Florida Coastal Ocean Observing System (FL COOS Caucus)
... Many Floridians of diverse ocean-related backgrounds (including academic, government, NGO and private industry) have expressed interest in the development, implementation and use of a comprehensive and integrated Coastal Ocean Observing System (COOS). A venue was needed for discussions between membe ...
... Many Floridians of diverse ocean-related backgrounds (including academic, government, NGO and private industry) have expressed interest in the development, implementation and use of a comprehensive and integrated Coastal Ocean Observing System (COOS). A venue was needed for discussions between membe ...
Tectonic Plates &
... ocean. Weathering also releases soluble constituents, such as calcium and sodium that dissolve in water and are transported in solution to the ocean. Image of two deltas being formed by Mississippi River Sediments that accumulate on the sea floor differ in source, composition, size and the rate at w ...
... ocean. Weathering also releases soluble constituents, such as calcium and sodium that dissolve in water and are transported in solution to the ocean. Image of two deltas being formed by Mississippi River Sediments that accumulate on the sea floor differ in source, composition, size and the rate at w ...
Report of the IOC/FAO/ UNEP International Workshop on
... High temperature processes (volcanism, combustion of fossil fuels and production of cement in particular) contribute the more volatile metals to The particles settle small particles. the atmosphere, either as gase, ...
... High temperature processes (volcanism, combustion of fossil fuels and production of cement in particular) contribute the more volatile metals to The particles settle small particles. the atmosphere, either as gase, ...
Report of the 2011 Scientific Steering Committee Meeting
... (ToRs) until that work is completed. A total of 12 potential contributions plus a synthesis paper have been identified for the MEPS special theme section. The deadline for manuscript submissions was set as 1 November 2011. The WG will continue to complete the papers for the MEPS special issue, and w ...
... (ToRs) until that work is completed. A total of 12 potential contributions plus a synthesis paper have been identified for the MEPS special theme section. The deadline for manuscript submissions was set as 1 November 2011. The WG will continue to complete the papers for the MEPS special issue, and w ...
marine benthic populations in antarctica
... Sampling difficulties have meant that there have been more studies of population patterns than of processes in Antarctic benthos, but a number of generalizations can be made. Benthic marine invenebrates in Antarctica have species/abundance relationships similar to those found in temperate or tropica ...
... Sampling difficulties have meant that there have been more studies of population patterns than of processes in Antarctic benthos, but a number of generalizations can be made. Benthic marine invenebrates in Antarctica have species/abundance relationships similar to those found in temperate or tropica ...
Coral reefs in crisis
... Coral reefs are calcium carbonate structures, made up of reef-building stony corals. Coral grows only as deep as light penetrates, so reefs occur in shallow water up to 60 metres. This dependence on light also means reefs are only found where the surrounding waters contain relatively small amounts o ...
... Coral reefs are calcium carbonate structures, made up of reef-building stony corals. Coral grows only as deep as light penetrates, so reefs occur in shallow water up to 60 metres. This dependence on light also means reefs are only found where the surrounding waters contain relatively small amounts o ...
Chapter 14. Biogenic and authigenic sediment
... (5) Once buried, they cease to grow, but don't dissolve as long as pore waters remain oxic. Shapes i. Spherical to subspherical nodules and micronudules ii. Pavements rather than nodules of MnO2 form in some areas, especially areas swept by bottom currents. Mystery of nodules - not how they grow, bu ...
... (5) Once buried, they cease to grow, but don't dissolve as long as pore waters remain oxic. Shapes i. Spherical to subspherical nodules and micronudules ii. Pavements rather than nodules of MnO2 form in some areas, especially areas swept by bottom currents. Mystery of nodules - not how they grow, bu ...
Elana McDermott Final Paper Global Coral Reefs: Concerns
... The preservation of our natural resources has taken high national and global importance during the last few decades. Our world and resources are easily impacted by human interactions. While scientific research continues to produce new methods for conserving our national resources, many global ecosys ...
... The preservation of our natural resources has taken high national and global importance during the last few decades. Our world and resources are easily impacted by human interactions. While scientific research continues to produce new methods for conserving our national resources, many global ecosys ...
1: Introduction
... controlled drilling in up to 13,000 feet water depths and up to 20,000 feet below the sea floor. ...
... controlled drilling in up to 13,000 feet water depths and up to 20,000 feet below the sea floor. ...
Harmful Algal Blooms in Southern Californian Waters
... food webs, a few are capable of producing substances that are noxious or toxic, resulting in illness and even death of marine life and occasionally humans who consume contaminated seafood. When microalgae create these conditions, we refer to them as harmful algal blooms (HABs). An older term often u ...
... food webs, a few are capable of producing substances that are noxious or toxic, resulting in illness and even death of marine life and occasionally humans who consume contaminated seafood. When microalgae create these conditions, we refer to them as harmful algal blooms (HABs). An older term often u ...
