Document
... and hydrogen as well as oxygen and nitrogen. Matter that does not contain a combination of carbon and hydrogen atoms is called inorganic. ...
... and hydrogen as well as oxygen and nitrogen. Matter that does not contain a combination of carbon and hydrogen atoms is called inorganic. ...
Science Study Guide (Unit A ~ Plants #1)
... nutrients – a substance, such as mineral, which all living things need in order to grow ...
... nutrients – a substance, such as mineral, which all living things need in order to grow ...
Week 4:
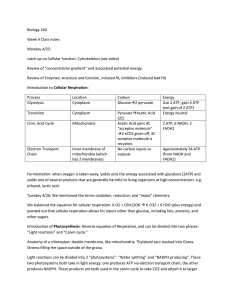
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
... We balanced the equation for cellular respiration: 6 O2 + C6H12O6 6 CO2 + 6 H2O (plus energy) and pointed out that cellular respiration allows for inputs other than glucose, including fats, proteins, and other sugars. Introduction of Photosynthesis: Reverse equation of Respiration, and can be divi ...
the 4 per mil concept - Agriculture and agricultural soils facing
... 4‰ target would result in a carbon sequestration that could peak at 3.5 billion tons C per year (Gt C/ yr) when considering soils from all biomes. • Agricultural soils have a technical carbon sequestration potential between 0.7 and 1.2 GtC/yr, while the potential from all other land uses (including ...
... 4‰ target would result in a carbon sequestration that could peak at 3.5 billion tons C per year (Gt C/ yr) when considering soils from all biomes. • Agricultural soils have a technical carbon sequestration potential between 0.7 and 1.2 GtC/yr, while the potential from all other land uses (including ...
Document
... removing two carbons at a time. If the beta carbon is the terminal carbon (as it would be for the last round of oxidation of a 3 carbon FA), this oxidation would produce a formal group, which is cannot be cleaved by thiolase from the FA chain. ...
... removing two carbons at a time. If the beta carbon is the terminal carbon (as it would be for the last round of oxidation of a 3 carbon FA), this oxidation would produce a formal group, which is cannot be cleaved by thiolase from the FA chain. ...
CARBON DIOXIDE EMISSIONS Atmosphere Climate Change Core
... including economies in transition, to aim to return emissions of CO2 and other GHGs not controlled by the Montreal Protocol to their 1990 levels by 2000. This was achieved: in 2000, GHG emissions from Annex I Parties were about 6 per cent below the 1990 level. The Kyoto Protocol sets individual emi ...
... including economies in transition, to aim to return emissions of CO2 and other GHGs not controlled by the Montreal Protocol to their 1990 levels by 2000. This was achieved: in 2000, GHG emissions from Annex I Parties were about 6 per cent below the 1990 level. The Kyoto Protocol sets individual emi ...
Perils lurking in Permafrost By J. Gillis, New York Times/Standard
... If a substantial amount of the carbon should enter the atmosphere, it would intensify the planetary warming. An especially worrisome possibility is that a significant proportion will emerge not as carbon dioxide, the gas that usually forms when organic material breaks down, but as methane, produced ...
... If a substantial amount of the carbon should enter the atmosphere, it would intensify the planetary warming. An especially worrisome possibility is that a significant proportion will emerge not as carbon dioxide, the gas that usually forms when organic material breaks down, but as methane, produced ...
How Does Carbon Sequestration Affect the
... are themselves reservoirs of carbon). Many different agricultural production practices exist that can capitalize on carbon sequestration in both soil and biomass to reduce environmental impact. The goal of these methods is to modify current production practices in a way that enables the use of the n ...
... are themselves reservoirs of carbon). Many different agricultural production practices exist that can capitalize on carbon sequestration in both soil and biomass to reduce environmental impact. The goal of these methods is to modify current production practices in a way that enables the use of the n ...
Turfgrass Carbon Sequestration
... answer this we need to take a step back. A lot has been reported in the news lately about global warming and climate change and the possible catastrophic effects it could have on planet Earth. I would like to address that topic sometime because it has become such a politically charged, emotionally d ...
