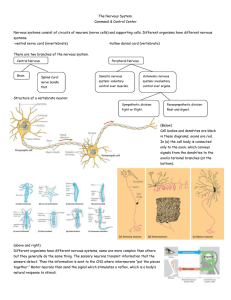
The Great Brain Drain Review - New Paltz Central School District
... E. verbally report that a key was seen C. do none of the above. IV. Which type of procedure is described in each of the following methods of evaluation? a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses gluc ...
... E. verbally report that a key was seen C. do none of the above. IV. Which type of procedure is described in each of the following methods of evaluation? a. Uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce computer generated images to distinguish among different types of brain tissue. MRI b. Uses gluc ...
Bio 111 Lab 8: The Nervous System and the Senses
... The cerebrum is divided into the right and left hemispheres. Each hemisphere has four “lobes” (or areas): frontal (solving problems, making decisions about appropriate behavior, planning), parietal (expressing thoughts and feelings), temporal (hearing, converting sensory information into memory), oc ...
... The cerebrum is divided into the right and left hemispheres. Each hemisphere has four “lobes” (or areas): frontal (solving problems, making decisions about appropriate behavior, planning), parietal (expressing thoughts and feelings), temporal (hearing, converting sensory information into memory), oc ...
Unit II Practice Exam – Answer Key
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
... Which of the following was a major problem with phrenology? a. It was “ahead of its time” and no one believed it could be true b. The brain is not neatly organized into structures that correspond to our categories of behavior c. The brains of humans and animals are much less similar than they theory ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 07 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System, Part 3
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
... • Important fact. On the whole, the right side of the brain processes sensory information from the left side of the body and issues motor commands to the left side of the body. Likewise, the left side of the brain processes sensory information from the right side of the body and issues motor command ...
Griggs_Chapter_02_Neuroscience
... major role in regulating basic drives such as eating, thirst, and sex The hippocampus is involved in the formation of memories The amygdala plays a major role in regulating our emotional experiences, especially fear, anger, and aggression ...
... major role in regulating basic drives such as eating, thirst, and sex The hippocampus is involved in the formation of memories The amygdala plays a major role in regulating our emotional experiences, especially fear, anger, and aggression ...
Orbitofrontal Cortex and Its Contribution to Decision
... Research paradigm: Reverse contingencies ...
... Research paradigm: Reverse contingencies ...
Inside the Human Brain - Hale
... The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the limbic system). The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum. The hindbrain is made of the cerebellum, pons and ...
... The brain is made of three main parts: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus (part of the limbic system). The midbrain consists of the tectum and tegmentum. The hindbrain is made of the cerebellum, pons and ...
Griggs Chapter 2: Neuroscience
... major role in regulating basic drives such as eating, thirst, and sex The hippocampus is involved in the formation of memories The amygdala plays a major role in regulating our emotional experiences, especially fear, anger, and aggression ...
... major role in regulating basic drives such as eating, thirst, and sex The hippocampus is involved in the formation of memories The amygdala plays a major role in regulating our emotional experiences, especially fear, anger, and aggression ...
The Brain - Academic Computer Center
... Located dorsal to the pons and medulla and lies under the occipital lobe of the cerebral hemisphere from which it is separated by the transverse fissure ...
... Located dorsal to the pons and medulla and lies under the occipital lobe of the cerebral hemisphere from which it is separated by the transverse fissure ...
MS-PowerPoint
... Lobes • Frontal Lobes—receive and coordinate messages from other lobes as well as motor control, speech and higher functions • Parietal Lobes—receives information about pressure, pain, touch and temperature ...
... Lobes • Frontal Lobes—receive and coordinate messages from other lobes as well as motor control, speech and higher functions • Parietal Lobes—receives information about pressure, pain, touch and temperature ...
doc - Shoreline Community College
... 39. According to lecture, what are the major structures of the hindbrain and midbrain and the major functions associated with each? (Four structures were mentioned and these four structures, along with a some additional brain structures, are discussed under the heading “older brain structures” in th ...
... 39. According to lecture, what are the major structures of the hindbrain and midbrain and the major functions associated with each? (Four structures were mentioned and these four structures, along with a some additional brain structures, are discussed under the heading “older brain structures” in th ...
The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous
... messages originating in cortex travel to other areas of brain; impulses from sense organs travel along white nerve fibers to cerebral cortex • lobes: regions that corresponds to major bones in the cranium; each body part controlled by a specific location on a specific lobe; each hemisphere has its o ...
... messages originating in cortex travel to other areas of brain; impulses from sense organs travel along white nerve fibers to cerebral cortex • lobes: regions that corresponds to major bones in the cranium; each body part controlled by a specific location on a specific lobe; each hemisphere has its o ...
article
... surgery. Split-brain patients then are able to engage in virtually all the behaviors that anyone else can perform. In fact, it takes special tests to demonstrate that their left and right hemispheres have been separated. What is happening in these cases is that the patients’ left hemispheres, which ...
... surgery. Split-brain patients then are able to engage in virtually all the behaviors that anyone else can perform. In fact, it takes special tests to demonstrate that their left and right hemispheres have been separated. What is happening in these cases is that the patients’ left hemispheres, which ...
3 - smw15.org
... the cerebral cortex after an injury in which sometimes a large part of it simply dies – This is the exception and not the rule For example, not all stroke victims recover ...
... the cerebral cortex after an injury in which sometimes a large part of it simply dies – This is the exception and not the rule For example, not all stroke victims recover ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
... Amygdala – coordinates emotion, autonomic and endocrine systems via hypothalamus. ...
Allison Bynum Neurobiology A.1 – A.3 Allison Bynum A.1 Neural
... heart The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are divisions of the ANS. ...
... heart The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are divisions of the ANS. ...
Biological Basis of Emotions - California Training Institute
... the hippocampus, and other critical structures of the brain. These connections make it possible for the amygdala to play its important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mai ...
... the hippocampus, and other critical structures of the brain. These connections make it possible for the amygdala to play its important role on the mediation and control of major affective activities like friendship, love and affection, on the expression of mood and, mai ...
Ch 2 Biology and Behavior
... – Emotions & formation of new memories – Shrinks as you get older, 40% smaller in Alzheimer suffers ...
... – Emotions & formation of new memories – Shrinks as you get older, 40% smaller in Alzheimer suffers ...
Nervous
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
... The limbic system, a ring of cortical and noncortical centers around the brainstem, mediates primary emotions and attaches emotional “feelings” to survival–related functions. The association of primary emotions with different situations during human development requires parts of the neocortex, espec ...
Emotion Explained
... 4.5.5 Neurophysiology and functional neuroimaging ofthe orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.6 The human orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.7 A neurophysiological and computational basis for stimulus-reinforcer association learning and reversal in the orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.8 Executive functions of the orbitofrontal co ...
... 4.5.5 Neurophysiology and functional neuroimaging ofthe orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.6 The human orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.7 A neurophysiological and computational basis for stimulus-reinforcer association learning and reversal in the orbitofrontal cortex 4.5.8 Executive functions of the orbitofrontal co ...










![The Brain [Fig 7.2 p. 98] • largest, most important part of the nervous](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005074380_1-b4c54e7cf592b472b621b12b4eff42cc-300x300.png)