Introduction Cosmic Radiation
... In answering the previous question you probably calculated the speed of the proton using the formula for kinetic energy E = 12 mv2 . In doing so you obtained a speed higher than the speed of light, something which is impossible. We need to take into account relativity and the famous equations of Alb ...
... In answering the previous question you probably calculated the speed of the proton using the formula for kinetic energy E = 12 mv2 . In doing so you obtained a speed higher than the speed of light, something which is impossible. We need to take into account relativity and the famous equations of Alb ...
Formulae For DUAL NATURE AND RADIATION
... of electric field and gravity and E is the applied electric field. Photocell. It is an arrangement which converts light energy into electric energy. It works on the principle of photoelectric effect. It is used in cinematography for the reproduction of sound. Dual Nature of Radiation: Light has dual ...
... of electric field and gravity and E is the applied electric field. Photocell. It is an arrangement which converts light energy into electric energy. It works on the principle of photoelectric effect. It is used in cinematography for the reproduction of sound. Dual Nature of Radiation: Light has dual ...
Phys202_Final_Exam_Spr2007.doc
... area 0.4 m2 and a distance apart of 0.3 m. Then if the capacitor is neutralized in a time of 2 seconds, what total magnetic field (summed around a circle encompassing the capacitor) would be created? a. 4E12 b. 6E14 c. 2E10 d. 8E16 ...
... area 0.4 m2 and a distance apart of 0.3 m. Then if the capacitor is neutralized in a time of 2 seconds, what total magnetic field (summed around a circle encompassing the capacitor) would be created? a. 4E12 b. 6E14 c. 2E10 d. 8E16 ...
CMock exam IV paper 2
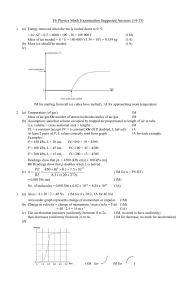
... Gradually increase the vibrator frequency from zero. (1M) When the frequency of the vibrator is slowly increased from zero, at first no stationary wave is produced. (1M) When the frequency is increased to fo, a transverse stationary wave with one loop is formed. (1M) When the frequency is further i ...
... Gradually increase the vibrator frequency from zero. (1M) When the frequency of the vibrator is slowly increased from zero, at first no stationary wave is produced. (1M) When the frequency is increased to fo, a transverse stationary wave with one loop is formed. (1M) When the frequency is further i ...
interference
... µm. If the fourth dark fringe appears at an angle of 10.0o, calculate the wavelength of light used. What colour is this? 2. A helium–neon laser is used to produce light with a wavelength of 632.7 nm which is passed through a single slit. If the adjacent minima are separated by a distance of 7.50 cm ...
... µm. If the fourth dark fringe appears at an angle of 10.0o, calculate the wavelength of light used. What colour is this? 2. A helium–neon laser is used to produce light with a wavelength of 632.7 nm which is passed through a single slit. If the adjacent minima are separated by a distance of 7.50 cm ...
87essay - PLK Vicwood KT Chong Sixth Form College
... forces and are difficult to break. They are imbedded in a weaker yielding plastic material (matrix). The matrix (1) binds and holds the fibres together so that any applied load is transmitted to them, (2) it protects the surface of the fibres from scratches/and possibility of cracks/breaks occurring ...
... forces and are difficult to break. They are imbedded in a weaker yielding plastic material (matrix). The matrix (1) binds and holds the fibres together so that any applied load is transmitted to them, (2) it protects the surface of the fibres from scratches/and possibility of cracks/breaks occurring ...
Document
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
... In an analysis relating Bohr's theory to the de Broglie wavelength of electrons, when an electron moves from the n = 1 level to the n = 3 level, the circumference of its orbit becomes 9 times greater. This occurs because (a) there are 3 times as many wavelengths in the new orbit, (b) there are 3 tim ...
E due to arc P25
... a. Write down the linear charge density, λ in terms of q, π and r; for the rod. ________________ b. Show that the magnitude of the electric field at P is given by, √2 ...
... a. Write down the linear charge density, λ in terms of q, π and r; for the rod. ________________ b. Show that the magnitude of the electric field at P is given by, √2 ...
Test Review Jeopardy
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
... the left end of the conductor, but do not touch it. What charge will the right end of the conductor have? ...
Example 1. Find the electrostatic force between a +3.0 C charge and
... a) What is the electric force acting on the electron? b) How much time is taken for the electron to pass through the plates? c) How far will the electron “fall” from its path while in-between the two plates? Hint: for b) and c), you’ll have to examine horizontal and vertical components, just like fo ...
... a) What is the electric force acting on the electron? b) How much time is taken for the electron to pass through the plates? c) How far will the electron “fall” from its path while in-between the two plates? Hint: for b) and c), you’ll have to examine horizontal and vertical components, just like fo ...
Lecture 14.1 : Electromagnetic Fields
... Alec creates a region with zero electric field, and magnetic field BA. He observes a particle with velocity vCA traveling through this region to experience force FA. ...
... Alec creates a region with zero electric field, and magnetic field BA. He observes a particle with velocity vCA traveling through this region to experience force FA. ...