1. Progress in Understanding c. Calculations of Ocean Circulation
... The inflow from rivers were not considered . Because of the coarse grid system, this estimation of the concentration in seawater and the internal exposure from marine products is valid not in coastal sea but in open ocean. ...
... The inflow from rivers were not considered . Because of the coarse grid system, this estimation of the concentration in seawater and the internal exposure from marine products is valid not in coastal sea but in open ocean. ...
Governance of marine biodiversity beyond national jurisdictions
... more systematically towards the protection of high seas areas, especially by establishing marine protected areas. 5. A global debate is on going Although a decisive effort must be made towards the effective application and consolidation of existing tools, at both the global and regional scales, this ...
... more systematically towards the protection of high seas areas, especially by establishing marine protected areas. 5. A global debate is on going Although a decisive effort must be made towards the effective application and consolidation of existing tools, at both the global and regional scales, this ...
Sea-Floor Spreading
... • Deep ocean trenches are swallowing more oceanic crust than the mid-ocean ridge can produce. Thus, the width of the Pacific will shrink. • The Atlantic is expanding. It has short trenches. In some places, the oceanic crust is attached to the continental crust which moves the continents. ...
... • Deep ocean trenches are swallowing more oceanic crust than the mid-ocean ridge can produce. Thus, the width of the Pacific will shrink. • The Atlantic is expanding. It has short trenches. In some places, the oceanic crust is attached to the continental crust which moves the continents. ...
1. Progress in Understanding c. Calculations of Ocean Circulation
... The inflow from rivers were not considered . Because of the coarse grid system, this estimation of the concentration in seawater and the internal exposure from marine products is valid not in coastal sea but in open ocean. ...
... The inflow from rivers were not considered . Because of the coarse grid system, this estimation of the concentration in seawater and the internal exposure from marine products is valid not in coastal sea but in open ocean. ...
Chapter 2
... 1) Landforms- The shore line of South America would fit with the Africa shore. Mnts. In South Africa line up wit Mnts is Argentina. Coal fields in Brazil match with coal fields in Africa. 2) Fern-like fossils have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, India, Antarctica 3) Continents were e ...
... 1) Landforms- The shore line of South America would fit with the Africa shore. Mnts. In South Africa line up wit Mnts is Argentina. Coal fields in Brazil match with coal fields in Africa. 2) Fern-like fossils have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, India, Antarctica 3) Continents were e ...
274 - CIESM
... presence of healthy photosynthetic active diatoms across the global oligotrophic ocean at bathypelagic depths down to 4000 m [1]. Their vertical transportation rate is estimated to 124 - 724 m/day, i.e. time of few days to few weeks to reach the depths of the dark ocean [1]. A range of biological me ...
... presence of healthy photosynthetic active diatoms across the global oligotrophic ocean at bathypelagic depths down to 4000 m [1]. Their vertical transportation rate is estimated to 124 - 724 m/day, i.e. time of few days to few weeks to reach the depths of the dark ocean [1]. A range of biological me ...
Geology Chapter 14
... Michael Wysession Washington University Big Ideas Seventy-one percent of Earth's surface is covered by ocean water. There are four main ocean basins: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. The bathymetry of the ocean seafloor is very varied, a result of many different geological processes. Space ...
... Michael Wysession Washington University Big Ideas Seventy-one percent of Earth's surface is covered by ocean water. There are four main ocean basins: the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, and Arctic. The bathymetry of the ocean seafloor is very varied, a result of many different geological processes. Space ...
The Structure and Origin of the Ocean Basins The water Planet
... edge of the continent. It extends from roughly 10 km to over 300 km from the strand line. Though they make up only about 8% of the ocean’s surface area, continental shelves are the biologically richest part of the ocean, with the most life and the best fishing. The continental shelf ends at the shel ...
... edge of the continent. It extends from roughly 10 km to over 300 km from the strand line. Though they make up only about 8% of the ocean’s surface area, continental shelves are the biologically richest part of the ocean, with the most life and the best fishing. The continental shelf ends at the shel ...