... answer this we need to take a step back. A lot has been reported in the news lately about global warming and climate change and the possible catastrophic effects it could have on planet Earth. I would like to address that topic sometime because it has become such a politically charged, emotionally d ...
DC = Dissolved Carbon
... interact and affect organisms Activity 1 – 8 minutes, add missing terms in empty arrows (i.e., processes) and circles (organisms). When you have completed this figure, then pair up with another student in class and discuss your answers. ...
... interact and affect organisms Activity 1 – 8 minutes, add missing terms in empty arrows (i.e., processes) and circles (organisms). When you have completed this figure, then pair up with another student in class and discuss your answers. ...
G C D
... Global warming is increasing ocean temperatures and raising sea levels. New scientific research shows that our oceans are beginning to face yet another threat due to global warming-related emissions – their basic chemistry is changing because of the uptake of carbon dioxide released by human activit ...
... Global warming is increasing ocean temperatures and raising sea levels. New scientific research shows that our oceans are beginning to face yet another threat due to global warming-related emissions – their basic chemistry is changing because of the uptake of carbon dioxide released by human activit ...
File
... 1. Polymers are chains of repeating units (poly means “many”) 2. The units they’re made up of are called monomers (mono means “one”) 3. Take a brick wall, for example: each individual brick would be a monomer. The wall would be the polymer. Carbohydrates A. Polymers that are also known as polysaccha ...
... 1. Polymers are chains of repeating units (poly means “many”) 2. The units they’re made up of are called monomers (mono means “one”) 3. Take a brick wall, for example: each individual brick would be a monomer. The wall would be the polymer. Carbohydrates A. Polymers that are also known as polysaccha ...
Ch 8 Carbon Chem
... C. Plastics- Synthetic polymers made from coal or oil that can be molded or shaped. D. Composite- 2 or more substances combined to form a new material with different properties. Usually includes 1 or more polymers. ...
... C. Plastics- Synthetic polymers made from coal or oil that can be molded or shaped. D. Composite- 2 or more substances combined to form a new material with different properties. Usually includes 1 or more polymers. ...
1. The table below gives the percentage of world energy supplied
... Explain why the rate of increase in the amount of carbon in the atmosphere should be controlled. ...
... Explain why the rate of increase in the amount of carbon in the atmosphere should be controlled. ...
box modelling - Wesleyan University
... Higher Corg burial rates in Western LIS compared to Central and East LIS •E-W gradient in BSi: about 2.5 % in Central LIS, up to 4.5 % in WLIS. Biogenic Silica storage also increased over the last 150 years ...
... Higher Corg burial rates in Western LIS compared to Central and East LIS •E-W gradient in BSi: about 2.5 % in Central LIS, up to 4.5 % in WLIS. Biogenic Silica storage also increased over the last 150 years ...
7.3 - WMO
... Scope of activities, guiding principles and safeguards; Phased-approach for implementation Means of implementation, Measurement, Reporting and Verification (MRV) of actions (e.g. establishing reference emission levels, national monitoring systems, use of IPCC guidelines) ...
... Scope of activities, guiding principles and safeguards; Phased-approach for implementation Means of implementation, Measurement, Reporting and Verification (MRV) of actions (e.g. establishing reference emission levels, national monitoring systems, use of IPCC guidelines) ...
deepen your understanding about green house gases
... Methane is also a significant contributor to global warming Methane, CH4, is formed when an organic compound decays in the absence of oxygen. It can be found in seabed and in swamps. Termites emit CH4. The food that ruminants ingest, ferment in the stomach and cause emissions of CH4. Human induced ...
... Methane is also a significant contributor to global warming Methane, CH4, is formed when an organic compound decays in the absence of oxygen. It can be found in seabed and in swamps. Termites emit CH4. The food that ruminants ingest, ferment in the stomach and cause emissions of CH4. Human induced ...
mitigation ClimATe ChAnge BRiefing pApeR
... 2050 targets. Recent research indicates this ‘clean tech’ revolution has begun and some green roots have been planted. United Nations Environment Programme data released earlier this year shows that overall, renewable energy investment last year was more than four times greater than in 2004. Global ...
