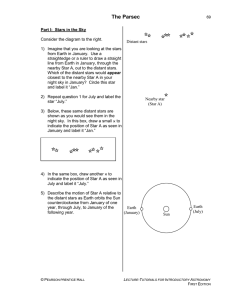
The Parsec
... Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the star. Since even the nearest stars are still ...
... Earth-Sun distance as its base. The small angle, just below Star A, formed by the two longest sides of this triangle is called the parallax angle for Star A. Label this angle “pA.” Knowing a star’s parallax angle allows us to calculate the distance to the star. Since even the nearest stars are still ...
1b91: answers to problem sheet no 1
... First two were revolutionary because they showed that heavenly bodies were not pure or perfect – third must also show this to some extent. Last three supported revolutionary view that the Earth and the other planets must orbit the Sun. Marks – total 8 (1 for each discovery and 1 for showing why it w ...
... First two were revolutionary because they showed that heavenly bodies were not pure or perfect – third must also show this to some extent. Last three supported revolutionary view that the Earth and the other planets must orbit the Sun. Marks – total 8 (1 for each discovery and 1 for showing why it w ...
- Lowell Observatory
... Is the eruptive event unique? We checked the old observations obtained between 1955 and 1962 in Radcliff Observatory, South Africa. Fig. 2 below shows the comparison between the spectra obtained in 1961 and 2005. The similarity is striking. At that time, star A was a WN6 star as it is now. We do not ...
... Is the eruptive event unique? We checked the old observations obtained between 1955 and 1962 in Radcliff Observatory, South Africa. Fig. 2 below shows the comparison between the spectra obtained in 1961 and 2005. The similarity is striking. At that time, star A was a WN6 star as it is now. We do not ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Indeed, the team of 15 astronomers from seven institutions on four continents had picked Tau Ceti specifically because meticulous observations strongly suggested the star had no planetary system. From the earliest days of the hunt for exoplanets almost 20 years ago, astronomers suspected that eviden ...
... Indeed, the team of 15 astronomers from seven institutions on four continents had picked Tau Ceti specifically because meticulous observations strongly suggested the star had no planetary system. From the earliest days of the hunt for exoplanets almost 20 years ago, astronomers suspected that eviden ...
Notes: Astronomy and Groups of Stars
... Made of gas and dust, Least common Looks like a wheel with arm extensions Most common type Arms consist of younger stars, gas/dust. - our galaxy -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our galaxy - our galaxy revolves slowly (225 million years) as the stars orbit ...
... Made of gas and dust, Least common Looks like a wheel with arm extensions Most common type Arms consist of younger stars, gas/dust. - our galaxy -100’s of billions of stars - it takes 100,000 light years to travel across our galaxy - our galaxy revolves slowly (225 million years) as the stars orbit ...
Star Maps and Constellations
... chases the bears (Ursa Major, Ursa Minor) around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
... chases the bears (Ursa Major, Ursa Minor) around in circles, i.e. keeps them at the North pole ...
Handout Life of Stars
... nucleus, like a ball bouncing off a brick wall, resulting in ultra-hot shock-waves which are imparted to the rest of the star. In this way, the star ulimately ends its life in a cataclysmic explosion known as a supernova, and for a few short weeks it burns as brightly as several billion suns, briefl ...
... nucleus, like a ball bouncing off a brick wall, resulting in ultra-hot shock-waves which are imparted to the rest of the star. In this way, the star ulimately ends its life in a cataclysmic explosion known as a supernova, and for a few short weeks it burns as brightly as several billion suns, briefl ...
The Search for Earth-Like Planets
... Premise: If there is intelligent life “out there”, it probably is similar to life as we know it on Earth. ...
... Premise: If there is intelligent life “out there”, it probably is similar to life as we know it on Earth. ...
File
... crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
... crust, about a kilometer thick. This crust is very hard and very smooth. Gravity would probably prevent any irregularities larger than half a centimeter. ...
Essay - CLC Charter School
... Supernovae A supernova is a stellar explosion that happends in result of the death of a massive star. It involves the expulsion of the stars outer layers. A supernova is a relatively rare event in our galaxy, it happens about every 50 years. When a supernova explodes, briefly it can outshine an enti ...