Marine environmental monitoring programmes in South Africa: a
... same time of year (Fig. 4). Data are used to explain unusual distributions, fish condition or feeding behaviour, to attempt to predict future trends in recruitment or to determine ecosystem effects.4–8 Similarly for demersal surveys, environmental data such as light levels, turbidity, oxygen and tem ...
... same time of year (Fig. 4). Data are used to explain unusual distributions, fish condition or feeding behaviour, to attempt to predict future trends in recruitment or to determine ecosystem effects.4–8 Similarly for demersal surveys, environmental data such as light levels, turbidity, oxygen and tem ...
Marine wildlife of WA`s north
... seagrass, usually in quite shallow water one to five metres deep, but are known to feed on seagrass at depths of over 20 metres. They are the only herbivorous marine mammals. Their movement over an area can be followed by the sand cloud made as they move along the seafloor. Their movements are usual ...
... seagrass, usually in quite shallow water one to five metres deep, but are known to feed on seagrass at depths of over 20 metres. They are the only herbivorous marine mammals. Their movement over an area can be followed by the sand cloud made as they move along the seafloor. Their movements are usual ...
Bio-logging of Marine Migratory Species In Law of the Sea by Kraska, Crespo Johnston
... that can be attached to marine animals in order to collect scientific data and transmit it remotely, often by satellite or other wireless technologies [3]. Data collected through these techniques generally includes information on the behavior and activities of tagged animals such as diving behavior, ...
... that can be attached to marine animals in order to collect scientific data and transmit it remotely, often by satellite or other wireless technologies [3]. Data collected through these techniques generally includes information on the behavior and activities of tagged animals such as diving behavior, ...
chapt07 discussion
... near intestines of host or other tissues • Larval stages may be harbored in snails, clams, or fish. These are eaten by other vertebrates like larger fish, seabirds, and marine mammals where they grow to adulthood. ...
... near intestines of host or other tissues • Larval stages may be harbored in snails, clams, or fish. These are eaten by other vertebrates like larger fish, seabirds, and marine mammals where they grow to adulthood. ...
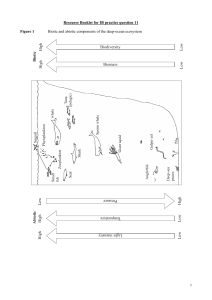
Resource Booklet for IB practice question 11
... The habitat is a predominately dark and cold environment with much lower productivity than shallower waters. No light penetrates beyond 1000 m and even at depths of 150 m light levels are reduced to 1 % of those at the surface and are insufficient to support photosynthesis. Therefore, organic materi ...
... The habitat is a predominately dark and cold environment with much lower productivity than shallower waters. No light penetrates beyond 1000 m and even at depths of 150 m light levels are reduced to 1 % of those at the surface and are insufficient to support photosynthesis. Therefore, organic materi ...
Ocean Web Quest Task Sheet PLEASE REMEMBER TO WRITE IN
... FOR FILL-IN THE BLANK QUESTIONS. http://www.mos.org/oceans/motion/wind.html 1. The size of a wave depends on It depends on how far, how fast, or how long the wind blows. 2. Waves travel through water, they do not take the water with them. http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/ocean/Waves.shtml 3 ...
... FOR FILL-IN THE BLANK QUESTIONS. http://www.mos.org/oceans/motion/wind.html 1. The size of a wave depends on It depends on how far, how fast, or how long the wind blows. 2. Waves travel through water, they do not take the water with them. http://www.enchantedlearning.com/subjects/ocean/Waves.shtml 3 ...
BC Science 8 - Chapter 11
... Oceans control Earth’s temperature, create weather patterns, and are the source of the water that falls as fresh water on land, supporting all life forms. ...
... Oceans control Earth’s temperature, create weather patterns, and are the source of the water that falls as fresh water on land, supporting all life forms. ...
