Significant Figure Rules
... Rule 4: Zeros to the right of a number are only significant if there is a decimal point. 200 is considered to have only ONE significant figure while 25,000 has two. This is based on the way each number is written. When whole numbers are written as above, the zeros, BY DEFINITION, did not require a ...
... Rule 4: Zeros to the right of a number are only significant if there is a decimal point. 200 is considered to have only ONE significant figure while 25,000 has two. This is based on the way each number is written. When whole numbers are written as above, the zeros, BY DEFINITION, did not require a ...
Targil 9 (following Alexey`s story, about catastrophes and linear
... edges are vertexes. Hence, the volume of each corner tetrahedron is either 0 (if these point was chosen as one of those 12 points) or 1/6 (if all neighbor vertices were chosen). Divide all vertices into 4 subsets of 2, members of the same subgroup are connected by vertical edges. Only one of the me ...
... edges are vertexes. Hence, the volume of each corner tetrahedron is either 0 (if these point was chosen as one of those 12 points) or 1/6 (if all neighbor vertices were chosen). Divide all vertices into 4 subsets of 2, members of the same subgroup are connected by vertical edges. Only one of the me ...
Topic 2: Comparing Numbers and Absolute Value
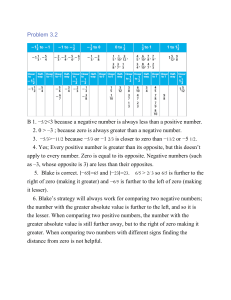
... Madison has 2. Alexis is not quite sure where to stand. Madison tells her that "4 is 2 and "9 is 3. Where should Alexis stand? ...
... Madison has 2. Alexis is not quite sure where to stand. Madison tells her that "4 is 2 and "9 is 3. Where should Alexis stand? ...
Ch. 1.1 PowerPoint
... There is exactly one real number for each point on a number line The positive numbers are shown to the right of zero and the negative to the left. Zero is neither positive nor negative. ...
... There is exactly one real number for each point on a number line The positive numbers are shown to the right of zero and the negative to the left. Zero is neither positive nor negative. ...
Infinity

Infinity (symbol: ∞) is an abstract concept describing something without any limit and is relevant in a number of fields, predominantly mathematics and physics.In mathematics, ""infinity"" is often treated as if it were a number (i.e., it counts or measures things: ""an infinite number of terms"") but it is not the same sort of number as natural or real numbers. In number systems incorporating infinitesimals, the reciprocal of an infinitesimal is an infinite number, i.e., a number greater than any real number; see 1/∞.Georg Cantor formalized many ideas related to infinity and infinite sets during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. In the theory he developed, there are infinite sets of different sizes (called cardinalities). For example, the set of integers is countably infinite, while the infinite set of real numbers is uncountable.























