Electromagnetic generation of sound in metals located in a magnetic
... that they allow us to infer properties of different groups of electrons on the Fermi surface from various features of the kinetic characteristics. In the problem of electromagnetic generation of sound, such a condition is smallness of the sound wave in comparison with the characteristic scales of el ...
... that they allow us to infer properties of different groups of electrons on the Fermi surface from various features of the kinetic characteristics. In the problem of electromagnetic generation of sound, such a condition is smallness of the sound wave in comparison with the characteristic scales of el ...
1 In an Oil-drop experiment, a drop of oil with mass 4.1x10
... specific velocity to exit the fields. The electrons then enter an area with only a magnetic field, where the electron beam is deflected in a circular shape with a radius of 8.0 mm. In the velocity selector, E = 400.0 V/m and B = 4.7 x 10-4 T. The same value of B exists in the area where the electron ...
... specific velocity to exit the fields. The electrons then enter an area with only a magnetic field, where the electron beam is deflected in a circular shape with a radius of 8.0 mm. In the velocity selector, E = 400.0 V/m and B = 4.7 x 10-4 T. The same value of B exists in the area where the electron ...
Quantum Contributions to Cosmological Correlations
... two different kinds of wave number: the fixed wave numbers q associated with external lines, and the internal wave numbers p circulating in loops, over which we must integrate. It is only if the integrals over internal wave numbers p are dominated by values of order p ≈ q that we can speak of a defi ...
... two different kinds of wave number: the fixed wave numbers q associated with external lines, and the internal wave numbers p circulating in loops, over which we must integrate. It is only if the integrals over internal wave numbers p are dominated by values of order p ≈ q that we can speak of a defi ...
Gauss`s Law and Electric Potential Homework
... conducting plates, oppositely charged, separated by 2.3 cm, a) what is the magnitude of the surface charge density assumed to be uniform on the plates and b) in which direction does the field point? Draw a picture of this situation below. Label appropriately. Show the field lines emanating from each ...
... conducting plates, oppositely charged, separated by 2.3 cm, a) what is the magnitude of the surface charge density assumed to be uniform on the plates and b) in which direction does the field point? Draw a picture of this situation below. Label appropriately. Show the field lines emanating from each ...
Simulation Fabrication Dielectrophoretic Separation Structure
... maturity, it has become more difficult to make fundamental improvements in separation resolution, system complexity, sample size, and device cost. Therefore, novel physical methods by which different particle types may be effectively discriminated and selectively manipulated are desirable. To this e ...
... maturity, it has become more difficult to make fundamental improvements in separation resolution, system complexity, sample size, and device cost. Therefore, novel physical methods by which different particle types may be effectively discriminated and selectively manipulated are desirable. To this e ...
Physics 1425: General Physics I
... • This means that since the electron has a charge, if the inverse square law holds up at smaller and smaller distances, it can’t be infinitely small! • A lower limit on its size is given by assuming its mass comes entirely from this electrostatic energy, using U = E = mc2. • This gives R about 10-15 ...
... • This means that since the electron has a charge, if the inverse square law holds up at smaller and smaller distances, it can’t be infinitely small! • A lower limit on its size is given by assuming its mass comes entirely from this electrostatic energy, using U = E = mc2. • This gives R about 10-15 ...
The Electric Potential and Potential Difference
... 6.0 nm) is 70 mV. The inside of the cell is more negative than the outside. When an “ion channel” embedded in the cell membrane is activated a water-filled pathway is opened and ions can flow through the channel. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this ion channel? Ans. ...
... 6.0 nm) is 70 mV. The inside of the cell is more negative than the outside. When an “ion channel” embedded in the cell membrane is activated a water-filled pathway is opened and ions can flow through the channel. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this ion channel? Ans. ...
Discrete Symmetries
... a third quark generation could accommodate CP violation in the Standard Model by a complex phase in the CKM matrix. Since then, however, CP (or T ) violation has not been observed in any other system and we do not understand its mechanisms and rare processes. The discovery of the b-quark in 1977 ope ...
... a third quark generation could accommodate CP violation in the Standard Model by a complex phase in the CKM matrix. Since then, however, CP (or T ) violation has not been observed in any other system and we do not understand its mechanisms and rare processes. The discovery of the b-quark in 1977 ope ...
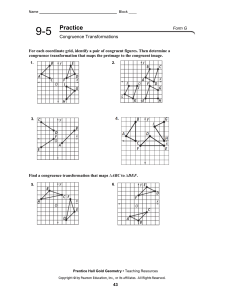
YL 9.5
... For each coordinate grid, identify a pair of congruent figures. Then determine a congruence transformation that maps the preimage to the congruent image. 1. Compare each pair of figures on the grid. ...
... For each coordinate grid, identify a pair of congruent figures. Then determine a congruence transformation that maps the preimage to the congruent image. 1. Compare each pair of figures on the grid. ...
Phy213_CH24_worksheet-s07
... 6.0 nm) is 70 mV. The inside of the cell is more negative than the outside. When an “ion channel” embedded in the cell membrane is activated a water-filled pathway is opened and ions can flow through the channel. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this ion channel? Ans. ...
... 6.0 nm) is 70 mV. The inside of the cell is more negative than the outside. When an “ion channel” embedded in the cell membrane is activated a water-filled pathway is opened and ions can flow through the channel. a. What is the magnitude of the electric field inside this ion channel? Ans. ...
Potential to Fields - Seattle Central College
... The units for electric potential are then "energy/charge" or in the MKS system: Joule/Coulomb = Volt, or 1 J/C = 1V. When you go hiking in the mountains and you decide where to put your boot next you can choose a point that is higher, lower, or at the same altitude. There will most likely exist a po ...
... The units for electric potential are then "energy/charge" or in the MKS system: Joule/Coulomb = Volt, or 1 J/C = 1V. When you go hiking in the mountains and you decide where to put your boot next you can choose a point that is higher, lower, or at the same altitude. There will most likely exist a po ...
Acoustomagnetoelectric Effect in Graphene
... in the hypersound regime, Bau et. al. [13] studied the AME of cylindrical quantum wires. Also, AME effect in mono-polar semiconductor for both weak and quantizing field were studied [14]. Experimentally, AME has been observed in n-InSb [15], and in graphite [16] for ql << 1. In this paper, AME in gr ...
... in the hypersound regime, Bau et. al. [13] studied the AME of cylindrical quantum wires. Also, AME effect in mono-polar semiconductor for both weak and quantizing field were studied [14]. Experimentally, AME has been observed in n-InSb [15], and in graphite [16] for ql << 1. In this paper, AME in gr ...
Chapter 16 Concept tests - University of Colorado Boulder
... None of the preceding statements must be true. ...
... None of the preceding statements must be true. ...