Folie 1
... • During the initial parts of its contraction, a cloud won't heat up -- radiation escapes and carries away the energy. The Jeans mass decreases because T is staying constant but the density is increasing. Eventually the cloud breaks into fragments which in turn collapse to become stars. • Hayashi li ...
... • During the initial parts of its contraction, a cloud won't heat up -- radiation escapes and carries away the energy. The Jeans mass decreases because T is staying constant but the density is increasing. Eventually the cloud breaks into fragments which in turn collapse to become stars. • Hayashi li ...
network of amateur astronomers (CBA) to gather data on CV`s.
... a. Celestron C11, 0.62 fc/fr, O.87 arcsec/pixel b. Typical take 30 images (10 to 30 seconds). Stack as needed. c. Calibrate with dark frame for sure. Flat if available. d. Preselection becomes important. Comma can be a killer. e. Analysis can take much longer than observations. It is all about esta ...
... a. Celestron C11, 0.62 fc/fr, O.87 arcsec/pixel b. Typical take 30 images (10 to 30 seconds). Stack as needed. c. Calibrate with dark frame for sure. Flat if available. d. Preselection becomes important. Comma can be a killer. e. Analysis can take much longer than observations. It is all about esta ...
Luminosity of sun
... every collision. Chemistry tells us that doesn’t always happen: sometimes they stick together and make molecules! In AY2, you can always assume a gas is “perfect” ...
... every collision. Chemistry tells us that doesn’t always happen: sometimes they stick together and make molecules! In AY2, you can always assume a gas is “perfect” ...
Document
... It has similar luminosity to Sculptor and it shows hints of age gradients (e.g. MartinezDelgado, Gallart and Aparicio 1999, wide area but shallow photometry) ...
... It has similar luminosity to Sculptor and it shows hints of age gradients (e.g. MartinezDelgado, Gallart and Aparicio 1999, wide area but shallow photometry) ...
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
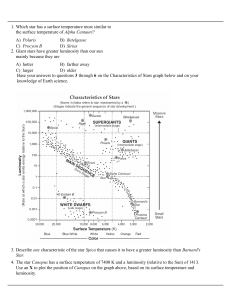
... D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. Which one of the following statements could explain this? A) Star A is hotter than star B. B) Star A is more distant than star B. C) Star A appears brighter in the sky than star B. D ...
... D) red dwarf star 60. Two stars of the same color are plotted on an H-R diagram. Star A is more luminous than star B. Which one of the following statements could explain this? A) Star A is hotter than star B. B) Star A is more distant than star B. C) Star A appears brighter in the sky than star B. D ...
Stars M. R. W. Masheder Room 4.15
... a. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram b. Mass – luminosity relationship C. Internal Structure of Stars a. Hydrostatic equilibrium; types of pressure D. Energy Sources in Stars a. Gravity b. Nuclear energy – various schemes; stability E. Stellar Evolution a. Star formation b. Main sequence c. Post-main sequ ...
... a. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram b. Mass – luminosity relationship C. Internal Structure of Stars a. Hydrostatic equilibrium; types of pressure D. Energy Sources in Stars a. Gravity b. Nuclear energy – various schemes; stability E. Stellar Evolution a. Star formation b. Main sequence c. Post-main sequ ...
High-Resolution Spectroscopy of the Transiting Planet Host Star
... standard local thermodynamic equilibrium (LTE) using a modified version of the spectral synthesis code MOOG (Sneden 1973) and a grid of Kurucz (1993) stellar atmospheres. We selected a set of 30 Fe i and four Fe ii lines (with lower excitation potentials 0.86 ≤ x l ≤ 5.03 eV and 2.58 ≤ x l ≤ 3.90 eV ...
... standard local thermodynamic equilibrium (LTE) using a modified version of the spectral synthesis code MOOG (Sneden 1973) and a grid of Kurucz (1993) stellar atmospheres. We selected a set of 30 Fe i and four Fe ii lines (with lower excitation potentials 0.86 ≤ x l ≤ 5.03 eV and 2.58 ≤ x l ≤ 3.90 eV ...