... Supernovae A supernova is a stellar explosion that happends in result of the death of a massive star. It involves the expulsion of the stars outer layers. A supernova is a relatively rare event in our galaxy, it happens about every 50 years. When a supernova explodes, briefly it can outshine an enti ...
Note
... system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the faint star of an an unresolved binary system comprising a K ...
... system comprising a B5V star and an M0V companion. What wavelength regime would you choose to try to detect the M0V star? What is the ratio of the flux from the B star to the flux from the M star at that wavelength? • You want to detect the faint star of an an unresolved binary system comprising a K ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... brightest stars in the night sky are most likely to be bright because they are _________ or __________ not because they are ____________. ...
... brightest stars in the night sky are most likely to be bright because they are _________ or __________ not because they are ____________. ...
Star Lifecycle
... stars) Pulsars – Spinning neutron stars that give off pulses of radio sources. Left over from super massive star supernovas. Black Holes – From the most massive stars (More than 40 times bigger than our sun). Nothing can escape the gravity of a black hole, not even light. ...
... stars) Pulsars – Spinning neutron stars that give off pulses of radio sources. Left over from super massive star supernovas. Black Holes – From the most massive stars (More than 40 times bigger than our sun). Nothing can escape the gravity of a black hole, not even light. ...
Slide 1
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true: a) A reindeer grows a new set of antlers every year b) Reindeers have a poisonous spine on their back legs c) The reindeer is the only species where the males AND females grow antlers d) A reindeer’s antlers can grow up to 1.3m long ...
... 8) Which of the following statements is NOT true: a) A reindeer grows a new set of antlers every year b) Reindeers have a poisonous spine on their back legs c) The reindeer is the only species where the males AND females grow antlers d) A reindeer’s antlers can grow up to 1.3m long ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 1
... If the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters away, how far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? ...
... If the size of the Sun is represented by a baseball with the Earth is about 15 meters away, how far away, to scale, would the nearest stars to the Sun be? ...
where it is, how big it
... light colored bands are called zones; the dark ones belts. The colors correlate with the cloud's altitude: blue lowest, followed by browns and whites, with reds highest. Sometimes we see the lower layers through holes in the upper ones. The Great Red Spot (GRS) has been seen by Earthly observers for ...
... light colored bands are called zones; the dark ones belts. The colors correlate with the cloud's altitude: blue lowest, followed by browns and whites, with reds highest. Sometimes we see the lower layers through holes in the upper ones. The Great Red Spot (GRS) has been seen by Earthly observers for ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
final fate of a massive star
... because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity of such a singularity. The quantum gravity effects should dominate in such a regime. Thus, the collapsing star may hold secrets vital for man's search for a unified understanding of all forces of nature. The ...
... because the energies and all physical quantities reach their extreme values in the vicinity of such a singularity. The quantum gravity effects should dominate in such a regime. Thus, the collapsing star may hold secrets vital for man's search for a unified understanding of all forces of nature. The ...
Coherence of starlight The nearest star (other than
... Coherence of starlight The nearest star (other than our sun) to us is Proxima Centauri at a distance of 30 trillion kilometers, and it has an angular diameter of 2 millionth of a degree or 7 milliarseconds (1 milliarcsecond is 1 thousandth of an arcsecond which is one sixtieth of an arcminute which ...
... Coherence of starlight The nearest star (other than our sun) to us is Proxima Centauri at a distance of 30 trillion kilometers, and it has an angular diameter of 2 millionth of a degree or 7 milliarseconds (1 milliarcsecond is 1 thousandth of an arcsecond which is one sixtieth of an arcminute which ...
Planets beyond the solar system
... that we cannot see an eclipse from Earth if the orbit of the planet is tilted relative to our line of sight. • Only a few percent of planets are expected to have orbits at just the right angle so that we can see eclipses. • Need a more general way to search. ...
... that we cannot see an eclipse from Earth if the orbit of the planet is tilted relative to our line of sight. • Only a few percent of planets are expected to have orbits at just the right angle so that we can see eclipses. • Need a more general way to search. ...
Star Jeopardy Review #2
... They do not evolve off until helium is built up. Most of stars life time is spent as a main sequence star. ...
... They do not evolve off until helium is built up. Most of stars life time is spent as a main sequence star. ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.