SPH4UI
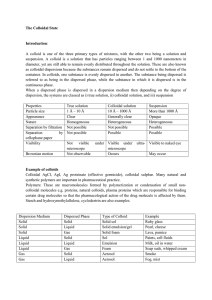
... this movement. The concept of electric potential can be applied to a simple battery-powered electric circuit. Work must be done on a positive test charge to move it through the battery from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This work would increase the potential energy of the charge an ...
... this movement. The concept of electric potential can be applied to a simple battery-powered electric circuit. Work must be done on a positive test charge to move it through the battery from the negative terminal to the positive terminal. This work would increase the potential energy of the charge an ...
On Exotic Orders in Stongly Correlated Systems
... many skills beyond those necessary to complete the task at hand. Always ready with unforeseen questions, he has repeatedly challenged me to understand things more deeply, and to recognize honestly the boundaries of my own understanding. But above all, he has been a constant reminder of what drew me ...
... many skills beyond those necessary to complete the task at hand. Always ready with unforeseen questions, he has repeatedly challenged me to understand things more deeply, and to recognize honestly the boundaries of my own understanding. But above all, he has been a constant reminder of what drew me ...
The Laby Experiment - Pavia Project Physics
... corpuscles that Thomson had discovered were indeed subatomic and carried a unit electric charge. Millikan (1862-1953) commenced his work on measuring the charge carried by the electron (as corpuscles were now known) in 1910. At this time Millikan was in his 40’s, was teaching in Chicago and had not ...
... corpuscles that Thomson had discovered were indeed subatomic and carried a unit electric charge. Millikan (1862-1953) commenced his work on measuring the charge carried by the electron (as corpuscles were now known) in 1910. At this time Millikan was in his 40’s, was teaching in Chicago and had not ...
New features of ion acoustic waves in inhomogeneous and
... n(x0 , z1 ), n(x0 , z2 ) at the points A(x0 , z1 ) and B(x0 , z2 ) will no longer be the same. ii) In addition, because of opposite motion of electrons and ions due to the transverse electric field in x-direction, there will be excess of charge of one or another sign at every point for any z, and th ...
... n(x0 , z1 ), n(x0 , z2 ) at the points A(x0 , z1 ) and B(x0 , z2 ) will no longer be the same. ii) In addition, because of opposite motion of electrons and ions due to the transverse electric field in x-direction, there will be excess of charge of one or another sign at every point for any z, and th ...
The Hall fields and fast magnetic reconnection
... the Hall term and the associated whistler dynamics were included in the model.5 Similarly, the rate of collisionless reconnection was found to be independent of the electron mass,6,7 which is a consequence of the electron flux away from the x-line ⌫ = cAede being independent of mass; for smaller me ...
... the Hall term and the associated whistler dynamics were included in the model.5 Similarly, the rate of collisionless reconnection was found to be independent of the electron mass,6,7 which is a consequence of the electron flux away from the x-line ⌫ = cAede being independent of mass; for smaller me ...
here.
... to study its features. With the benefit of hindsight, we can say that suitably interpreted, the predictions of KG are in reasonable agreement with experimental findings concerning relativistic spin-less particles (such as pionic atoms). Ultimately, this is the physical justification to study it. The ...
... to study its features. With the benefit of hindsight, we can say that suitably interpreted, the predictions of KG are in reasonable agreement with experimental findings concerning relativistic spin-less particles (such as pionic atoms). Ultimately, this is the physical justification to study it. The ...
unit 102-1: electric forces and fields
... into contact with objects that have been rubbed. These forces are attributed to a fundamental property of the constituents of atoms known as charge. The forces between particles that are not moving or that are moving relatively slowly are known as electrostatic forces. We start our study in the firs ...
... into contact with objects that have been rubbed. These forces are attributed to a fundamental property of the constituents of atoms known as charge. The forces between particles that are not moving or that are moving relatively slowly are known as electrostatic forces. We start our study in the firs ...
Wake Fields in Particle Accelerators with Finite Thickness and
... electrons, neutrons) impressing high kinetic energies by the action of electromagnetic or electrostatic fields. The accelerated particles are sent against an appropriate “target” to investigate further the structure of matter and its constituents. Atoms are not elementary particles but composite ent ...
... electrons, neutrons) impressing high kinetic energies by the action of electromagnetic or electrostatic fields. The accelerated particles are sent against an appropriate “target” to investigate further the structure of matter and its constituents. Atoms are not elementary particles but composite ent ...
Author`s personal copy
... molecular motors, microfluidic pumps, and colloidal separators. Most of them can be unified under the name ‘Brownian motors’ [3,4,7]. A recent comprehensive review by one of the authors [8] provides an up-do-date information on such Brownian machinery. Fast progress in experimental manipulations wit ...
... molecular motors, microfluidic pumps, and colloidal separators. Most of them can be unified under the name ‘Brownian motors’ [3,4,7]. A recent comprehensive review by one of the authors [8] provides an up-do-date information on such Brownian machinery. Fast progress in experimental manipulations wit ...
Hyperbolic Geometrodynamic Warp Drives
... applies locally to any region of space sufficiently small that its curvature can be neglected. General Relativity does not forbid apparent FTL travel (as seen by a preferred topological observer) or communication, but it does require that the local restrictions of special relativity must apply (that ...
... applies locally to any region of space sufficiently small that its curvature can be neglected. General Relativity does not forbid apparent FTL travel (as seen by a preferred topological observer) or communication, but it does require that the local restrictions of special relativity must apply (that ...
Pearson Physics Level 30 Unit VI Forces and Fields: Chapter 11
... whereas an electric force is the electrical influence of the field on a test charge placed in the electric field. The force is only produced when another charge is placed in the field, whereas the field can exist without the presence of the test charge. 2. A field theory was necessary to explain “ac ...
... whereas an electric force is the electrical influence of the field on a test charge placed in the electric field. The force is only produced when another charge is placed in the field, whereas the field can exist without the presence of the test charge. 2. A field theory was necessary to explain “ac ...
CHAPTER 19 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL ENERGY AND THE
... adding charges to the square, one at a time, and determining the electric potential energy at each step. According to Equation 19.3, the electric potential energy EPE is the product of the charge q and the electric potential V at the spot where the charge is placed, EPE = qV. The total electric pote ...
... adding charges to the square, one at a time, and determining the electric potential energy at each step. According to Equation 19.3, the electric potential energy EPE is the product of the charge q and the electric potential V at the spot where the charge is placed, EPE = qV. The total electric pote ...