ...
estimation of voltage ratio, vector - e
... No-load losses (also referred to as core losses and iron losses) are a very small part of the power rating of the transformer, usually less than 1%. Since these losses are essentially constant for the each transformer (do not vary with load), they generally represent a sizable operating expense espe ...
... No-load losses (also referred to as core losses and iron losses) are a very small part of the power rating of the transformer, usually less than 1%. Since these losses are essentially constant for the each transformer (do not vary with load), they generally represent a sizable operating expense espe ...
10.3 The ideal transformer
... The current flowing through the primary circuit generates magnetic flux, which influences the secondary circuit. Due to the magnetic flux, a repulsive voltage is induced on the secondary circuit. EMLAB ...
... The current flowing through the primary circuit generates magnetic flux, which influences the secondary circuit. Due to the magnetic flux, a repulsive voltage is induced on the secondary circuit. EMLAB ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
Thompson - WPI - Worcester Polytechnic Institute
... • Therefore, the inductor ripple current UP equals ripple DOWN • Several assumptions to simplify analysis: • Periodic steady state --- all startup transients have ...
... • Therefore, the inductor ripple current UP equals ripple DOWN • Several assumptions to simplify analysis: • Periodic steady state --- all startup transients have ...
PSS Series - eprom, sa
... •Output voltage: 1-5VDC ±2% F.S. •Linear: Max. ±1% F.S. •Output impedance: 1㏀ •Output current: DC4-20mA ±2% F.S. •Linear: Max. ±1% F.S. Max. ±2% F.S. of output voltage/current at 25℃ within temperature range 0 to 50℃ Over. 50㏁ (at 500VDC megger) 2000VAC 50/60Hz for 1 minute 1.5mm amplitude at freque ...
... •Output voltage: 1-5VDC ±2% F.S. •Linear: Max. ±1% F.S. •Output impedance: 1㏀ •Output current: DC4-20mA ±2% F.S. •Linear: Max. ±1% F.S. Max. ±2% F.S. of output voltage/current at 25℃ within temperature range 0 to 50℃ Over. 50㏁ (at 500VDC megger) 2000VAC 50/60Hz for 1 minute 1.5mm amplitude at freque ...
LLC Resonant Converter for Front End DC/DC Conversion
... drops to lower than output voltage. Both of the output rectifier diodes see reverse voltage. So during this period, ...
... drops to lower than output voltage. Both of the output rectifier diodes see reverse voltage. So during this period, ...
Document
... b. Determine the short-circuit current In = isc. c. Zero the sources and find the Thévenin resistance Rt looking back into the ...
... b. Determine the short-circuit current In = isc. c. Zero the sources and find the Thévenin resistance Rt looking back into the ...
Catalog
... voltages from 10% raise (boost) to 10% lower (buck) in thirty-two steps of approximately 5/8% each. Voltage ratings are available from 2400 volts (60 kV BIL) to 34,500 volts (200 kV BIL) for 60 Hz and 50 Hz systems. Internal potential winding taps and an external ratio correction transformer are pro ...
... voltages from 10% raise (boost) to 10% lower (buck) in thirty-two steps of approximately 5/8% each. Voltage ratings are available from 2400 volts (60 kV BIL) to 34,500 volts (200 kV BIL) for 60 Hz and 50 Hz systems. Internal potential winding taps and an external ratio correction transformer are pro ...
The PXS Series of proportional extra-small high
... characteristics, as well as superior temperature stability performance. The small size of the units, ease of control, and high stability, make the PXS Series optimal for handheld devices, portable equipment, and other small high voltage projects. ...
... characteristics, as well as superior temperature stability performance. The small size of the units, ease of control, and high stability, make the PXS Series optimal for handheld devices, portable equipment, and other small high voltage projects. ...
Electric Fields - King`s Senior Science
... Why do electricians work with one hand behind their back or in a pocket? You're harmed only if current passes through part of your body. In order for that to happen, you must be touching two places that have a voltage difference between them. So the best way to avoid most dangerous situations is: W ...
... Why do electricians work with one hand behind their back or in a pocket? You're harmed only if current passes through part of your body. In order for that to happen, you must be touching two places that have a voltage difference between them. So the best way to avoid most dangerous situations is: W ...
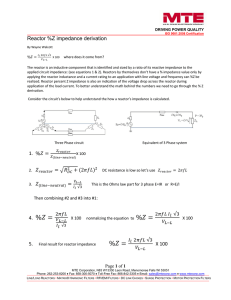
Reactor Z% Impedance Derivation
... derivation. Consider the circuit’s below to help understand the how a reactor’s impedance is calculated. ...
... derivation. Consider the circuit’s below to help understand the how a reactor’s impedance is calculated. ...
Motor-Starting Sags
... starting torque vary with the square of the voltage applied to the motor, so the 50 percent tap will deliver only 25 percent of the full-voltage starting current and torque. The lowest tap which will supply the required starting torque is selected. Resistance and reactance starters initially insert ...
... starting torque vary with the square of the voltage applied to the motor, so the 50 percent tap will deliver only 25 percent of the full-voltage starting current and torque. The lowest tap which will supply the required starting torque is selected. Resistance and reactance starters initially insert ...
EEE-PP-004 - 2027
... As explained in the aforementioned Section, the unbalance phenomena of the rectifying current in the proposed converter are influenced by the gain difference of each converters’reso-nant network. When the input voltage of the converter is fixed, the unbalance problem cannot be solved using the conve ...
... As explained in the aforementioned Section, the unbalance phenomena of the rectifying current in the proposed converter are influenced by the gain difference of each converters’reso-nant network. When the input voltage of the converter is fixed, the unbalance problem cannot be solved using the conve ...
Buck converter
A buck converter is a voltage step down and current step up converter.The simplest way to reduce the voltage of a DC supply is to use a linear regulator (such as a 7805), but linear regulators waste energy as they operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Buck converters, on the other hand, can be remarkably efficient (95% or higher for integrated circuits), making them useful for tasks such as converting the main voltage in a computer (12V in a desktop, 12-24V in a laptop) down to the 0.8-1.8V needed by the processor.