PDF
... above square root. Instead of R we may use the discriminant D := −108R of the equation. As in examining the number of real roots of a quadratic equation, we get three different cases also for the cubic (1): 1. D = 0. This is possible only p when either p < p 0 or p = q = 0. Then we get the real root ...
... above square root. Instead of R we may use the discriminant D := −108R of the equation. As in examining the number of real roots of a quadratic equation, we get three different cases also for the cubic (1): 1. D = 0. This is possible only p when either p < p 0 or p = q = 0. Then we get the real root ...
x - Greater Nanticoke Area School District
... 10. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers. CS 2.2.11B. Use estimation to solve problems. 11. Create a mental model to predict a possible answer. 12. Use computation to validate the estimate. CS 2.2.11C. Construct and apply math models using estimation. 13. Interpret data and make predicti ...
... 10. Add, subtract, multiply, and divide real numbers. CS 2.2.11B. Use estimation to solve problems. 11. Create a mental model to predict a possible answer. 12. Use computation to validate the estimate. CS 2.2.11C. Construct and apply math models using estimation. 13. Interpret data and make predicti ...
Extra Practice = Bonus Points
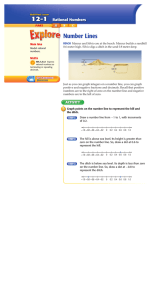
... Then… Line up numbers to see both GCF and LCM. Example: 60 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 72 = 2 x 2 x 3 x _ x 2 x 3 GCF uses the columns that have two numbers in it: (2 x 2 x 3) = 12 LCM uses any column that has a number in it: (2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 2 x 3) = 360 ...
... Then… Line up numbers to see both GCF and LCM. Example: 60 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 5 72 = 2 x 2 x 3 x _ x 2 x 3 GCF uses the columns that have two numbers in it: (2 x 2 x 3) = 12 LCM uses any column that has a number in it: (2 x 2 x 3 x 5 x 2 x 3) = 360 ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.