Section 4.1 - Montgomery College
... 2. Each variable or constant appears as a base as few times as possible. For example, we write x2x4 = x6 3. Each numerical expression (such as 72) has been calculated, and each numerical fraction has been ...
... 2. Each variable or constant appears as a base as few times as possible. For example, we write x2x4 = x6 3. Each numerical expression (such as 72) has been calculated, and each numerical fraction has been ...
Aalborg Universitet Impedance relay
... In order to implement the proposed wide area protection strategy based on the improved relay algorithms, multi agent system (MAS) based structure is adopted, as shown in Figure 4. A three-level control structure is adopted in this MAS based control system, which is comprised of distributed agent lev ...
... In order to implement the proposed wide area protection strategy based on the improved relay algorithms, multi agent system (MAS) based structure is adopted, as shown in Figure 4. A three-level control structure is adopted in this MAS based control system, which is comprised of distributed agent lev ...
QUANTUM – TYPE AND CONTINUOUS COMPRESSIONS Author:I. Szalay
... x c is called the c –compressed of x and R c is called the c- compressed of the real number line. If S R then the set S c x c R c : x S is called the c – compressed of S. The inverse of compressor ...
... x c is called the c –compressed of x and R c is called the c- compressed of the real number line. If S R then the set S c x c R c : x S is called the c – compressed of S. The inverse of compressor ...
Applied Science 174: Linear Algebra Lecture Notes
... It is strongly recommended that you read these lecture notes carefully as a complement to the classroom lectures. Almost every lecture in these notes contains examples which have been worked out in detail. It is strongly recommended that you examine those in detail, and it is equally strongly recomm ...
... It is strongly recommended that you read these lecture notes carefully as a complement to the classroom lectures. Almost every lecture in these notes contains examples which have been worked out in detail. It is strongly recommended that you examine those in detail, and it is equally strongly recomm ...
Solving Quadratic Equations Notes Part Two
... real-world problems can be found my modeling them with quadratic equations and graphs. Systems of equations may be solved using graphs, tables, eliminations or substitution. The solution to a linear and quadratic system, if it exists, is an ordered pair or two ordered pairs. ...
... real-world problems can be found my modeling them with quadratic equations and graphs. Systems of equations may be solved using graphs, tables, eliminations or substitution. The solution to a linear and quadratic system, if it exists, is an ordered pair or two ordered pairs. ...
Student Notes - 3.1, 3.2
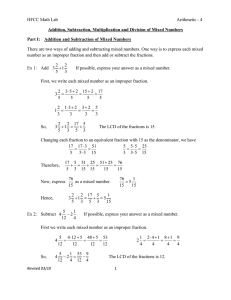
... Given two or more numbers, the Least Common Multiple (it is often called LCM for short) is the smallest number that all of given numbers will evenly divide INTO. The LCM will always be bigger than or the same size as your given numbers – NEVER smaller! Ex: The LCM of 8, 6 and 4 is 24 because it is t ...
... Given two or more numbers, the Least Common Multiple (it is often called LCM for short) is the smallest number that all of given numbers will evenly divide INTO. The LCM will always be bigger than or the same size as your given numbers – NEVER smaller! Ex: The LCM of 8, 6 and 4 is 24 because it is t ...
Revision for II Unit Test [50 mks] If a sum of money becomes 915 Rs
... 21.A ladder 15m long reaches a window which is 9m above the ground on one side of the street, keeping its foot at the same point , the ladder is turned to the other side of the street to reach a window 12m high. Find the width of the road. [ans : 9 +12 = 21] 22.Two poles 18m and 13m high stand uprig ...
... 21.A ladder 15m long reaches a window which is 9m above the ground on one side of the street, keeping its foot at the same point , the ladder is turned to the other side of the street to reach a window 12m high. Find the width of the road. [ans : 9 +12 = 21] 22.Two poles 18m and 13m high stand uprig ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.


















![Revision for II Unit Test [50 mks] If a sum of money becomes 915 Rs](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009650893_1-a9f3d513ea66f8c3e6d116ea9e98c814-300x300.png)