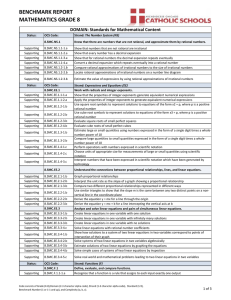
MATH103-FINAL-EXAM
... 30.) The bill for the repair of your car was itemized into two categories - parts and labor. The total bill was $210.00. The parts totaled $90.00. If the rate for the mechanic was $45.00/hour. a. 3pts. Create a mathematical model (equation) to determine the number of hours the mechanic worked on you ...
... 30.) The bill for the repair of your car was itemized into two categories - parts and labor. The total bill was $210.00. The parts totaled $90.00. If the rate for the mechanic was $45.00/hour. a. 3pts. Create a mathematical model (equation) to determine the number of hours the mechanic worked on you ...
CMPE-552 Database and File Security
... 15.What are the main sources of security vulnerabilities of software? 16. How asymmetric encryption can be used for secure communication? 17. How asymmetric encryption can be used for establishing session key? 18. What is digital signature? What is hash (digest) function? What is one-way function? W ...
... 15.What are the main sources of security vulnerabilities of software? 16. How asymmetric encryption can be used for secure communication? 17. How asymmetric encryption can be used for establishing session key? 18. What is digital signature? What is hash (digest) function? What is one-way function? W ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.