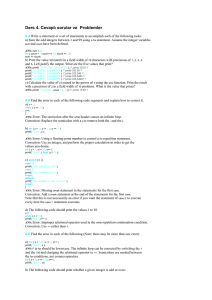
To test whether a fraction is in lowest terms, you need to know the
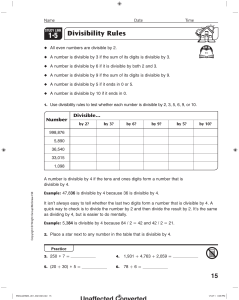
... 11—A number is divisible by 11 if the alternating sum of the digits is divisible by 11. Ex. To check if 65432532 is divisible by 11 look at 6-5+4-3+2-5+3-2=0. Since 0 is divisible by 11 (11 goes into 0 zero times) 65432532 is divisible by 0 also. You can stop when you get to the square root of a num ...
... 11—A number is divisible by 11 if the alternating sum of the digits is divisible by 11. Ex. To check if 65432532 is divisible by 11 look at 6-5+4-3+2-5+3-2=0. Since 0 is divisible by 11 (11 goes into 0 zero times) 65432532 is divisible by 0 also. You can stop when you get to the square root of a num ...
generatingfunctionology - Penn Math
... the method of generating functions works, it is often the simplest method known. (f) Prove identities. Many, many identities are known, in combinatorics and elsewhere in mathematics. The identities that we refer to are those in which a certain formula is asserted to be equal to another formula for s ...
... the method of generating functions works, it is often the simplest method known. (f) Prove identities. Many, many identities are known, in combinatorics and elsewhere in mathematics. The identities that we refer to are those in which a certain formula is asserted to be equal to another formula for s ...
Sums of Two Triangulars and of Two Squares Associated with Sum
... Notice that only three (8n! + 1) from the list in Table 2 can be represented as a square. In addition, by examining the end digits of both factorial and triangular numbers it can be deduced that Ft n = Tx + Tn or n! x( x 1) / 2 is true only if, x belongs to any of the sequences {15, 35, 55, 75, ...
... Notice that only three (8n! + 1) from the list in Table 2 can be represented as a square. In addition, by examining the end digits of both factorial and triangular numbers it can be deduced that Ft n = Tx + Tn or n! x( x 1) / 2 is true only if, x belongs to any of the sequences {15, 35, 55, 75, ...