... 2050 targets. Recent research indicates this ‘clean tech’ revolution has begun and some green roots have been planted. United Nations Environment Programme data released earlier this year shows that overall, renewable energy investment last year was more than four times greater than in 2004. Global ...
The Evolving Soil Interface of the Earth System Soils are the
... carbon pool) soils play a prominent role in climate change and CO2 sequestration. Model scenarios of soil carbon emissions indicate it is one of our most serious yet poorly constrained variables in climate models. Notably, future emissions from soils almost certainly exceed any plausible scenario of ...
... carbon pool) soils play a prominent role in climate change and CO2 sequestration. Model scenarios of soil carbon emissions indicate it is one of our most serious yet poorly constrained variables in climate models. Notably, future emissions from soils almost certainly exceed any plausible scenario of ...
Greenhouse gas emissions and dairy farms
... KEY POINTS •Production improvement options are linked to greenhouse gas emissions reduction. •Consider emissions reduction options that lead to productivity gains or have cost benefits. ...
... KEY POINTS •Production improvement options are linked to greenhouse gas emissions reduction. •Consider emissions reduction options that lead to productivity gains or have cost benefits. ...
Organic Chemistry and Macromolecules
... fast energy; examples are sugars and starch • Lipids—organic molecule that is not soluble in water, stores energy and provides insulation; ex: fats and oils • Proteins—organic molecule that is structural and speeds up chemical reactions; ex: enzymes and hemaglobin ...
... fast energy; examples are sugars and starch • Lipids—organic molecule that is not soluble in water, stores energy and provides insulation; ex: fats and oils • Proteins—organic molecule that is structural and speeds up chemical reactions; ex: enzymes and hemaglobin ...
ENERGY SUSTAINABILITY IN LATIN AMERICA
... Again, CO2 emissions per capita levels in Latin America are located at an intermediate position between OECD (5.5 times higher in 1990) and the developing countries in Africa and Asia, but still 47 % below the world average. Latinamerican energy supply/demand ratio and the carbon intensity are not f ...
... Again, CO2 emissions per capita levels in Latin America are located at an intermediate position between OECD (5.5 times higher in 1990) and the developing countries in Africa and Asia, but still 47 % below the world average. Latinamerican energy supply/demand ratio and the carbon intensity are not f ...
What is the top priority on climate change? Paul Klemperer
... retrofitted to traditional plants. China, after all, is building one such plant every five days. Crucially, however, it will always be cheaper to burn coal (and oil and gas) without CCS than with it. We can encourage developing countries to use CCS through a revised Clean Development Mechanism21, or ...
... retrofitted to traditional plants. China, after all, is building one such plant every five days. Crucially, however, it will always be cheaper to burn coal (and oil and gas) without CCS than with it. We can encourage developing countries to use CCS through a revised Clean Development Mechanism21, or ...
Paying for Climate Change
... worth incurring depends on the weight one attaches to the well-being of future generations, and how much allowance to make for the likelihood that they will be better off than we are. The discount rate used to compare current costs and future benefits then proves critical in evaluating and forming c ...
... worth incurring depends on the weight one attaches to the well-being of future generations, and how much allowance to make for the likelihood that they will be better off than we are. The discount rate used to compare current costs and future benefits then proves critical in evaluating and forming c ...
Biosequestration

Biosequestration is the capture and storage of the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide by biological processes.This may be by increased photosynthesis (through practices such as reforestation / preventing deforestation and genetic engineering); by enhanced soil carbon trapping in agriculture; or by the use of algal bio sequestration (see algae bioreactor) to absorb the carbon dioxide emissions from coal, petroleum (oil) or natural gas-fired electricity generation.Biosequestration as a natural process has occurred in the past, and was responsible for the formation of the extensive coal and oil deposits which are now being burned. It is a key policy concept in the climate change mitigation debate. It does not generally refer to the sequestering of carbon dioxide in oceans (see carbon sequestration and ocean acidification) or rock formations, depleted oil or gas reservoirs (see oil depletion and peak oil), deep saline aquifers, or deep coal seams (see coal mining) (for all see geosequestration) or through the use of industrial chemical carbon dioxide scrubbing.