Sixth Grade Pacing Guide
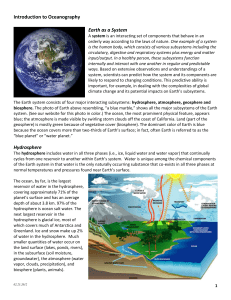
... The ocean is connected to major lakes, watersheds, and waterways because all major watersheds on Earth drain to the ocean Most rain that falls on land evaporated from the tropical ocean; Ocean absorbs solar radiation that reaches Earth; Ocean loses heat by evaporation which is released as wa ...
... The ocean is connected to major lakes, watersheds, and waterways because all major watersheds on Earth drain to the ocean Most rain that falls on land evaporated from the tropical ocean; Ocean absorbs solar radiation that reaches Earth; Ocean loses heat by evaporation which is released as wa ...
2011 Annual Report
... closely reflects the mean carbon-14 in the atmosphere whereas the Florida record shows more evidence of mixing with deeper low-radiocarbon waters. The WHOI NOSAMS laboratory produces data with very small errors, allowing us to resolve very small changes in surface radiocarbon, that might be signific ...
... closely reflects the mean carbon-14 in the atmosphere whereas the Florida record shows more evidence of mixing with deeper low-radiocarbon waters. The WHOI NOSAMS laboratory produces data with very small errors, allowing us to resolve very small changes in surface radiocarbon, that might be signific ...
Chapter 36 F Open Ocean Deep Sea
... source of bacterial diversity and genetic innovation (Sogin et al., 2006). Several faunal groups also exhibit latitudinal gradients in species diversity (Narayanaswamy et al., 2010; Rex and Etter, 2010; Yasuhara et al., 2009): diversity of crustaceans, molluscs and foraminifera declines poleward (Ga ...
... source of bacterial diversity and genetic innovation (Sogin et al., 2006). Several faunal groups also exhibit latitudinal gradients in species diversity (Narayanaswamy et al., 2010; Rex and Etter, 2010; Yasuhara et al., 2009): diversity of crustaceans, molluscs and foraminifera declines poleward (Ga ...
hydrothermal vents and chemosynthesis
... 360°C (680°F)! Yet this water does not boil because it is under so much pressure from the tremendous weight of the ocean above. Hydrothermal vents are so deep that light is unable to penetrate. Without light, plants, algae (seaweed) and phytoplankton are unable to perform the process of photosynthes ...
... 360°C (680°F)! Yet this water does not boil because it is under so much pressure from the tremendous weight of the ocean above. Hydrothermal vents are so deep that light is unable to penetrate. Without light, plants, algae (seaweed) and phytoplankton are unable to perform the process of photosynthes ...
Coastal and Ocean Observing Supports People Who Live, Work
... Understanding Impacts to Marine Ecosystems Understanding the connectivity between the ocean environment and upland ecosystems is critical for monitoring water quality and understanding impacts to marine ecosystems such as coral reefs. Remotely sensed ocean color products provide a mechanism to unde ...
... Understanding Impacts to Marine Ecosystems Understanding the connectivity between the ocean environment and upland ecosystems is critical for monitoring water quality and understanding impacts to marine ecosystems such as coral reefs. Remotely sensed ocean color products provide a mechanism to unde ...
Carbonate Chemistry of the Oceans
... At high latitudes, however, especially in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica, large amounts of nutrients remain in the water all year round because of a limited amount of iron. If they were taken up, then the pCO2 in the ocean, and subsequently the pCO2 in the atmosphere, could be drawn down furth ...
... At high latitudes, however, especially in the Southern Ocean around Antarctica, large amounts of nutrients remain in the water all year round because of a limited amount of iron. If they were taken up, then the pCO2 in the ocean, and subsequently the pCO2 in the atmosphere, could be drawn down furth ...
22 June 2007
... A scoping paper is the second step, following on from a short proposal, in the GESAMP New and Emerging Issues process and should cover: the need for, the scale and the feasibility of assessing the issue, as well as identify expert communities and potential sources of funding. The purpose of this doc ...
... A scoping paper is the second step, following on from a short proposal, in the GESAMP New and Emerging Issues process and should cover: the need for, the scale and the feasibility of assessing the issue, as well as identify expert communities and potential sources of funding. The purpose of this doc ...
Oceans_I - Geophile.net
... Average 65-100 km in width Formed by: • Thick accumulations of shallow-water sediments • Some areas are mantled by extensive glacial ...
... Average 65-100 km in width Formed by: • Thick accumulations of shallow-water sediments • Some areas are mantled by extensive glacial ...
Zipangu in the Ocean Program Tetsuro Urabe
... to a variety of unique life forms, including microorganisms that live on chemosynthesis, surviving without oxygen near hydrothermal vents spouting water at more than 300°C. We need more investigation to know the complex interaction existing between hydrothermal ecosystems and surrounding deep sea ec ...
... to a variety of unique life forms, including microorganisms that live on chemosynthesis, surviving without oxygen near hydrothermal vents spouting water at more than 300°C. We need more investigation to know the complex interaction existing between hydrothermal ecosystems and surrounding deep sea ec ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.