1 CARBON ON EARTH - Princeton University Press
... in the global biosphere carbon cycle: the weathering co2 thermostat, the oxygen homeostat, and the ocean’s calcium carbonate pH-stat. carbon Dioxide earth’s climate has navigated a path that stayed within a narrow range, the freezing and boiling points of water, since the very first sedimentary rock ...
... in the global biosphere carbon cycle: the weathering co2 thermostat, the oxygen homeostat, and the ocean’s calcium carbonate pH-stat. carbon Dioxide earth’s climate has navigated a path that stayed within a narrow range, the freezing and boiling points of water, since the very first sedimentary rock ...
I. Cellular Respiration – complex process in which cells make ATP
... Activity – chemical energy is stored as C, F, & P. The body can not use these organic compounds as immediate energy. They must be converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a high-energy compound. Another compound, CP (creatine phosphate) serves to replace ATP as it is used up. A. 3 types of energ ...
... Activity – chemical energy is stored as C, F, & P. The body can not use these organic compounds as immediate energy. They must be converted into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), a high-energy compound. Another compound, CP (creatine phosphate) serves to replace ATP as it is used up. A. 3 types of energ ...
The Calvin Cycle
... Note that the product is not glucose, fructose, or sucrose. Another step is required to fuse 2 G3P to form a 6 carbon sugar. – This process takes 6 turns of the cycle! – Glucose is formed from the fusion of 2 molecules of G3P ...
... Note that the product is not glucose, fructose, or sucrose. Another step is required to fuse 2 G3P to form a 6 carbon sugar. – This process takes 6 turns of the cycle! – Glucose is formed from the fusion of 2 molecules of G3P ...
Note sheet Chap 5, Sect 3
... Chapter 5, Section 3 The main point of photosynthesis is to produce __glucose__, which is then used _______________. Most of our energy comes in the form of _ATP_, which is produced more efficiently in the presence of __oxygen___. This is called __aerobic respiration__. Where does this occur? mitoch ...
... Chapter 5, Section 3 The main point of photosynthesis is to produce __glucose__, which is then used _______________. Most of our energy comes in the form of _ATP_, which is produced more efficiently in the presence of __oxygen___. This is called __aerobic respiration__. Where does this occur? mitoch ...
The Case for a Carbon Tax in Canada
... Yet some hope can perhaps be derived from other similar public goods problems, albeit on a much smaller scale. Elinor Ostrom received the 2009 Nobel Prize in Economics for her work in examining the emergence of self-government institutions in similar prisoners dilemma-type environments.16 For examp ...
... Yet some hope can perhaps be derived from other similar public goods problems, albeit on a much smaller scale. Elinor Ostrom received the 2009 Nobel Prize in Economics for her work in examining the emergence of self-government institutions in similar prisoners dilemma-type environments.16 For examp ...
Larrea, C. (2010), Yasun ITT: An Initiative to Change History
... As Nicholas Stern says, “Even if the rich world assumes all its responsibility and secures absolute cuts in emissions of up to 60-80% by 2050, developing countries are not excused from their own share of equally significant steps”. Ecuador proposes taking on its own share of responsibility and facin ...
... As Nicholas Stern says, “Even if the rich world assumes all its responsibility and secures absolute cuts in emissions of up to 60-80% by 2050, developing countries are not excused from their own share of equally significant steps”. Ecuador proposes taking on its own share of responsibility and facin ...
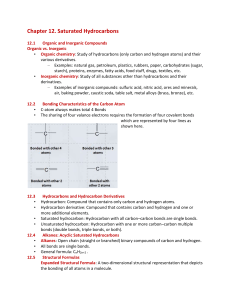
Notes-C12-121
... – Examples: natural gas, petroleum, plastics, rubbers, paper, carbohydrates (sugar, starch), proteins, enzymes, fatty acids, food stuff, drugs, textiles, etc. • Inorganic chemistry: Study of all substances other than hydrocarbons and their derivatives. – Examples of inorganic compounds: sulfuric aci ...
... – Examples: natural gas, petroleum, plastics, rubbers, paper, carbohydrates (sugar, starch), proteins, enzymes, fatty acids, food stuff, drugs, textiles, etc. • Inorganic chemistry: Study of all substances other than hydrocarbons and their derivatives. – Examples of inorganic compounds: sulfuric aci ...
biomass - definition
... technical issues of corrosivity and low fuel density, which impede its widespread use. Vegetable oils combined with gasoline have achieved a moderate reception in powering diesel motor vehicles. Gaseous biomass fuels include (a) low energy molecular gases from gasification processes and (b) methane ...
