File - Operations with Integers
... 9. How did zero come to be a number? Compare and contrast (Link 1) with (Link 3) 10. What is the additive identity? Give your own example. (Link 1) (Link 3) ...
... 9. How did zero come to be a number? Compare and contrast (Link 1) with (Link 3) 10. What is the additive identity? Give your own example. (Link 1) (Link 3) ...
Y3 New Curriculum Maths planning 17
... Children find 1/2, 1/4, 1/10, 1/3 or 1/5 of numbers by using known multiplication and division facts. They read and write proper fractions such as 2/3 and understand the denominator as the number of parts of the whole and the numerator as the number of parts. They count in fractions along a number l ...
... Children find 1/2, 1/4, 1/10, 1/3 or 1/5 of numbers by using known multiplication and division facts. They read and write proper fractions such as 2/3 and understand the denominator as the number of parts of the whole and the numerator as the number of parts. They count in fractions along a number l ...
TUSD`s Mathematics Curriculum - Algebra 1
... High School - Modeling Modeling links classroom mathematics and statistics to everyday life, work, and decision-making. Modeling is the process of choosing and using appropriate mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to improve decisions. Quantiti ...
... High School - Modeling Modeling links classroom mathematics and statistics to everyday life, work, and decision-making. Modeling is the process of choosing and using appropriate mathematics and statistics to analyze empirical situations, to understand them better, and to improve decisions. Quantiti ...
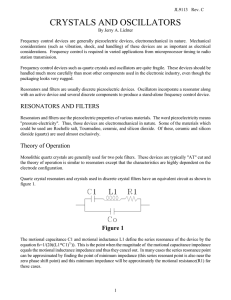
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.