Torque and Motion Relationships
... What is radius of gyration (k)? An indicator of distribution of mass about the axis. It is the distance from the axis to a point at which all the mass of a system of equal mass would be concentrated to have the MOI equal the original system. It is, then, the average weighted distance of the mass of ...
... What is radius of gyration (k)? An indicator of distribution of mass about the axis. It is the distance from the axis to a point at which all the mass of a system of equal mass would be concentrated to have the MOI equal the original system. It is, then, the average weighted distance of the mass of ...
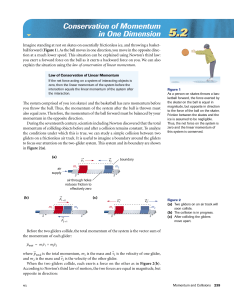
The Law of Momentum Conservation
... That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2. In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. ...
... That is, the momentum lost by object 1 is equal to the momentum gained by object 2. In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. ...
Sub-Planckian black holes and the Generalized Uncertainty Principle
... holes. Such a scenario has the following three properties: ...
... holes. Such a scenario has the following three properties: ...
Slide 1
... System of Particles; General Motion The angular momentum of a system of particles can change only if there is an external torque—torques due to internal forces cancel. ...
... System of Particles; General Motion The angular momentum of a system of particles can change only if there is an external torque—torques due to internal forces cancel. ...
Impulse and Momentum AP Physics 1 packet answers
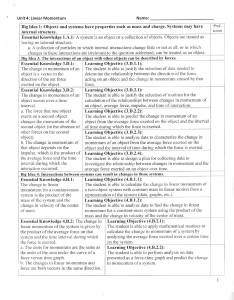
... the match between the prediction and the outcome. a. In a closed system, the linear momentum is Lea,'ning Objective (5.D.2.4): constant throughout the The student is able to analyze data that veri fy conservation of momentum in collisions with and without an cxternal friction force. collision. Learn ...
... the match between the prediction and the outcome. a. In a closed system, the linear momentum is Lea,'ning Objective (5.D.2.4): constant throughout the The student is able to analyze data that veri fy conservation of momentum in collisions with and without an cxternal friction force. collision. Learn ...
Quantum Field Theory, its Concepts Viewed from a Semiotic
... converted into its energy equivalent ∆E = mc2 or vice versa. Hence, definite configurations of particles exist only asymptotically in time before and after a process of collision, when the particles are well separated and mutually non-interacting, due to the short range of their interaction. Because ...
... converted into its energy equivalent ∆E = mc2 or vice versa. Hence, definite configurations of particles exist only asymptotically in time before and after a process of collision, when the particles are well separated and mutually non-interacting, due to the short range of their interaction. Because ...
Student Text, pp. 239-245
... An important application of conservation of momentum is rocket propulsion, both on Earth and in the “vacuum” of outer space. As the rocket thruster exerts an action force on the hot gases ejected backward, the gases exert a reaction force equal in magnitude on the spacecraft, causing it to accelerat ...
... An important application of conservation of momentum is rocket propulsion, both on Earth and in the “vacuum” of outer space. As the rocket thruster exerts an action force on the hot gases ejected backward, the gases exert a reaction force equal in magnitude on the spacecraft, causing it to accelerat ...
Use example problem 9-3 to solve practice problems 9-3
... Suppose you place several sugar cubes in a box and close it. We can call the box and the sugar in it a system, a defined collection of objects. Shake the box hard for several minutes. When you open it, you find that the shapes of the cubes have changed. In addition, there are sugar grains in the box ...
... Suppose you place several sugar cubes in a box and close it. We can call the box and the sugar in it a system, a defined collection of objects. Shake the box hard for several minutes. When you open it, you find that the shapes of the cubes have changed. In addition, there are sugar grains in the box ...
Chapter 11 PPT
... At any instant of time, the sphere and the block have a common velocity v Write expressions for the total angular momentum and the net external torque ...
... At any instant of time, the sphere and the block have a common velocity v Write expressions for the total angular momentum and the net external torque ...
angular momentum
... B. The total kine3c energy of the rod and bullet a:er the bullet is embedded is the same as the ini3al kine3c energy of the bullet. 1. A only 2. B only 3. both A and B 4. There is not enough informa3on to determine. ...
... B. The total kine3c energy of the rod and bullet a:er the bullet is embedded is the same as the ini3al kine3c energy of the bullet. 1. A only 2. B only 3. both A and B 4. There is not enough informa3on to determine. ...
6th Grade - Northern Highlands
... Inelastic Collisions In an inelastic collision objects change shape or stick together. (An egg dropped on the floor) ...
... Inelastic Collisions In an inelastic collision objects change shape or stick together. (An egg dropped on the floor) ...