NASSP Class Test – 2008 April 7th Section A
... Answer FOUR questions from section A (10 marks and approximately 10 minutes each) and FIVE questions from section B (20 marks and approximately 20 minutes each). The marks allocated to each part question are indicated in brackets. ...
... Answer FOUR questions from section A (10 marks and approximately 10 minutes each) and FIVE questions from section B (20 marks and approximately 20 minutes each). The marks allocated to each part question are indicated in brackets. ...
Astr 102 Lec 6: Basic Properties of Stars
... • What are density, temperature, and pressure, and how are they related? • What is the difference between luminosity ...
... • What are density, temperature, and pressure, and how are they related? • What is the difference between luminosity ...
Metal Abundances of Subdwarf B Stars from SPY
... measured in five stars only and upper limits are given for all others. ...
... measured in five stars only and upper limits are given for all others. ...
Chapter 25.2 - Planet Earth
... thousands of times its main-sequence size, as shown in Figure 10. As the star expands, its surface cools, which explains the star’s reddish appearance. During expansion, the core continues to collapse and heat until it reaches 100 million K. At this temperature, it is hot enough to convert helium to ...
... thousands of times its main-sequence size, as shown in Figure 10. As the star expands, its surface cools, which explains the star’s reddish appearance. During expansion, the core continues to collapse and heat until it reaches 100 million K. At this temperature, it is hot enough to convert helium to ...
Diapositiva 1 - Dipartimento di Fisica
... The first extrasolar planet around a main-sequence star was found in 1995 around 51 Pegasi, a G5V star, analyzing the radial velocity variations of the parent star due to its motion around the barycenter of the system [3]. The radial velocity method allow to detect only Jupiter-like planets, in part ...
... The first extrasolar planet around a main-sequence star was found in 1995 around 51 Pegasi, a G5V star, analyzing the radial velocity variations of the parent star due to its motion around the barycenter of the system [3]. The radial velocity method allow to detect only Jupiter-like planets, in part ...
On the binding energy of the common envelope - UvA-DARE
... to be located further out, since it is based on the transition between the convective and the radiative layer in the stellar envelope. Unlike evolved low-mass (1 M ) stars, these more massive stars do not have an outer convection zone which penetrates all the way down to the H-shell near the standa ...
... to be located further out, since it is based on the transition between the convective and the radiative layer in the stellar envelope. Unlike evolved low-mass (1 M ) stars, these more massive stars do not have an outer convection zone which penetrates all the way down to the H-shell near the standa ...
Flow of Energy through the Star and Construction of Stellar Models
... their number and their speed. These variables set an upper limit to the rate of energy transport. In addition, the "opacity" of the material to the motion of the energycarrying particles will also affect the efficiency. In the case of radiation, we have characterized this opacity by a collision cros ...
... their number and their speed. These variables set an upper limit to the rate of energy transport. In addition, the "opacity" of the material to the motion of the energycarrying particles will also affect the efficiency. In the case of radiation, we have characterized this opacity by a collision cros ...
Vibrational instability of Population III very massive mainsequence
... Very massive stars are thought to be formed in the early Universe because of a lack of cooling process by heavy elements, and might have been responsible for the later evolution of the Universe. We had an interest in the vibrational stability of their evolution and have carried out a linear non-adia ...
... Very massive stars are thought to be formed in the early Universe because of a lack of cooling process by heavy elements, and might have been responsible for the later evolution of the Universe. We had an interest in the vibrational stability of their evolution and have carried out a linear non-adia ...
ph507lecnote07
... Protostars shine because they are hotter than their surroundings: Need an energy source to stay hot, but Central temperature is too cool for nuclear fusion to ignite Initial energy source is Gravitational Contraction (aka, the KelvinHelmholz Mechanism): The Protostar shrinks slowly, releasing gr ...
