Electric Charge and Its Conservation Electric Charge in the Atom
... • Charge is quantized in units of e • Objects can be charged by conduction or ...
... • Charge is quantized in units of e • Objects can be charged by conduction or ...
Chapter 26
... Electric potential difference V is the electric potential energy / unit charge = U/q For uniform electric field, U r qE r V r ...
... Electric potential difference V is the electric potential energy / unit charge = U/q For uniform electric field, U r qE r V r ...
Paired states of fermions in two dimensions with breaking of parity
... viewed as a p-wave paired state of two-component composite fermions [13,35,36]. It is likely that this is closely related to a FQHE state observed in double-layer and single-thick-layer systems at ν = 1/2 [37,38]. Moore and Read [14] suggested that nonabelian statistics might occur in QH states, and ...
... viewed as a p-wave paired state of two-component composite fermions [13,35,36]. It is likely that this is closely related to a FQHE state observed in double-layer and single-thick-layer systems at ν = 1/2 [37,38]. Moore and Read [14] suggested that nonabelian statistics might occur in QH states, and ...
An old test (ch 20 only)
... Part II – Multiple choice questions: For questions 6 – 15 select the only one choice that best answers or completes each statement. 6. How far June must travel to get away from the earth’s gravitational field? A) To a region above the earth atmosphere. B) To a region well beyond the moon. C) To a re ...
... Part II – Multiple choice questions: For questions 6 – 15 select the only one choice that best answers or completes each statement. 6. How far June must travel to get away from the earth’s gravitational field? A) To a region above the earth atmosphere. B) To a region well beyond the moon. C) To a re ...
Atomic Structure and Periodicity – web
... strontium salts such as Sr(NO3)2 and SrCO3 are heated. Calculate the frequency of red light of wavelength 6.50 × 102 nm. You must be able to convert nm to m because the speed of light constant is in meters per second. 1 nm = 1 x10-9m ...
... strontium salts such as Sr(NO3)2 and SrCO3 are heated. Calculate the frequency of red light of wavelength 6.50 × 102 nm. You must be able to convert nm to m because the speed of light constant is in meters per second. 1 nm = 1 x10-9m ...
PowerPoint
... “The charge enclosed is negative. Therefore, the electric field points towards the center.” This is always true for a solid conductor (within the material of the conductor) “Electric field inside a conductor should be zero.“ Here we have a charge “inside” ...
... “The charge enclosed is negative. Therefore, the electric field points towards the center.” This is always true for a solid conductor (within the material of the conductor) “Electric field inside a conductor should be zero.“ Here we have a charge “inside” ...
Weak Interactions - University of Tennessee Physics
... This makes our theory predictive even as E → ∞! It is “UV complete”! This line of thinking ultimately yields a SU(3)c × SU(2)L × U(1)Y gauge theory we call the Standard Model (SM). It is predictive — and successful — once all its parameters are fixed. In 2015 the existence of known unknowns (e.g., d ...
... This makes our theory predictive even as E → ∞! It is “UV complete”! This line of thinking ultimately yields a SU(3)c × SU(2)L × U(1)Y gauge theory we call the Standard Model (SM). It is predictive — and successful — once all its parameters are fixed. In 2015 the existence of known unknowns (e.g., d ...
Majorana Fermions and Non-Abelian Statistics in
... which the quantum information encoded in the Majorana states can be manipulated without moving or measuring [17] them. To determine whether a Majorana mode is enclosed in a volume V, we topologically classify BdG Hamiltonians on @V, the 2D surface V. We assume the Hamiltonian varies slowly, so we ca ...
... which the quantum information encoded in the Majorana states can be manipulated without moving or measuring [17] them. To determine whether a Majorana mode is enclosed in a volume V, we topologically classify BdG Hamiltonians on @V, the 2D surface V. We assume the Hamiltonian varies slowly, so we ca ...
Chapter5_Final.doc
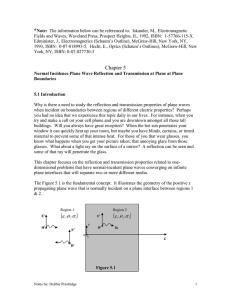
... waves constructively interfere. 3. When z = λ/2, z = λ, z = 3λ/2, etc., in front of the perfect conductor the total electric field is always zero. This is happening when the two fields are going through destructive interference process for all values of ωt, also known as null locations. 4. The occur ...
... waves constructively interfere. 3. When z = λ/2, z = λ, z = 3λ/2, etc., in front of the perfect conductor the total electric field is always zero. This is happening when the two fields are going through destructive interference process for all values of ωt, also known as null locations. 4. The occur ...
Computing Quark and Gluon Distribution Functions for Very Large
... compared to the QCD scale. For this to be consistent, the low momentum range of integration must be cutoff for small momentum transfer for the range of dynamically important momenta. Presumably this happens due to media effects caused by the high density of partons. Although the arguments given abov ...
... compared to the QCD scale. For this to be consistent, the low momentum range of integration must be cutoff for small momentum transfer for the range of dynamically important momenta. Presumably this happens due to media effects caused by the high density of partons. Although the arguments given abov ...
Electric Potential Practice Problems
... 19. Two conducting spheres of different radii are charged with the same charge -Q. What will happen to the charge if the spheres are connected with a conducting wire? (A) Negative charge flows from the large sphere to the smaller sphere until the electric field at the surface of each sphere is the ...
... 19. Two conducting spheres of different radii are charged with the same charge -Q. What will happen to the charge if the spheres are connected with a conducting wire? (A) Negative charge flows from the large sphere to the smaller sphere until the electric field at the surface of each sphere is the ...