What is Mathematical Modeling? - SERC
... teachers they will need in the fall. •It is how you calculate how much money you must save each month to retire at 55 as a millionaire (or not have to work two jobs in the summer). One type of mathematical modeling looks for ways to describe trends in data using a least squares or linear regression ...
... teachers they will need in the fall. •It is how you calculate how much money you must save each month to retire at 55 as a millionaire (or not have to work two jobs in the summer). One type of mathematical modeling looks for ways to describe trends in data using a least squares or linear regression ...
+ Inference for Linear Regression
... Linear The scatterplot shows a clear linear form. For each drop height used in the experiment, the residuals are centered on the horizontal line at 0. The residual plot shows a random scatter about the horizontal line. Independent Because the helicopters were released in a random order and no he ...
... Linear The scatterplot shows a clear linear form. For each drop height used in the experiment, the residuals are centered on the horizontal line at 0. The residual plot shows a random scatter about the horizontal line. Independent Because the helicopters were released in a random order and no he ...
Spatial Statistics - The University of Texas at Dallas
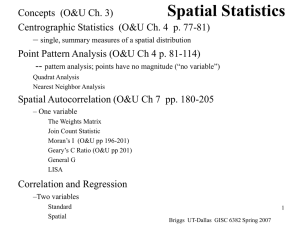
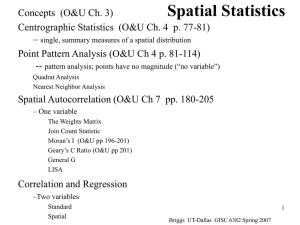
... • Point interaction approach using Nearest Neighbor Analysis based on distances of points one from another Although the above would suggest that the first approach examines first order effects and the second approach examines second order effects, in practice the two cannot be separated. ...
... • Point interaction approach using Nearest Neighbor Analysis based on distances of points one from another Although the above would suggest that the first approach examines first order effects and the second approach examines second order effects, in practice the two cannot be separated. ...
Simple Linear Regression - Computer Science Department
... Estimation of a simple linear regression relationship involves finding estimated or predicted values of the intercept and slope of the linear regression line. The estimated regression equation: y= a+ bx + e where a estimates the intercept of the population regression line, a ; b estimates the slope ...
... Estimation of a simple linear regression relationship involves finding estimated or predicted values of the intercept and slope of the linear regression line. The estimated regression equation: y= a+ bx + e where a estimates the intercept of the population regression line, a ; b estimates the slope ...
No Slide Title
... Copyright Christopher Dougherty 2011. These slideshows may be downloaded by anyone, anywhere for personal use. Subject to respect for copyright and, where appropriate, attribution, they may be used as a resource for teaching an econometrics course. There is no need to refer to the author. The conte ...
... Copyright Christopher Dougherty 2011. These slideshows may be downloaded by anyone, anywhere for personal use. Subject to respect for copyright and, where appropriate, attribution, they may be used as a resource for teaching an econometrics course. There is no need to refer to the author. The conte ...
Practical Statistical Questions
... Which of the following sentences is descriptive and which is inferential: 1. 80% of THESE people of Luserna has Nicolussi as last name. 2. 80% of THE people of ITALY has Nicolussi as last name. On the last 3 Sundays, Henry D. Carsalesman sold 2, 1, and 0 new cars respectively. Which of the following ...
... Which of the following sentences is descriptive and which is inferential: 1. 80% of THESE people of Luserna has Nicolussi as last name. 2. 80% of THE people of ITALY has Nicolussi as last name. On the last 3 Sundays, Henry D. Carsalesman sold 2, 1, and 0 new cars respectively. Which of the following ...
Coefficient of determination
In statistics, the coefficient of determination, denoted R2 or r2 and pronounced R squared, is a number that indicates how well data fit a statistical model – sometimes simply a line or a curve. An R2 of 1 indicates that the regression line perfectly fits the data, while an R2 of 0 indicates that the line does not fit the data at all. This latter can be because the data is utterly non-linear, or because it is random.It is a statistic used in the context of statistical models whose main purpose is either the prediction of future outcomes or the testing of hypotheses, on the basis of other related information. It provides a measure of how well observed outcomes are replicated by the model, as the proportion of total variation of outcomes explained by the model (pp. 187, 287).There are several definitions of R2 that are only sometimes equivalent. One class of such cases includes that of simple linear regression where r2 is used instead of R2. In this case, if an intercept is included, then r2 is simply the square of the sample correlation coefficient (i.e., r) between the outcomes and their predicted values. If additional explanators are included, R2 is the square of the coefficient of multiple correlation. In both such cases, the coefficient of determination ranges from 0 to 1.Important cases where the computational definition of R2 can yield negative values, depending on the definition used, arise where the predictions that are being compared to the corresponding outcomes have not been derived from a model-fitting procedure using those data, and where linear regression is conducted without including an intercept. Additionally, negative values of R2 may occur when fitting non-linear functions to data. In cases where negative values arise, the mean of the data provides a better fit to the outcomes than do the fitted function values, according to this particular criterion.