... Protostars shine because they are hotter than their surroundings: Need an energy source to stay hot, but Central temperature is too cool for nuclear fusion to ignite Initial energy source is Gravitational Contraction (aka, the KelvinHelmholz Mechanism): The Protostar shrinks slowly, releasing gr ...
Photometric variability of the Pre
... face. Some times the variability can be periodic due to long lived hot spots. This periodicity typically persists for only a couple of rotation cycles. The UXor type of variability is seen in HAEBE and some CTT stars from F-G spectral types. The typical amplitudes are of the order of 2-3 mag (V), an ...
... face. Some times the variability can be periodic due to long lived hot spots. This periodicity typically persists for only a couple of rotation cycles. The UXor type of variability is seen in HAEBE and some CTT stars from F-G spectral types. The typical amplitudes are of the order of 2-3 mag (V), an ...
Giant Planets at Small Orbital Distances
... a diamond in the lower right-hand corner of Figure 2. Its evolutionary track closely follows the convective Hayashi track. For a given mass and composition, every fully convective model lies on the same curve in the H-R diagram. No model can exist to the right of this curve (at lower Te ). This reg ...
... a diamond in the lower right-hand corner of Figure 2. Its evolutionary track closely follows the convective Hayashi track. For a given mass and composition, every fully convective model lies on the same curve in the H-R diagram. No model can exist to the right of this curve (at lower Te ). This reg ...
astronomy - Scioly.org
... - Main-sequence (hydrogen-burning core) star, spectral type O and luminosity class V - Very rare, very massive, with extremely short lifespans (first to leave main seq.) - 0.00003% of local stars are of spectral type O. - Most output is in the ultraviolet range - Main-sequence star, spectral class B ...
... - Main-sequence (hydrogen-burning core) star, spectral type O and luminosity class V - Very rare, very massive, with extremely short lifespans (first to leave main seq.) - 0.00003% of local stars are of spectral type O. - Most output is in the ultraviolet range - Main-sequence star, spectral class B ...
sun.galaxy.notes
... • The combining of lighter elements to form heavier elements • In the Sun’s core, ___ hydrogen atoms (a light element [don’t write] ) combine to form 1 helium atom (a heavier element [don’t write] ) & energy is released H H H ...
... • The combining of lighter elements to form heavier elements • In the Sun’s core, ___ hydrogen atoms (a light element [don’t write] ) combine to form 1 helium atom (a heavier element [don’t write] ) & energy is released H H H ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 6 Notes: Internal Energy
... not able to exchange heat with its environment or extract it from internal sources (like nuclear burning), so any work it does must be balanced by a change in its internal energy. The classic example of this is a gas that is sealed in an insulated box, which is then compressed or allowed to expand. ...
... not able to exchange heat with its environment or extract it from internal sources (like nuclear burning), so any work it does must be balanced by a change in its internal energy. The classic example of this is a gas that is sealed in an insulated box, which is then compressed or allowed to expand. ...
The Evolutionary Status of Be Stars in Clusters and in the Galactic
... by a scenario of evolutionary enhancement of the rotational velocity over the main sequence lifetime. The likelihood of such hypothesis is supported by recent theoretical and observational results. ¿From theoretical evolutionary models taking into account the stellar rotation, Meynet & Maeder (2000) ...
... by a scenario of evolutionary enhancement of the rotational velocity over the main sequence lifetime. The likelihood of such hypothesis is supported by recent theoretical and observational results. ¿From theoretical evolutionary models taking into account the stellar rotation, Meynet & Maeder (2000) ...
Stellar Evolution : The Life and Death of Our Luminous Neighbors
... e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's core remain under control so long as a. b. c. d. ...
... e. they are all so far away that the light hasn't reached us yet. 2. The nuclear reactions in a star's core remain under control so long as a. b. c. d. ...