IM3314481452
... zero, we get the relaxation time approximation result after the first iteration. We have found that convergence can normally be achieved after only a few iterations for small electric fields. Once f 1 (k) has been evaluated to the required accuracy, it is possible to calculate quantities such as the ...
... zero, we get the relaxation time approximation result after the first iteration. We have found that convergence can normally be achieved after only a few iterations for small electric fields. Once f 1 (k) has been evaluated to the required accuracy, it is possible to calculate quantities such as the ...
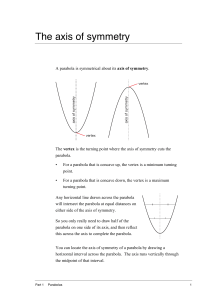
The axis of symmetry
... will intersect the parabola at equal distances on either side of the axis of symmetry. So you only really need to draw half of the parabola on one side of its axis, and then reflect this across the axis to complete the parabola. You can locate the axis of symmetry of a parabola by drawing a horizont ...
... will intersect the parabola at equal distances on either side of the axis of symmetry. So you only really need to draw half of the parabola on one side of its axis, and then reflect this across the axis to complete the parabola. You can locate the axis of symmetry of a parabola by drawing a horizont ...
Topological Classification of Insulators and Superconductors
... possible to study general properties. This means that Hamiltonians will usually not be given explicitly, which has the effect that the theory is very generally applicable but also a bit abstract. By studying these classes using topology it is possible to see where states like the quantum Hall state ...
... possible to study general properties. This means that Hamiltonians will usually not be given explicitly, which has the effect that the theory is very generally applicable but also a bit abstract. By studying these classes using topology it is possible to see where states like the quantum Hall state ...
Lab 6: Complex Electrical Circuits
... along an equipotential surface (in 3 dimensions). If no work is done, then the potential must be the same everywhere. Clearly there must be zero electric force in the direction of motion along an equipotential. This is all you need to know about electric fields and potentials to begin the experiment ...
... along an equipotential surface (in 3 dimensions). If no work is done, then the potential must be the same everywhere. Clearly there must be zero electric force in the direction of motion along an equipotential. This is all you need to know about electric fields and potentials to begin the experiment ...
20 ElectroMagnetic field: energy, momentum and angular momentum
... time per unit area perpendicular to the direction of energy flow); this is called the intensity of EM radiation. Note that only the entire surface-integral of the Poynting vector, on a closed surface, has a clear physical meaning. In fact one has to be careful with the strict identification of the P ...
... time per unit area perpendicular to the direction of energy flow); this is called the intensity of EM radiation. Note that only the entire surface-integral of the Poynting vector, on a closed surface, has a clear physical meaning. In fact one has to be careful with the strict identification of the P ...
ElectroGravitics_01
... region of the electron. This has some profound implications -- one of which is that the motional electric force field is immune to electrostatic or magnetic shielding. Experimentally, it can be confirmed that the motional electric field is immune to shielding and follows the boundary conditions of t ...
... region of the electron. This has some profound implications -- one of which is that the motional electric force field is immune to electrostatic or magnetic shielding. Experimentally, it can be confirmed that the motional electric field is immune to shielding and follows the boundary conditions of t ...
Review Lecture: March 15, 2013
... At sufficient low temperatures, CV T AT 3 . Where is the Sommerfeld parameter. The ratio of the observed to the free electron values of the electronic heat capacity is related to thermal effective mass as: ...
... At sufficient low temperatures, CV T AT 3 . Where is the Sommerfeld parameter. The ratio of the observed to the free electron values of the electronic heat capacity is related to thermal effective mass as: ...
TOWARDS THE FRACTIONAL QUANTUM HALL EFFECT: A
... lowering the temperature below 1 K, quantum effects dominate, and the relation of Hall conductance to filling factor shows plateaux at integer values, [20]. The effect is measured with very high precision (of the order of 10−8 ) and allows for a very accurate measurement of the fine structure consta ...
... lowering the temperature below 1 K, quantum effects dominate, and the relation of Hall conductance to filling factor shows plateaux at integer values, [20]. The effect is measured with very high precision (of the order of 10−8 ) and allows for a very accurate measurement of the fine structure consta ...
1 - Sumner
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
Structure - Bhoj University
... changes with change in sign, the particle is said to be in odd state and is said to have negative or odd parity. Nuclear states are characterized by a definite parity which may be different for different states of the same nucleus. According to the parity law, two particles which are the mirror imag ...
... changes with change in sign, the particle is said to be in odd state and is said to have negative or odd parity. Nuclear states are characterized by a definite parity which may be different for different states of the same nucleus. According to the parity law, two particles which are the mirror imag ...
Anisotropic pyrochlores and the global phase diagram of the checkerboard... Oleg A. Starykh, Akira Furusaki, and Leon Balents
... all orders would require tuning an infinite number of interchain couplings to zero兲. Such derivative terms are commonly neglected on the grounds of their irrelevance with respect to the Luttinger liquid fixed point of the independent spin chain. However, the quasi-1D problem is not the same as the p ...
... all orders would require tuning an infinite number of interchain couplings to zero兲. Such derivative terms are commonly neglected on the grounds of their irrelevance with respect to the Luttinger liquid fixed point of the independent spin chain. However, the quasi-1D problem is not the same as the p ...
Jackson 4.9 Homework Solution
... The electric field near the center of the sphere points away from the point charge, in the negative z direction, just as if the sphere was not there, but its magnitude is weakened by the amount in square brackets. For instance, if the dielectric constant of the sphere is 4, then the field near its c ...
... The electric field near the center of the sphere points away from the point charge, in the negative z direction, just as if the sphere was not there, but its magnitude is weakened by the amount in square brackets. For instance, if the dielectric constant of the sphere is 4, then the field near its c ...
physics
... by a few special rules or laws that can be expressed in mathematical formulae. Newton’s combination of logical experimentation and mathematical analysis shaped the way science has been done ever since. In this section, we begin by examining kinematics, which is a study of motion without regard for t ...
... by a few special rules or laws that can be expressed in mathematical formulae. Newton’s combination of logical experimentation and mathematical analysis shaped the way science has been done ever since. In this section, we begin by examining kinematics, which is a study of motion without regard for t ...