Mathematics - Triumph Learning
... collected 24 oranges and 36 apples. The teacher wants the same number of oranges in every basket. The teacher also wants the same number of apples in every basket. What is the greatest number of baskets the class can make? Step 1: Determine whether you will use common multiples or common factors to ...
... collected 24 oranges and 36 apples. The teacher wants the same number of oranges in every basket. The teacher also wants the same number of apples in every basket. What is the greatest number of baskets the class can make? Step 1: Determine whether you will use common multiples or common factors to ...
Week 4 Power Point Slides
... – Answer: We use == – Example: if (x == y) • How do we compare object variables for equality? – Answer: We use the object’s .equals method – Example: if (str.equals(“quit”)); • Question: Why the difference? Answer: Because == will compare where in memory the object is and not its contents. Note: The ...
... – Answer: We use == – Example: if (x == y) • How do we compare object variables for equality? – Answer: We use the object’s .equals method – Example: if (str.equals(“quit”)); • Question: Why the difference? Answer: Because == will compare where in memory the object is and not its contents. Note: The ...
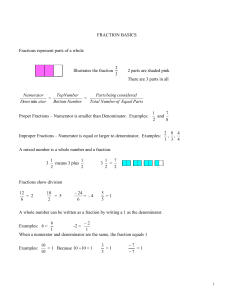
FRACTION BASICS
... We multiply 2 2 3 to get 12 which is the LCM or LCD of 4 and 6. NOTE: We could have multiplied 4 and 6 together and used 24 as a common denominator but it would not have been the least common denominator because 4 and 6 had factors in common. ...
... We multiply 2 2 3 to get 12 which is the LCM or LCD of 4 and 6. NOTE: We could have multiplied 4 and 6 together and used 24 as a common denominator but it would not have been the least common denominator because 4 and 6 had factors in common. ...
TestCracker CAT Quant
... = 24 + 4 = 28. (We cannot do it further since 121 is less than 5! = 125) ...
... = 24 + 4 = 28. (We cannot do it further since 121 is less than 5! = 125) ...
Unit 4 The Number System: Decimals
... Materials. We recommend that students always work in grid paper notebooks. Paper with 1/4-inch grids works well in most lessons. Grid paper is very helpful when comparing decimals, drawing base ten blocks or number lines, and performing operations with multi-digit numbers and decimals using standard ...
... Materials. We recommend that students always work in grid paper notebooks. Paper with 1/4-inch grids works well in most lessons. Grid paper is very helpful when comparing decimals, drawing base ten blocks or number lines, and performing operations with multi-digit numbers and decimals using standard ...
Floating-Point Arithmetic
... 2. Multiply the significands. Set the result sign to positive if operands have same sign, and negative otherwise 3. Normalize the product if necessary, shifting its significand right and incrementing the exponent 4. Round the significand to the appropriate number of bits, and renormalize if rounding ...
... 2. Multiply the significands. Set the result sign to positive if operands have same sign, and negative otherwise 3. Normalize the product if necessary, shifting its significand right and incrementing the exponent 4. Round the significand to the appropriate number of bits, and renormalize if rounding ...
Recursion
... • Evaluating algebraic expressions in postfix form (how did we do this earlier?) • etc. ...
... • Evaluating algebraic expressions in postfix form (how did we do this earlier?) • etc. ...
mixed number
... To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction: 1. Multiply the denominator by the whole number. 2. Add in the numerator. 3. Write the answer as the numerator of the improper fraction, and the original denominator as the improper fraction’s denominator. ...
... To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction: 1. Multiply the denominator by the whole number. 2. Add in the numerator. 3. Write the answer as the numerator of the improper fraction, and the original denominator as the improper fraction’s denominator. ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.