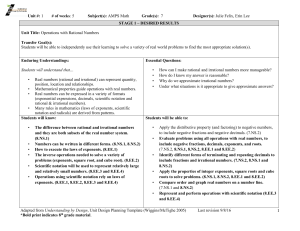
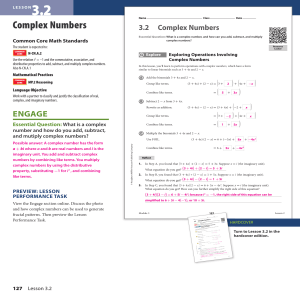
Important Radical Information
... ODD ROOTS: Every real number has just one real odd root (index is odd): odd roots of positive numbers are positive and odd roots of negative numbers are negative. EX: 5 32 = 2 and 5 32 2 . It’s not a problem to have a negative radicand with an odd root. EVEN ROOTS: Every positive real number ha ...
... ODD ROOTS: Every real number has just one real odd root (index is odd): odd roots of positive numbers are positive and odd roots of negative numbers are negative. EX: 5 32 = 2 and 5 32 2 . It’s not a problem to have a negative radicand with an odd root. EVEN ROOTS: Every positive real number ha ...
Self-Paced Study Guide in Algebra March 31, 2011 1
... The Review Modules are designed to introduce the core material for each topic area. A numbering system facilitates easy tracking of subject material. For example, in Algebra, the subtopic Linear Equations is numbered with 2.3. Problems and the self-evaluations are categorized using this numbering sy ...
... The Review Modules are designed to introduce the core material for each topic area. A numbering system facilitates easy tracking of subject material. For example, in Algebra, the subtopic Linear Equations is numbered with 2.3. Problems and the self-evaluations are categorized using this numbering sy ...
Addition concept and implications
... We can use the same general strategy for comparing two or three (or more) common fractions or decimal fractions. That strategy is 1. Set the fractions up as if to add. 2. Get a common denominator. The idea of a common denominator is not normally in our thinking when we set up decimal fractions to ad ...
... We can use the same general strategy for comparing two or three (or more) common fractions or decimal fractions. That strategy is 1. Set the fractions up as if to add. 2. Get a common denominator. The idea of a common denominator is not normally in our thinking when we set up decimal fractions to ad ...
Full text
... terms of ones and twos, by using Fn^1, in the rightmost column, and taking the Fibonacci numbers as placeholders. We index each composition in the order in which it was written in the array by assigning each to a natural number taken in order and, further, assign the index k to set A if the kth comp ...
... terms of ones and twos, by using Fn^1, in the rightmost column, and taking the Fibonacci numbers as placeholders. We index each composition in the order in which it was written in the array by assigning each to a natural number taken in order and, further, assign the index k to set A if the kth comp ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.