... technical issues of corrosivity and low fuel density, which impede its widespread use. Vegetable oils combined with gasoline have achieved a moderate reception in powering diesel motor vehicles. Gaseous biomass fuels include (a) low energy molecular gases from gasification processes and (b) methane ...
The Relation Between Net Carbon Emissions
... such as removing carbon dioxide from the air and cooling it for transport to some place for some other purpose (dry ice is an example) or as the result of natural processes or human-induced activities with unintended consequences. The warming of dry ice would, for example, return the carbon to the a ...
... such as removing carbon dioxide from the air and cooling it for transport to some place for some other purpose (dry ice is an example) or as the result of natural processes or human-induced activities with unintended consequences. The warming of dry ice would, for example, return the carbon to the a ...
Green race is on Low carbon economy index 2010 www.pwc.co.uk
... Many of the world’s largest economies have in the past year remained on their business-as-usual pathways. While global carbon intensity in 2009 fell by 0.7% compared to 2008, this is significantly below the average rate of decarbonisation to 2050 of 3.5% that was needed to meet the low carbon challe ...
... Many of the world’s largest economies have in the past year remained on their business-as-usual pathways. While global carbon intensity in 2009 fell by 0.7% compared to 2008, this is significantly below the average rate of decarbonisation to 2050 of 3.5% that was needed to meet the low carbon challe ...
L10v02-glycolysis and TCA
... This is an overview of the relevant metabolic processes going on in the mitochondria. We have produced NADH Via glycolysis and citric acid cycle, which will be used for oxidative phosphorylation for a very much larger payoff in ATP ( on Wednesday). Here for the first time, you can see why we bre ...
... This is an overview of the relevant metabolic processes going on in the mitochondria. We have produced NADH Via glycolysis and citric acid cycle, which will be used for oxidative phosphorylation for a very much larger payoff in ATP ( on Wednesday). Here for the first time, you can see why we bre ...
Ch. 2 Notes Organic Chemistry
... are a special type of protein that acts as a biological catalyst. Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the Ea but are not affected themselves. * (This means that they do not become part of the product.) Enzymes can be affected by: changes in pH, temperature ...
... are a special type of protein that acts as a biological catalyst. Catalysts speed up a chemical reaction by lowering the Ea but are not affected themselves. * (This means that they do not become part of the product.) Enzymes can be affected by: changes in pH, temperature ...
Biomolecules
... Two Carbon Rings2(C6H12O6) Test: Benedicts Digested with pancreatic enzymes in small intestine in duodenum ...
... Two Carbon Rings2(C6H12O6) Test: Benedicts Digested with pancreatic enzymes in small intestine in duodenum ...
A largescale field assessment of carbon stocks in humanmodified
... stocks in tropical forests. Live vegetation, the largest carbon pool, was extremely sensitive to disturbance: forests that experienced both selective logging and understory fires stored, on average, 40% less aboveground carbon than undisturbed forests and were structurally similar to secondary fores ...
... stocks in tropical forests. Live vegetation, the largest carbon pool, was extremely sensitive to disturbance: forests that experienced both selective logging and understory fires stored, on average, 40% less aboveground carbon than undisturbed forests and were structurally similar to secondary fores ...
Combined biogeophysical and biogeochemical
... Studies of the net effect of historical land cover change on global temperature have shown that biogeophysical and biogeochemical mechanisms are of the same order of magnitude (Matthews et al., 2004; Brovkin et al., 2006). Therefore, in order to quantifiy the impacts of large scale land cover change ...
... Studies of the net effect of historical land cover change on global temperature have shown that biogeophysical and biogeochemical mechanisms are of the same order of magnitude (Matthews et al., 2004; Brovkin et al., 2006). Therefore, in order to quantifiy the impacts of large scale land cover change ...
LESSON PLAN: Stomatal Density - AIM-UP!
... 4. Pass out the Student Worksheet “Stomata” and explain that students will follow the directions on the sheet to create leaf molds. 5. When students have completed the worksheet, discuss the purpose of stomata. Ask students to describe what the stomata look like. 6. Distribute the Student Worksheet ...
... 4. Pass out the Student Worksheet “Stomata” and explain that students will follow the directions on the sheet to create leaf molds. 5. When students have completed the worksheet, discuss the purpose of stomata. Ask students to describe what the stomata look like. 6. Distribute the Student Worksheet ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... A simple, 6 carbon sugar that serves as the primary energy source ATP (Adenosine triphosphate): The major energy currency of the cell. NADH and FADH2: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain. ...
