Simple Harmonic Motion
... oscillating mass is observed over time, and the stiffness of the spring is determined from measurements associated with the time-dependent motion of the mass on a spring. Equations (6) and (7) relate the stiffness of a spring to the time-varying displacement of the oscillating mass. In this part of ...
... oscillating mass is observed over time, and the stiffness of the spring is determined from measurements associated with the time-dependent motion of the mass on a spring. Equations (6) and (7) relate the stiffness of a spring to the time-varying displacement of the oscillating mass. In this part of ...
General Physics II
... The protons should be placed at a distance a/2 from the center of the sphere of negative charge, symmetric about the sphere’s midpoint. The forces on the protons from each other will be equal and opposite. Therefore, the forces on them from the negative charge distribution must be equal and opposite ...
... The protons should be placed at a distance a/2 from the center of the sphere of negative charge, symmetric about the sphere’s midpoint. The forces on the protons from each other will be equal and opposite. Therefore, the forces on them from the negative charge distribution must be equal and opposite ...
ILQ
... 24.11.1. Consider the system shown in the drawing. A positive charge Q is placed at the center of a hollow conductor that was initially electrically neutral. The arrows are pointing to four locations: (1) a point in the conductor near the outer surface, (2) a point in the hollow space located halfw ...
... 24.11.1. Consider the system shown in the drawing. A positive charge Q is placed at the center of a hollow conductor that was initially electrically neutral. The arrows are pointing to four locations: (1) a point in the conductor near the outer surface, (2) a point in the hollow space located halfw ...
New atomic masses related to fundamental physics measured with SMILETRAP
... values can be to determine how much a particle called a neutrino weighs. There are three known types of neutrinos called the electron-neutrino, muonneutrino and tau-neutrino. Until recently, according to the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, neutrinos were assumed to be massless. However, rec ...
... values can be to determine how much a particle called a neutrino weighs. There are three known types of neutrinos called the electron-neutrino, muonneutrino and tau-neutrino. Until recently, according to the Standard Model (SM) of particle physics, neutrinos were assumed to be massless. However, rec ...
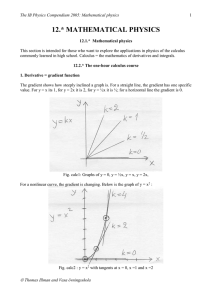
12. MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS
... For constant velocity, s = vt which is the area of a rectangle in a velocity-as-function-of-time curve. If the velocity is not constant but the acceleration is then the v-curve is a straight line, and the area under it can be found as a trapeze (here a triangle on top of a rectangle). From this the ...
... For constant velocity, s = vt which is the area of a rectangle in a velocity-as-function-of-time curve. If the velocity is not constant but the acceleration is then the v-curve is a straight line, and the area under it can be found as a trapeze (here a triangle on top of a rectangle). From this the ...
Electromagnetism 电磁学
... While physics aims to discover universal laws, its theories lie in explicit domains of applicability. Loosely speaking, the laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. ...
... While physics aims to discover universal laws, its theories lie in explicit domains of applicability. Loosely speaking, the laws of classical physics accurately describe systems whose important length scales are greater than the atomic scale and whose motions are much slower than the speed of light. ...
Chapter 6 Momentum and Impulse
... – Mi is the initial mass of the rocket plus fuel – Mf is the final mass of the rocket plus any remaining fuel – The speed of the rocket is proportional to the exhaust ...
... – Mi is the initial mass of the rocket plus fuel – Mf is the final mass of the rocket plus any remaining fuel – The speed of the rocket is proportional to the exhaust ...
Lecture 17 - Yale University
... medium. In reality, the medium will be highly inhomogeneous. What happens when the blastwave shockfront runs over a dense cloud of gas? ...
... medium. In reality, the medium will be highly inhomogeneous. What happens when the blastwave shockfront runs over a dense cloud of gas? ...
MASSIVE CLOSE BINARIES
... trivial to understand that Case A components have smaller final masses whereas it is obvious that Case C (and non-interacting) binaries are similar to single stars. Equation 1 decides upon the mass loss during the RSG phase. The top-figure holds for the WR rates predicted by Equation 2 whereas the b ...
... trivial to understand that Case A components have smaller final masses whereas it is obvious that Case C (and non-interacting) binaries are similar to single stars. Equation 1 decides upon the mass loss during the RSG phase. The top-figure holds for the WR rates predicted by Equation 2 whereas the b ...
Quantum Mechanics Potential energy
... where r is the position vector from Q to q and ε0 is the vacuum permittivity. This may also be written using Coulomb's constant ke = 1 ⁄ 4πε0. If the electric charge of an object can be assumed to be at rest, then it has potential energy due to its position relative to other charged objects. The ele ...
... where r is the position vector from Q to q and ε0 is the vacuum permittivity. This may also be written using Coulomb's constant ke = 1 ⁄ 4πε0. If the electric charge of an object can be assumed to be at rest, then it has potential energy due to its position relative to other charged objects. The ele ...
June 2010 - fixurscore
... A uniform electric field is then applied in the same region as the magnetic field. For an electric field strength of 12 kV m–1, the particles are undeviated as they pass through the region of the fields. (a) On Fig. 7.1, mark with an arrow the direction of the electric field. ...
... A uniform electric field is then applied in the same region as the magnetic field. For an electric field strength of 12 kV m–1, the particles are undeviated as they pass through the region of the fields. (a) On Fig. 7.1, mark with an arrow the direction of the electric field. ...
Production of negative hydrogen ions using a low
... and another group of cold electrons for producing H− ions by dissociative electron attachment, have stimulated our interest in the analysis of this reflex discharge plasma as a potential source of negative ions. To our knowledge, this is the first time when the reflex discharge plasma is analyzed as ...
... and another group of cold electrons for producing H− ions by dissociative electron attachment, have stimulated our interest in the analysis of this reflex discharge plasma as a potential source of negative ions. To our knowledge, this is the first time when the reflex discharge plasma is analyzed as ...