Hydrothermal Vents
... times a day. It spouts a column of water heated by volcanic rock deep within the Earth's crust. A hydrothermal vent is a geyser on the seafloor. It continuously spews super-hot, mineral-rich water that helps support a diverse community of organisms. Although most of the deep sea is sparsely populate ...
... times a day. It spouts a column of water heated by volcanic rock deep within the Earth's crust. A hydrothermal vent is a geyser on the seafloor. It continuously spews super-hot, mineral-rich water that helps support a diverse community of organisms. Although most of the deep sea is sparsely populate ...
Exploitation of sea-based resources and acidification
... increasing concern over the past 15 years. Raw material resources are acquired through a relatively new process called deep sea mining, which occurs on the ocean floor. Deep sea mining takes place over 1400m below the ocean’s surface and usually around areas of polymetallic nodules and on areas of a ...
... increasing concern over the past 15 years. Raw material resources are acquired through a relatively new process called deep sea mining, which occurs on the ocean floor. Deep sea mining takes place over 1400m below the ocean’s surface and usually around areas of polymetallic nodules and on areas of a ...
Climate Change and the Occurrence of Harmful
... temperatures and stimulates increased occurrence of toxic and pathogenic microorganisms, it could threaten fish, marine life, shellfish, and human health. A worst-case scenario is one where in the future, swimming at our beaches becomes more regularly associated with respiratory irritation; our coas ...
... temperatures and stimulates increased occurrence of toxic and pathogenic microorganisms, it could threaten fish, marine life, shellfish, and human health. A worst-case scenario is one where in the future, swimming at our beaches becomes more regularly associated with respiratory irritation; our coas ...
bio 30 marine biology lecture manual
... distinguish between different types of multicellular seaweeds. list reasons to study marine algae. define photosynthesis. name the characteristics of the major marine invertebrate and vertebrate phyla. infer fish habitat from fish form. diagram the countercurrent system of flow in the gills of fishe ...
... distinguish between different types of multicellular seaweeds. list reasons to study marine algae. define photosynthesis. name the characteristics of the major marine invertebrate and vertebrate phyla. infer fish habitat from fish form. diagram the countercurrent system of flow in the gills of fishe ...
bio 30 marine biology lecture manual
... distinguish between different types of multicellular seaweeds. list reasons to study marine algae. define photosynthesis. name the characteristics of the major marine invertebrate and vertebrate phyla. infer fish habitat from fish form. diagram the countercurrent system of flow in the gills of fishe ...
... distinguish between different types of multicellular seaweeds. list reasons to study marine algae. define photosynthesis. name the characteristics of the major marine invertebrate and vertebrate phyla. infer fish habitat from fish form. diagram the countercurrent system of flow in the gills of fishe ...
EXPLORE AN OCEAN`S FLOOR
... meters (13,000 feet). The Pacific Ocean is deeper than the Atlantic Ocean, with the Marianas Trench in the South Pacific being the deepest area. An underwater vessel, the Trieste, went down 10,900 meters (35,800 feet) or about 11 kilometers (7 miles) to explore the bottom of the trench. If you could ...
... meters (13,000 feet). The Pacific Ocean is deeper than the Atlantic Ocean, with the Marianas Trench in the South Pacific being the deepest area. An underwater vessel, the Trieste, went down 10,900 meters (35,800 feet) or about 11 kilometers (7 miles) to explore the bottom of the trench. If you could ...
Ocean Currents
... Surface Currents – upper 10% of the ocean; upper 400 m Pycnocline – the layer between surface and deep waters; where a rapid change in salinity and density occur Thermocline-the layer of ocean water where there is a rapid change in temperature Deep Current – lower 90% of the ocean ...
... Surface Currents – upper 10% of the ocean; upper 400 m Pycnocline – the layer between surface and deep waters; where a rapid change in salinity and density occur Thermocline-the layer of ocean water where there is a rapid change in temperature Deep Current – lower 90% of the ocean ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.