... A simple, 6 carbon sugar that serves as the primary energy source ATP (Adenosine triphosphate): The major energy currency of the cell. NADH and FADH2: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain. ...
A Carbon Management Plan for Nottinghamshire County Council
... The broad thrust of the revised Travel Plan is to recognise that the past reliance on small scale incentives to change travel behaviour has only had limited impact and that consideration needs to be given to more affirmative measures, particularly regarding car parking. It should also be noted that ...
... The broad thrust of the revised Travel Plan is to recognise that the past reliance on small scale incentives to change travel behaviour has only had limited impact and that consideration needs to be given to more affirmative measures, particularly regarding car parking. It should also be noted that ...
Regulation on Carbon Emission Trading Pricing-to-Market: Based on
... mechanism. Carbon trading can be classified into two sorts. One is JI and CDM which are both based on the projects, the other is IET on the basis of distributed quotas. Carbon emission rights can be transacted as intangible property after the verified procedures of strict registrations, supervisions ...
... mechanism. Carbon trading can be classified into two sorts. One is JI and CDM which are both based on the projects, the other is IET on the basis of distributed quotas. Carbon emission rights can be transacted as intangible property after the verified procedures of strict registrations, supervisions ...
Carbon Tax: International Experiences and Inspirations
... predicts that 2/3-3/4 of the growth of the global GHG emission comes from the developing countries, in which also the main potential of emission reduction lies, so the sooner we take measures, the more economically feasible it is[1]. According to the forecasts of the International Energy Agency (IEA ...
... predicts that 2/3-3/4 of the growth of the global GHG emission comes from the developing countries, in which also the main potential of emission reduction lies, so the sooner we take measures, the more economically feasible it is[1]. According to the forecasts of the International Energy Agency (IEA ...
6430483991 - PastPapers.Co
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
... There are forty questions on this paper. Answer all questions. For each question there are four possible answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each corre ...
2013 Human Impact
... to control destructive insects minimizes pesticide use as well as crop damage ...
... to control destructive insects minimizes pesticide use as well as crop damage ...
Review Sheet Key - Spring Branch ISD
... Pyruvic Acid ADP ATP NADH Carbon dioxide NADH ATP FAHD2 Citric Acid Water NAD+ FAD ATP Ethyl Alcohol Carbon dioxide NAD+ ...
... Pyruvic Acid ADP ATP NADH Carbon dioxide NADH ATP FAHD2 Citric Acid Water NAD+ FAD ATP Ethyl Alcohol Carbon dioxide NAD+ ...
Influence of Climate and Land Use Change on Carbon in Agriculture
... total a NPP is 5.1 Mg ha−1 yr−1, comprising 3.4 Mg ha−1 yr−1 for aboveground and 1.7 Mg ha−1 yr−1 for belowground components. In comparison, marshes and swamps have higher total NPP (Table 4–4). Joosten and Clarke (2002) reported that pristine fens presently remove 2.5 Mg ha−1 yr−1 (as CO2) and rele ...
... total a NPP is 5.1 Mg ha−1 yr−1, comprising 3.4 Mg ha−1 yr−1 for aboveground and 1.7 Mg ha−1 yr−1 for belowground components. In comparison, marshes and swamps have higher total NPP (Table 4–4). Joosten and Clarke (2002) reported that pristine fens presently remove 2.5 Mg ha−1 yr−1 (as CO2) and rele ...
Biosequestration

Biosequestration is the capture and storage of the atmospheric greenhouse gas carbon dioxide by biological processes.This may be by increased photosynthesis (through practices such as reforestation / preventing deforestation and genetic engineering); by enhanced soil carbon trapping in agriculture; or by the use of algal bio sequestration (see algae bioreactor) to absorb the carbon dioxide emissions from coal, petroleum (oil) or natural gas-fired electricity generation.Biosequestration as a natural process has occurred in the past, and was responsible for the formation of the extensive coal and oil deposits which are now being burned. It is a key policy concept in the climate change mitigation debate. It does not generally refer to the sequestering of carbon dioxide in oceans (see carbon sequestration and ocean acidification) or rock formations, depleted oil or gas reservoirs (see oil depletion and peak oil), deep saline aquifers, or deep coal seams (see coal mining) (for all see geosequestration) or through the use of industrial chemical carbon dioxide scrubbing.